Online FirstMore>
Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
Display Method:
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202409017
Abstract:
Percutaneous administration is safety, convenience and high compliance. However, the skin structure is complex and individual differences are large, especially the barrier of the stratum corneum leads to the poor bioavailability of topical preparations for the skin. The composition of the prescription for dermal drug administration is complicated, and the quality of the product should be strictly controlled. Raman spectroscopy, as a non-destructive vibrational spectrum can be used to characterize key quality properties of dermal drug administration combined with stoichiometric methods, imaging techniques and other spectral techniques. The purpose of this paper is to review the application of Raman spectroscopy in the study of crystal form, particle size distribution, excipients and in vitro transdermal experiments of dermal drug administration. In vitro transdermal tests, Raman spectroscopy was used to distinguish skin of different species, study the spatial distribution of drugs in skin and the interaction between drugs and skin
Percutaneous administration is safety, convenience and high compliance. However, the skin structure is complex and individual differences are large, especially the barrier of the stratum corneum leads to the poor bioavailability of topical preparations for the skin. The composition of the prescription for dermal drug administration is complicated, and the quality of the product should be strictly controlled. Raman spectroscopy, as a non-destructive vibrational spectrum can be used to characterize key quality properties of dermal drug administration combined with stoichiometric methods, imaging techniques and other spectral techniques. The purpose of this paper is to review the application of Raman spectroscopy in the study of crystal form, particle size distribution, excipients and in vitro transdermal experiments of dermal drug administration. In vitro transdermal tests, Raman spectroscopy was used to distinguish skin of different species, study the spatial distribution of drugs in skin and the interaction between drugs and skin
In Press
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202312024
Abstract:
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors, which is a great threat to human life and health. The change of bile acid homeostasis can activate their corresponding receptors to regulate the immune functions, which is closely related to the occurrence of colorectal cancer. In addition, some bile acids can directly induce colorectal cancer and play an important role in the development of colorectal cancer. In this paper, the metabolic process of bile acids in vivo and the immunomodulatory role of bile acid receptors were reviewed, and the evidence of associations between bile acids and colorectal cancer were summarized, which showed the rebalancing the bile acid levels might play a role in the prevention or treatment of colorectal cancer.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors, which is a great threat to human life and health. The change of bile acid homeostasis can activate their corresponding receptors to regulate the immune functions, which is closely related to the occurrence of colorectal cancer. In addition, some bile acids can directly induce colorectal cancer and play an important role in the development of colorectal cancer. In this paper, the metabolic process of bile acids in vivo and the immunomodulatory role of bile acid receptors were reviewed, and the evidence of associations between bile acids and colorectal cancer were summarized, which showed the rebalancing the bile acid levels might play a role in the prevention or treatment of colorectal cancer.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202504044
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the efficacy and safety of EGFR-TKIs monotherapy and its combination therapy in the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC)patients with EGFR mutations. Methods Databases such as PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov were systematically searched to collect eligible phase II/III randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with the time range from the establishment of the databases to June 2023. Two researchers independently screened the literature, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias in the studies. Outcome data, including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), grade 3 or higher adverse events (≥3 AEs), and serious adverse events (SAEs), were collected. A network meta-analysis was performed using R software (version 4.2.1) under the Bayesian theoretical framework. Subgroup analyses of survival outcomes (OS, PFS) were conducted based on different clinical and pathophysiological characteristics of the patients. Results A total of t wenty-eight phase II/III RCTs were included in the study, involving a total of 7 460 patients and 18 first-line treatment regimens. The results showed that in terms of efficacy, gefitinib + pemetrexed-containing chemotherapy performed best in OS and ORR, while osimertinib + bevacizumab performed best in PFS. In terms of safety, furmonertinib had the lowest incidence of ≥3 grade AEs, and osimertinib had the lowest incidence of SAEs. Subgroup analysis results indicated that the efficacy and safety of various treatment regimens differed among patients with different clinical and pathological characteristics. Conclusion Monotherapy with third-generation EGFR-TKIs, represented by osimertinib, serves as the preferred therapeutic option considering both efficacy and safety profiles. While some combination therapies can enhance survival benefits, but need to be vigilant about increased toxicity. Clinical decision-making should be tailored based on patient' mutation subtypes, comorbidities, and tolerance.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202504131
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of a standardized management method based on Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) in optimizing the whole-process quality control system of the Intravenous Admixture Service (PIVAS). Methods The quality control management system of the IVAS was optimized by establishing six quality control groups led by the head nurse, with full participation of pharmacy, nursing, and logistical staff, ensuring comprehensive coverage and traceability of all quality control links. Each group conducted Risk Priority Number (RPN) scoring for potential failure modes in their respective quality control processes, and targeted improvement measures were formulated based on the scoring results. The RPN values of failure modes and quality control-related evaluation indicators before and after implementation were compared to achieve closed-loop management. Results After one year of management, the RPN values of the six major failure modes significantly decreased compared to those before implementation (P<0.05). The compounding error rate dropped to 0.13%, the dispensing error rate decreased to 0.95%, the compounding efficiency increased to 98%, the delivery time was shortened by 0.45 hours per batch, the intervention rate for irrational prescriptions rose to 94.87%, satisfaction improved to 96.78%, and the participation rate of quality control personnel reached 95.36% (P<0.05). Conclusion FMEA-based identification of potential failure modes in the whole-process quality control system of the IVAS, combined with risk quantification and targeted interventions, significantly reduces high-risk failure modes, improves compounding accuracy and efficiency, and ensures the safety of clinical intravenous medication and the effectiveness of healthcare quality management.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202502015
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of Xuetong capsule on blood lipids and liver lesion in hyperlipidemic model animals. Method Sixty ICR mice were randomly divided into six groups. The normal control group was fed with normal diet, the other groups were fed with high-fat diet to induce hyperlipidemia. After four weeks feeding, the three groups were given low, middle, and high doses of Xuetong capsules (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 g/kg ) by Gavage, and the positive control drug atorvastatin calcium (1.5 mg/kg). The model group was given solvent (0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose sodium). After treatment for 8 weeks, the body weight, organ index, blood lipids, blood glucose and liver function index were measured. The liver oil red staining was used to determine the lipid droplet content, and quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression of inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Result The body weight, the weight of liver and spleen were significantly increased by high-fat diet. High-fat diet increased the organ indexes of the liver and spleen, the degree of liver oil red staining, and also significantly increased the levels of glucose, triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (CHOL), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in serum. Compared with the model group, the level of TG has no significant change in low, middle and high doses groups. The level of CHOL in serum was reduced by Xuetong capsule with a dose dependent manner. There were significant difference between the model group and middle, high doses groups. The results of LDL-C were similar, the level of LDL-C was significantly reduced by middle and high doses groups (middle dose 0.55±0.21 mM, high dose 0.52±0.22 mM v.s. 0.81±0.29 mM in model group P<0.01). Compared with the normal control, there was no significant difference in HDL-C levels between the high-fat model and each drug-treated group. Liver function showed that Xuetong capsules significantly reduced the degree of liver oil red staining and decreased the level of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) induced by high-fat diet. The body weight, the weight and organ indexes of liver and spleen were significantly reduced by atorvastatin calcium. The levels of CHOL, LDL-C, and TG, and the degree of liver oil red staining were also significantly reduced in atorvastatin calcium group. Further studies have shown that high dose of Xuetong capsules significantly reduced the expression of TNF-α and IL-6 induced by high-fat diet (P<0.05), while the reduction of IL-1β was not so significant (P>0.05). Conclusion Xuetong capsules significantly reduces the body weight of animals with high fat, reduce liver size, fat deposition, inflammatory damage and also significantly reduces blood lipid CHOL and LDL-C levels and reduce transaminase elevation. The above effects may be related to Xuetong capsules reducing the expression of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 in the liver.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202409045
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of activating α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) on calcium chloride (CaCl2)-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) injury in mice. Methods AAA model was induced by CaCl2 in wild type (WT) mice and α7nAChR knockout (α7nAChR−/-) mice. The effects of knockout of α7nAChR on histological damage in CaCl2-induced AAA mice and expression of inflammatory factors were assessed by HE staining, EVG staining and IHC staining. Rat-derived primary vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) were stimulated with TNF-α, which mimicked the inflammatory environment of AAA. The expressions of inflammation-related proteins were detected by using Western-Blot with or without PNU-282987 to activate α7nAChR. Results Aortic dilatation was obvious, and the aortic structure was disrupted in CaCl2-induced AAA mice. Knockout of α7nAChR further exacerbated the histological injury and significantly up-regulated the expression of inflammation-related proteins in aorta of AAA mice. It was showed that TNF-α stimulation of VSMC increased inflammation-related protein expression, whereas activation of α7nAChR prevented the phenomenon. Conclusion Activation of α7nAChR could attenuate CaCl2-induced AAA injury in mice by suppressing the inflammatory response.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202406047
Abstract:
[ Abstract ] Objective To explore a feasible simplified premedication protocol for preventing hypersensitivity reactions to taxanes. Methods The electronic medical record system was used to search for data on 49 patients with advanced gastric cancer who received paclitaxel liposome treatment for the first time in the gastroenterology department of our hospital from 2021-06-01 to 2024-06-30, including premedication protocols, allergic reactions, and other adverse reactions. Results 31 cases took dexamethasone 9 mg at 12-hour and 6-hour, and took loratadine tablets 10 mg and ranitidine hydrochloride capsules 150 mg at 12-hour before paclitaxel liposomal; 18 cases took dexamethasone 9 mg at 12-hour and 6-hour, and took loratadine tablets 10 mg at 12-hour before paclitaxel liposomal. All patients did not experience any allergic reactions. There were no significant differences in the incidence of other adverse reactions between the two simplified protocols(P>0.05). Conclusion Based on literature and practice, a dual simplified premedication protocol of oral corticosteroids(GC)combined with oral H1 receptor blockers(H1RA)was proposed, which provided a new idea for doctors. Further clinical studies are needed to verify its effectiveness.
[ Abstract ]
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202304011
Abstract:
Objective To study the photodynamic performance and the killing effect of photodynamic therapy on lung cancer of novel chlorin compounds 2-(4-(5,15,20-triphenyl-7H,8H-porphyrin-10-yl) phenoxy) acetic acid(D1)and 4-(4-(5,15,20-triphenyl-7H,8H-porphyrin-10-yl) phenoxy) butanoic acid (D2). Methods The ultraviolet visible absorption spectrum and fluorescence spectrum of D1 and D2 were determined. The singlet oxygen generation capacity of D1 and D2 was measured by using DPBF as singlet oxygen capture agent. Fluorescence assay was used to detect the cellular phagocytosis rate of the compounds in A549 cells, and MTT assay was used to detect their dark toxicity and phototoxicity. A nude mouse model of lung cancer was established to investigate the antitumor activity of the compounds mediated photodynamic action in vivo, and the blood concentration of D2 in nude mice, its distribution in tumor tissue and skin tissue were further detected. Results D1 and D2 had strong absorption at 652 nm with the best excitation wavelength at 429 nm and 427 nm, and the optimal emission wavelength was at about 659 nm. They also had a higher singlet oxygen generation rate than the control drug m-THPC. D1 and D2 had no dark toxicity at concentrations below 10 μmol/L, and could be ingested by A549 cells, basically reaching saturation in 18~24 hours. After laser irradiation at 650 nm wavelength, D1 and D2 showed significant antitumor activity in vivo and in vitro (P<0.01). However, D2 could selectively accumulate in tumor tissues after administration, and the optimal treatment time was less than 30 min after administration. Conclusion D2 had excellent photodynamic antitumor activity and could selectively aggregate in tumor tissues, which had the potential to be a candidate drug for photosensitizer and treatment of lung cancer with independent intellectual property rights, and was worth further research.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.20240380
Abstract:
This study aimed to clarify the causal relationship between meaning in life and depression symptoms, explore the evolutionary patterns of meaning in life, and assess its impact on the incidence of depressive symptoms. A two-wave longitudinal study with a 12-month interval was conducted among 896 university students recruited from one university. The meaning in life questionnaire and the depression symptom screening questionnaire were administered. The findings showed that: 1)Meaning in life at T1 negatively predicted depression symptoms at T2. Conversely, depression symptoms at T1 did not significantly predict meaning in life at T2. 2)The evolutionary patterns of meaning in life from T1 to T2 could be categorized into four groups: sustained low meaning, meaning improvement, meaning reduction, and sustained high meaning. The incidence of depressive symptoms in these four groups was 13.00%, 5.00%, 12.00%, and 4.00%, respectively. 3)The evolutionary patterns of meaning in life significantly impacted the incidence of depressive symptoms. Compared to the sustained high meaning group, both the sustained low meaning group and the meaning reduction group exhibited significantly higher rates of depression symptoms. The results suggest that psychological health education in universities should focus on individuals with sustained low meaning or meaning reduction, and that enhancing meaning in life serves as an effective intervention approach to reducing the incidence of depression symptoms among university students.
This study aimed to clarify the causal relationship between meaning in life and depression symptoms, explore the evolutionary patterns of meaning in life, and assess its impact on the incidence of depressive symptoms. A two-wave longitudinal study with a 12-month interval was conducted among 896 university students recruited from one university. The meaning in life questionnaire and the depression symptom screening questionnaire were administered. The findings showed that: 1)Meaning in life at T1 negatively predicted depression symptoms at T2. Conversely, depression symptoms at T1 did not significantly predict meaning in life at T2. 2)The evolutionary patterns of meaning in life from T1 to T2 could be categorized into four groups: sustained low meaning, meaning improvement, meaning reduction, and sustained high meaning. The incidence of depressive symptoms in these four groups was 13.00%, 5.00%, 12.00%, and 4.00%, respectively. 3)The evolutionary patterns of meaning in life significantly impacted the incidence of depressive symptoms. Compared to the sustained high meaning group, both the sustained low meaning group and the meaning reduction group exhibited significantly higher rates of depression symptoms. The results suggest that psychological health education in universities should focus on individuals with sustained low meaning or meaning reduction, and that enhancing meaning in life serves as an effective intervention approach to reducing the incidence of depression symptoms among university students.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202503005
Abstract:
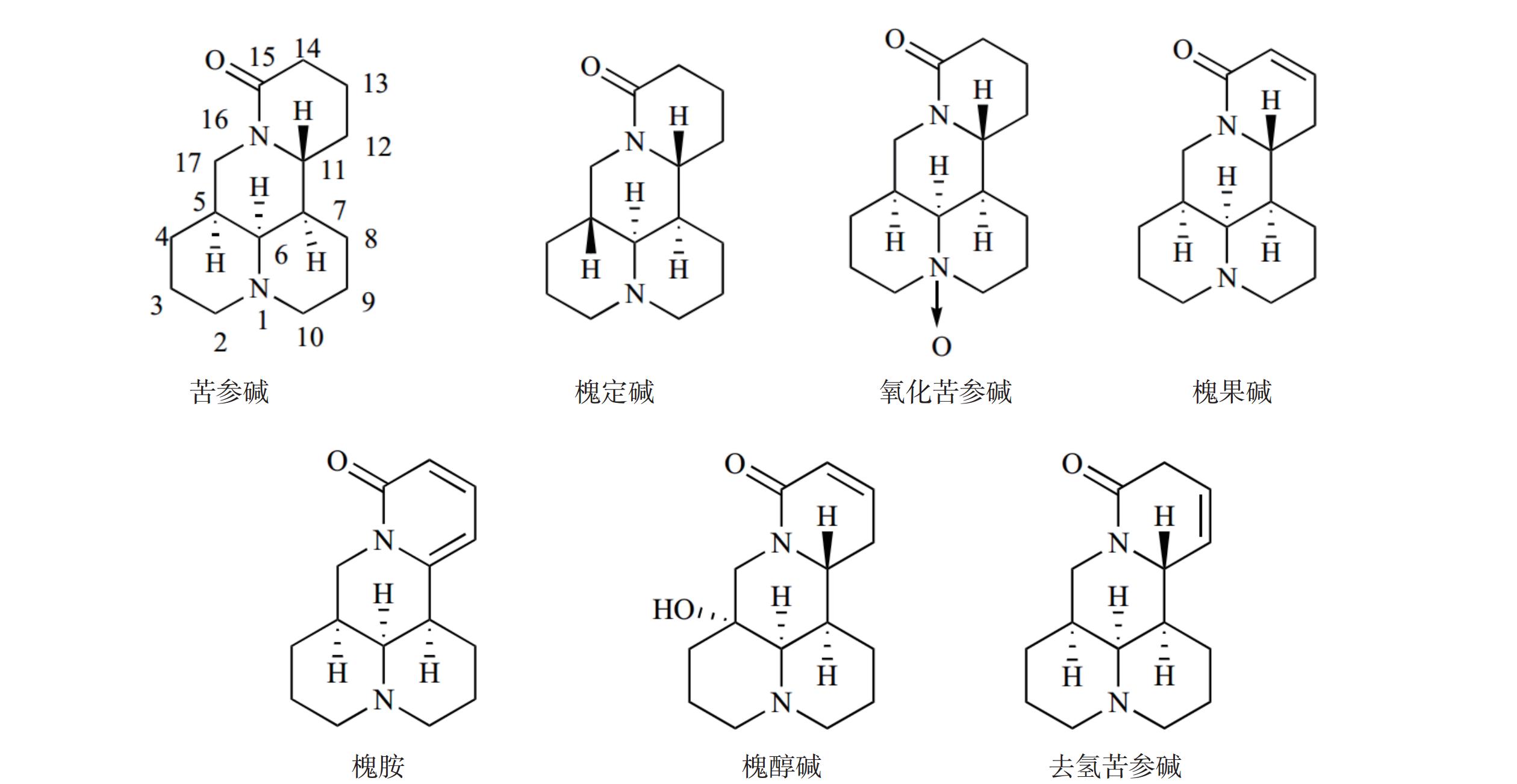
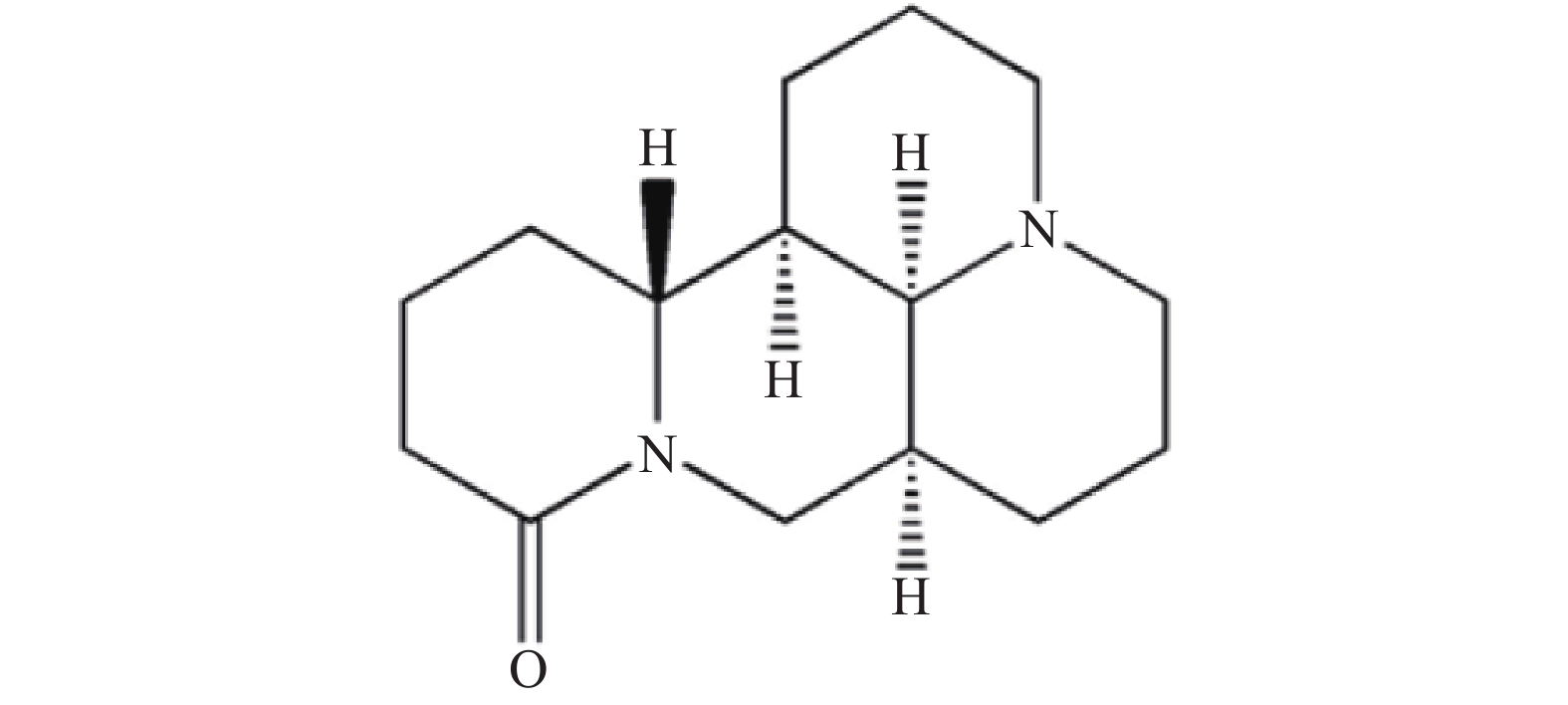
Objective The alkaloids contained in the Chinese herb Sophora flavescens have good anti-inflammatory activity. To investigate the structure-activity relationship between the novel Matrine and the anti-inflammatory activity by modifying the structure of Matrine . Methods Fourteen novel Matrine derivatives were obtained by chemical modification using Matrine as the lead compound with Matrine and M19 as positive controls. The cytotoxicity of Matrine derivatives against RAW264.7 cells was detected by the Cell Counting Kit 8 (CCK8) assay, and the relative amount of Nitric Oxide (NO) produced by Matrine derivatives against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation model of RAW264.7 cells was detected using an NO assay kit. The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) d was used to detect the secretion of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) by Matrine derivatives in LPS-induced inflammation model of RAW264.7 cells. Results The novel Matrine derivatives all exhibited lower cytotoxicity compared with M19. The NO inhibition rates of the novel Matrine derivatives were all higher than that of Matrine, and some were higher than that of M19 , with compound A12 having the highest NO inhibition rate. Compounds A11 and A12 showed higher IL-6 inhibition than the control M19 . Additionally, compound A12 had higher TNF-α inhibition than the control M19 . Conclusion Compound A12 inhibited the strongest inhibition of NO, IL-6 and TNF-α release and had the best anti-inflammatory activity, which provided an important lead compound for this subsequent in-depth study.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202406029
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the preventive and therapeutic effects of ethanol extracts derived from three sources of traditional Chinese medicine: Stellera chamaejasme L., Euphorbia fischeriana Steud., and Euphorbia kansuensis Prokh., on imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis in mice. Methods Thirty-six male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into the following 6 groups with 6 mice in each group: blank control, model, Stellera chamaejasme, Euphorbia fischeriana, Euphorbia kansuensis, and calcipotriol. PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) scores were used to record the changes of skin lesions in each group; HE (hematoxylin-eosin) staining was used to observe the pathological morphology of skin and measure the thickness of the epidermis. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of nuclear antigen Ki67 in the skin tissues of mice. Results Compared with the model group, the three kinds of ethanol extracts can reduce the PASI score, inhibit epidermal thickening, and decrease expression of Ki67 in the psoriasis mice. Among them, the therapeutic effect of Stellera chamaejasme was the most significant and it was better than the commonly used topical drug calcipotriol. Conclusion The ethanol extract of Stellera chamaejasme has good anti-psoriatic activity, can inhibit the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes, can reduce the expression of Ki67, and can significantly improve psoriasis-like skin lesions.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202306020
Abstract:
Objective To establish a central cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Methods External standard method was used. The first dimensional chromatographic column: SNCB(T)-1A(silica gel, 4.6 mm×50 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase A:VCV-1D mobile phase, flow rate: 0.4 ml/min; mobile phase B: water, flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; second dimensional chromatographic column: Symmetry C18 (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase: acetonitrile-10 mmol/L ammonium acetate solution(V/V=25∶75), flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; Intermediate column: SBX 4-MA(resin, 3.0 mm×10 mm, 5µm). The UV detection wavelength: 306 nm, the column temperature: 45 ℃, and the injection volume: 200 μl. Results The linear range of lamotrigine was 1.24-39.50 μg/ml, the lower limit of quantification was 1.24 μg/ml, the detection limit was 0.02 μg/ml, the intra-day precision RSD was less than 5%, the day-to-day precision RSD was less than 10%, the variation of intra-day accuracy ranged from 102.17% to 111.17%, and the daytime accuracy variation ranged from 99.80% to 107.31% the recovery RSD was less than 5%, and the variation range was 89.95% -96.16%. After 24 hours storage at room temperature, repeated freezing and thawing for 3 times and storage at-40 ℃ for 2 weeks, the ratio of the measured value / labeled value ranged from 87.01% to 115.88%. Conclusion In this study, a method with simple operation, good stability, high sensitivity and good reproducibility was established, which could be suitable for clinical monitoring of blood concentration of lamotrigine and provides reliable monitoring data support for clinical individualized medication guidance.
Objective To establish a central cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Methods External standard method was used. The first dimensional chromatographic column: SNCB(T)-1A(silica gel, 4.6 mm×50 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase A:VCV-1D mobile phase, flow rate: 0.4 ml/min; mobile phase B: water, flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; second dimensional chromatographic column: Symmetry C18 (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase: acetonitrile-10 mmol/L ammonium acetate solution(V/V=25∶75), flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; Intermediate column: SBX 4-MA(resin, 3.0 mm×10 mm, 5µm). The UV detection wavelength: 306 nm, the column temperature: 45 ℃, and the injection volume: 200 μl. Results The linear range of lamotrigine was 1.24-39.50 μg/ml, the lower limit of quantification was 1.24 μg/ml, the detection limit was 0.02 μg/ml, the intra-day precision RSD was less than 5%, the day-to-day precision RSD was less than 10%, the variation of intra-day accuracy ranged from 102.17% to 111.17%, and the daytime accuracy variation ranged from 99.80% to 107.31% the recovery RSD was less than 5%, and the variation range was 89.95% -96.16%. After 24 hours storage at room temperature, repeated freezing and thawing for 3 times and storage at-40 ℃ for 2 weeks, the ratio of the measured value / labeled value ranged from 87.01% to 115.88%. Conclusion In this study, a method with simple operation, good stability, high sensitivity and good reproducibility was established, which could be suitable for clinical monitoring of blood concentration of lamotrigine and provides reliable monitoring data support for clinical individualized medication guidance.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.
Abstract:
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202309021
Abstract:
Lactic acid bacteria is a good candidate in living drug delivery system for its safety, beneficial nature, and intestinal colonizability. At present, most studies use it as a protein drug delivery carrier for disease treatment. As a model organism, a variety of gene modification schemes enable it to be applied to various diseases and can play a significant therapeutic effect. Lactic acid bacteria drug carrier has many advantages, including non-invasive drug delivery, gene editing, large-scale production Therefore, the use of lactic acid bacteria as recombinant protein expression vector has attracted global attention. In this review, the application basis, bioavailability improvement, gene editing strategy and research and application status of lactobacillus drug delivery system were summarized.
Lactic acid bacteria is a good candidate in living drug delivery system for its safety, beneficial nature, and intestinal colonizability. At present, most studies use it as a protein drug delivery carrier for disease treatment. As a model organism, a variety of gene modification schemes enable it to be applied to various diseases and can play a significant therapeutic effect. Lactic acid bacteria drug carrier has many advantages, including non-invasive drug delivery, gene editing, large-scale production Therefore, the use of lactic acid bacteria as recombinant protein expression vector has attracted global attention. In this review, the application basis, bioavailability improvement, gene editing strategy and research and application status of lactobacillus drug delivery system were summarized.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202303006
Abstract:
Objective Study on the effect of Lishukang capsule on learning and memory impairment in mice with high altitude hypoxia based on Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway. Methods Sixty male Balb/C mice were randomly divided into normal control group, hypoxia model group, Rhodiola capsule group: 400 mg/kg, low, medium and high dose groups of Lishukang capsule: 400 mg/kg, 600 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg, with 10 mice in each group. The normal control group was fed at the local altitude (1500m) after 7 days of intragastric administration in each group, and the rest groups were fed at the low pressure and hypoxia animal experimental cabin to simulate the altitude of 7500 m for hypoxia for 3 days. During this period, the normal control group and the hypoxia model group were given normal saline once a day, and 1 hour after the last administration, the eight arm maze was used to test the spatial memory ability of mice under simulated high altitude hypoxia; HE staining was used to observe the morphological changes of hippocampus in mice; Western blot was used to detect the changes of protein content of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and apoptosis related protein in hippocampus of mice. Results Compared with the normal control group, the spatial memory ability of mice in the hypoxia model group was significantly impaired (P<0.01); HE staining showed that hippocampal neurons in mice were seriously injured; the content of brain tissue Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 increased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 decreased (P<0.01). Compared with the hypoxia model group, the error rate of mice in the high dose group of Lishukang capsule in the eight arm maze behavior experiment was significantly reduced (P<0.05, P<0.01); HE staining showed that the neurons were arranged orderly and the cell morphology was good; the content of Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 decreased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 increased (P<0.01). Conclusion High altitude hypoxia can lead to oxidative stress injury in mice and induce the expression of apoptosis related genes, thus aggravating the cognitive dysfunction of mice; Lishukang capsule can effectively improve the learning and memory impairment in mice caused by hypoxia, and its mechanism may be related to regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and reducing apoptosis.
currentMore>
Display Method:
2025, 43(11): 529-532, 539.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202305055
Abstract:
Infection is the main cause of death after burn. Rational application of anti-infective drugs is crucial to control the disease. At present, the commonly used drugs in clinic are silver sulfadiazine, sulfamethazine, silver nitrate, antibiotics, and so on, but the microbial resistance continues to increase. With the development of nanotechnology, as a new type of antibacterial material, nanoparticles have more stable physical and chemical properties. Nanoparticles can achieve the effect of sustained and controlled release of drugs, reduce toxicity and improve bioavailability, which is expected to provide new opportunities for reducing the occurrence of drug resistance. In this article, the current research progresses of topical anti-infection nano preparations for burns were reviewed, in order to provide references for the research of new nano-drug delivery systems.
Infection is the main cause of death after burn. Rational application of anti-infective drugs is crucial to control the disease. At present, the commonly used drugs in clinic are silver sulfadiazine, sulfamethazine, silver nitrate, antibiotics, and so on, but the microbial resistance continues to increase. With the development of nanotechnology, as a new type of antibacterial material, nanoparticles have more stable physical and chemical properties. Nanoparticles can achieve the effect of sustained and controlled release of drugs, reduce toxicity and improve bioavailability, which is expected to provide new opportunities for reducing the occurrence of drug resistance. In this article, the current research progresses of topical anti-infection nano preparations for burns were reviewed, in order to provide references for the research of new nano-drug delivery systems.
2025, 43(11): 533-539.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202308033
Abstract:
The prevalence and abuse of new psychoactive substances are becoming more and more serious. The structural characteristics and pharmacological and toxicological effects of new psychoactive substances of fentanyl compounds were summarized, which focused on the pre-treatment and analysis methods of fentanyl substances in different scenes such as biological samples, drugs or illegal drugs, and environmental samples. The difficulties of current laboratory detection and field rapid detection were also summarized, and the development trend and application prospect of various technologies were prospected.
The prevalence and abuse of new psychoactive substances are becoming more and more serious. The structural characteristics and pharmacological and toxicological effects of new psychoactive substances of fentanyl compounds were summarized, which focused on the pre-treatment and analysis methods of fentanyl substances in different scenes such as biological samples, drugs or illegal drugs, and environmental samples. The difficulties of current laboratory detection and field rapid detection were also summarized, and the development trend and application prospect of various technologies were prospected.
2025, 43(11): 540-547.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202402033
Abstract:
Influenza virus pneumonia (IVP) is an acute inflammatory disease of the lung with high incidence rate and infectivity caused by invading of the virus into the lower respiratory tract. At present, the treatment of IVP is mainly based on anti-influenza virus infection strategies, including the use of influenza vaccines and anti-influenza virus drugs. Due to the strong variability of viral antigens, it is difficult to obtain long-lasting immunity through vaccination. Commonly used chemical//biological antiviral drugs usually target a single specific viral protein. The mutation and evolution of the virus can reduce its efficacy or render it ineffective, which may lead to drug resistance, limiting the clinical application of these treatment options. Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) have a long history in the prevention and treatment of IVP and are widely used in clinical practice due to their unique advantages and clear therapeutic effects. The research progress on the pathogenesis of IVP, effective prevention and treatment of TCMs for IVP, and the mechanism of action of its active ingredients were reviewed, which could provide new ideas for the treatment of IVP and reference for the development of new multi-target and low toxicity drugs.
Influenza virus pneumonia (IVP) is an acute inflammatory disease of the lung with high incidence rate and infectivity caused by invading of the virus into the lower respiratory tract. At present, the treatment of IVP is mainly based on anti-influenza virus infection strategies, including the use of influenza vaccines and anti-influenza virus drugs. Due to the strong variability of viral antigens, it is difficult to obtain long-lasting immunity through vaccination. Commonly used chemical//biological antiviral drugs usually target a single specific viral protein. The mutation and evolution of the virus can reduce its efficacy or render it ineffective, which may lead to drug resistance, limiting the clinical application of these treatment options. Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) have a long history in the prevention and treatment of IVP and are widely used in clinical practice due to their unique advantages and clear therapeutic effects. The research progress on the pathogenesis of IVP, effective prevention and treatment of TCMs for IVP, and the mechanism of action of its active ingredients were reviewed, which could provide new ideas for the treatment of IVP and reference for the development of new multi-target and low toxicity drugs.
2025, 43(11): 548-554, 571.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202306028
Abstract:
Objective To analyze chemical constituents of compound Maxing Shigan decoction by ultra-high perfor-mance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF/MS). Methods The separation was performed on a UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm×100 mm, 2.5 µm), with a gradient elution applying 0.1% aqueous formic acid solution and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile as a mobile phase. The column temperature was 40 °C. The flow rate was 0.4 ml/min and the analysis time was 15 min. Mass spectrometry (MS) data were collected in both positive and negative ESI ion modes. Results Through UPLC-QTOF/MS analysis and reference validation, a total of 59 chemical components in Maxing Shigan decoction were identified. Conclusion An ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF/MS) method was established to identify the chemical components of Maxing Shigan decoction. This method is simple, efficient, sensitive and accurate, and provides a basis for the elucidation of the pharmacodynamic material basis and mechanism of Maxing Shigan decoction. It can provide data reference for the optimization of the compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of COVID-19.
2025, 43(11): 555-559.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401060
Abstract:
Objective To increase the antigen presentation and immune response of liposomal vaccines through IgM functionalization strategy. Methods Folic acid-modified liposomes loaded with ovalbumin (FA-sLip/OVA) were prepared. The binding ability of liposomal vaccines with IgM was investigated by ELISA method. The IgM in the protein corona was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western Blot. Mice were immunized by intravenous injection to investigate the spleen B cell targeting and immune activation of vaccines. Results The average particle size of FA-sLip/OVA was about 117 nm. The specific binding between FA-sLip and IgM was verified by ELISA method. Folic acid-modified liposomal vaccines could absorb IgM in mouse serum and form protein coronas on the surface. Intravenous immunization could stimulate mice to produce long-lasting, high-level antibody titers. Conclusion Natural IgM-enabled folic acid-modified liposomal vaccines were successfully prepared which could effectively induce immune response and provide a new idea for the research of nano-vaccines.
2025, 43(11): 560-563.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202402031
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the quality and in vitro release behavior of the sirolimus self-microemulsion-mesoporous silicon sustained release tablets and provide a basis for further research and development of related preparations. Methods The hardness, brittleness and content uniformity of the sustained-release tablets were tested refer to Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2020. Different diameters (10, 11, 12 mm), different hardness (50, 70, 90 N), different speed (50, 75, 100 r/min), different dissolution methods (pulp method, basket method) were investigated. The release conditions of the sustained-release tablets with different pH solution (distilled water solution and 0.4% SDS solution with pH of 1.2, 4.5 and 6.8, respectively) and the in vitro release conditions of the sustained-release tablets were observed. Results The hardness, brittleness and content uniformity of the self-made sustained-release tablets were qualified; different diameters and dissolution methods had no effect on the drug release behavior of the sustained-release tablets in vitro, while the different hardness, different rotational speed and the different pH release media had certain effects. Conclusion The sirolimus self-microemulsion-mesoporous silicon sustained release tablets had good sustained-release effect in vitro and was deserved to further study.
Establishment of quality standard of Bletilla compound spleen-tonifying Traditional Chinese Medicine
2025, 43(11): 564-566, 576.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202303040
Abstract:
Objective To establish a quality control method for Bletilla compound spleen-tonifying Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM). Methods The content of gallic acid was determined by HPLC. Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz, Codonopsis pilosula Nannf and Pulsatillae Radix were identified by TLC. Results The identification and determination methods showed good specificity. Gallic acid displayed good linearity within the range of 3.6-179.8 µg/ml (r=0.999 9 ). The average recovery was 101.12% (RSD 0.98%). Conclusion The TLC and HPLC could be used as quality control method for Bletilla compound spleen-tonifying TCM.
2025, 43(11): 567-571.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202506021
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the possible mechanism and drug treatment plan of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage induced by human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor injection, point out medication risks and provide reference for medical treatment and pharmaceutical care of such patients. Methods The abnormal lung conditions of a patient treated with human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor injection was found by clinical pharmacists, who participated in clinical diagnosis and treatment by analyzing of adverse drug reactions, optimization of medical treatment and pharmaceutical care. Results Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage was likely an adverse drug reaction caused by human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor injection. The physician discontinued the medication immediately and provided treatment such as oxygen inhalation, high-dose hormone shock, plasma exchange, etc. The patient’s oxygen saturation was improved, alveolar bleeding was decreased, and the condition was improved. Conclusion Clinical pharmacists participate in patients’ medication treatment, carry out pharmaceutical guardianship, and assist physicians in adjusting treatment plans, which could contribute to the effectiveness and safety of patient treatment.
2025, 43(11): 572-576.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202505036
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of lidocaine medicated plaster (LMP) combined with pregabalin (PGB) on patients with postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), and the impact on serum pain mediators. Methods 108 PHN patients admitted in our hospital from January 2024 to December 2024 were selected and grouped according to the time point of receiving treatment, 54 PHN patients treated with PGB from January 2024 to June 2024 were included in the PGB group, and 54 PHN patients treated with LMP on top of the PGB group from July 2024 to December 2024 were included in the PGB+LMP group. Comparisons were made between the two groups in terms of pain score, serum pain mediator levels, dosage of PGB, and incidence of adverse reactions. Results After 4 weeks of treatment, both groups showed a decrease in Pain Rating Index scores (sensory score and affective score), Present Pain Intensity score, Visual Analog Scale score, and total score. Meanwhile, above scores of the PGB+LMP group were lower than those of the PGB group (P<0.05). After 4 weeks of treatment, the levels of substance P(SP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in both groups were lower than those before treatment, while serum 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) levels were higher than those before treatment. Moreover, the levels of SP and NPY were lower, and 5-HT level was higher in the PGB+LMP group than in the PGB group (P<0.05). The dosages of PGB in the PGB+LMP group at T1, T, T3 and T4 were significantly lower than those in the PGB group (P<0.05). The incidence of adverse reactions was 1.85%(1/54) in the PGB+LMP group. Compared to 5.56%(3/54) in the PGB group, and the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusion LMP combined with PGB was effective in the treatment of patients with PHN, which could effectively alleviate pain and lower the levels of serum pain mediators, with good safety.
2025, 43(11): 577-582.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202504055
Abstract:
In recent years, China has systematically enhanced its policy framework for innovative pharmaceuticals and medical devices and established a comprehensive, full-cycle support mechanism encompassing research and development, regulatory approval, manufacturing, reimbursement, and clinical application. This integrated approach has markedly accelerated the review-approval process and market entry of innovative medical products. Key regions including Beijing, Shanghai and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area have demonstrated significant achievements through initiatives such as optimized clinical trial protocols, expedited regulatory pathways, and diversified payment models. Nevertheless, challenges persist, including restrictive performance metrics in hospital, underdeveloped multi-payer reimbursement systems, and interdepartmental coordination gaps. Moving forward, sustained efforts in policy harmonization, reimbursement mechanism innovation, core technology breakthroughs, and global collaboration should be critical to advancing the high-quality development of Chinese innovative pharmaceuticals and devices.
In recent years, China has systematically enhanced its policy framework for innovative pharmaceuticals and medical devices and established a comprehensive, full-cycle support mechanism encompassing research and development, regulatory approval, manufacturing, reimbursement, and clinical application. This integrated approach has markedly accelerated the review-approval process and market entry of innovative medical products. Key regions including Beijing, Shanghai and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area have demonstrated significant achievements through initiatives such as optimized clinical trial protocols, expedited regulatory pathways, and diversified payment models. Nevertheless, challenges persist, including restrictive performance metrics in hospital, underdeveloped multi-payer reimbursement systems, and interdepartmental coordination gaps. Moving forward, sustained efforts in policy harmonization, reimbursement mechanism innovation, core technology breakthroughs, and global collaboration should be critical to advancing the high-quality development of Chinese innovative pharmaceuticals and devices.
过刊浏览
- 2025 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2024 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2023 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2022 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2021 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2020 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2019 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2018 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2017 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2016 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2015 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2014 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2013 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2012 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2011 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2010 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2009 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2008 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2007 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2006 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2005 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2004 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2003 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2002 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2001 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2000 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1999 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1998 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1997 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1996 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1995 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1994 4 3 2 1
- 1993 4 3 2 1
- 1992 4 3 2 1
- 1991 4 3 2 1
- 1990 4 3 2 1
- 1989 4 3 2 1
- 1988 4 3 2 1
- 1987 4 3 2 1
- 1986 4 3 2 1
- 1985 4 3 2 1
- 1984 4 3 2 1
- 1983 3 2 1
Chief Editor: LI Jie Wei
Publication Number:
ISSN 2097-2024
CN 31-2185/R
Website: www.yxsjzz.cn or yxsj.smmu.edu.cn
Email: yxsjzzs@163.com
 NewsMore >
NewsMore >
Top View
Top Down
- 1Research progress on action mechanism and clinical application of hyaluronic acid
- 2The latest research progress of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
- 3Advances in mosquito repellents
- 4Research progress and coping strategy of the drug resistant mechanism of platinum anti-tumor drugs
- 5Research progresses on Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in inflammatory diseases
- 6
- 7Research progress on Sophora Flavescens of traditional Chinese medicine
- 8Review of pharmacological effects of Paeoniae Radix Rubra
- 9Research progress on the treatment of vascular dementia by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis
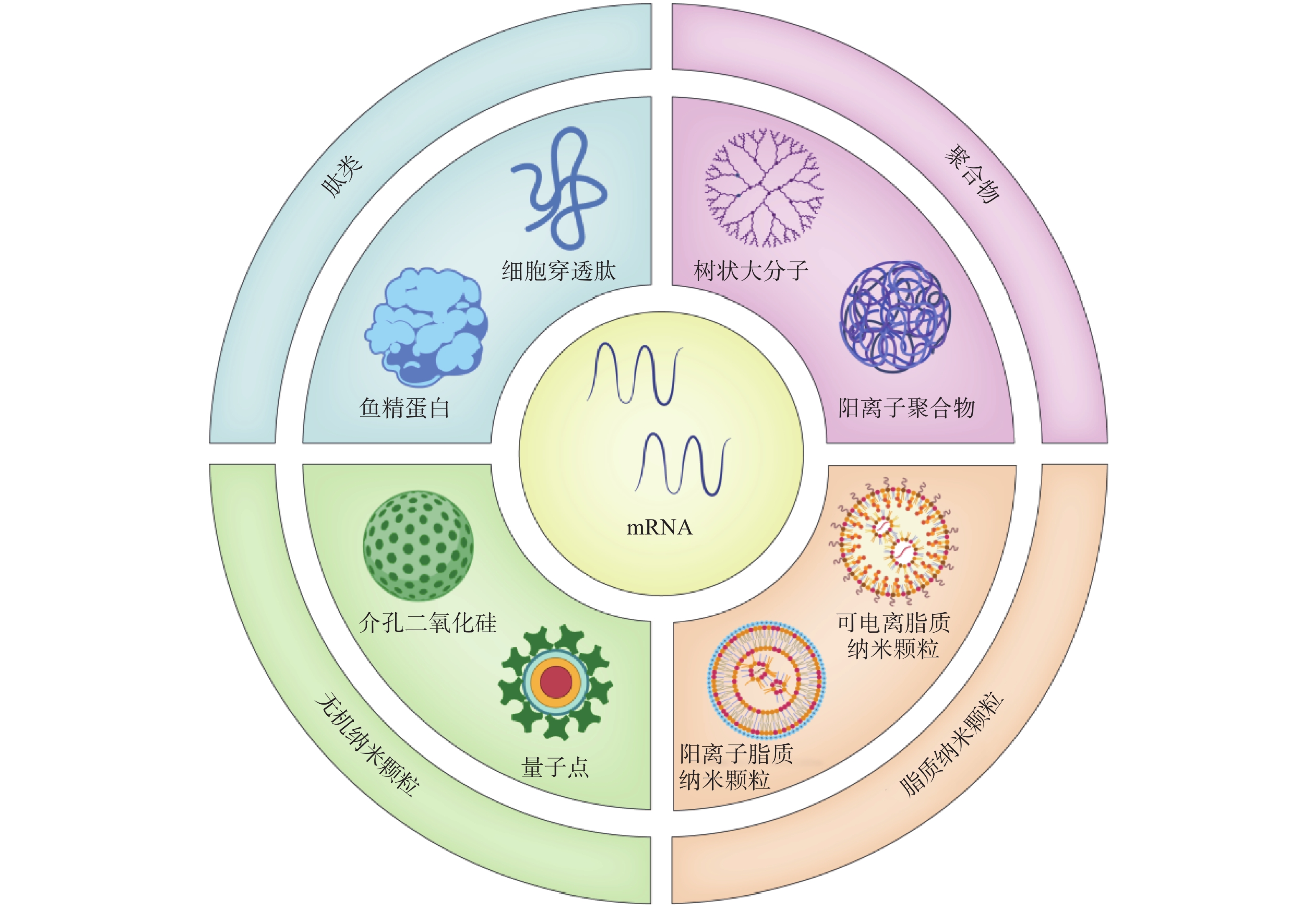
- 10Progress on mRNA tumor vaccine with non-viral delivery system
- More >
 Wechat
Wechat









 Contribution System
Contribution System Author Login
Author Login Review Login
Review Login Editor Login
Editor Login Reader Login
Reader Login



 友情链接
友情链接