-
据国际癌症研究机构(IARC,https://www.iarc.who.int/)提供的数据显示,2020年女性乳腺癌现已成为全球最常见的癌症之一[1]。其中有15%~25%的乳腺肿瘤存在人类表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)过表达。HER2阳性的乳腺癌浸润性强、无病生存期短、预后差,对化疗敏感性差,且易复发[2]。曲妥珠单抗是一株靶向HER2的人源化单克隆抗体。虽然曲妥珠单抗单药对乳腺癌治疗起到了很好的改善的效果, 但其疗效还有所不足,如对HER2过表达的乳腺癌患者初次治疗有效率仅在30%左右[3]。EGCG是绿茶中主要的多酚[4],有抑制肿瘤细胞生长、增殖、转移和血管生成,诱导细胞凋亡和增强抗肿瘤免疫等多种抗肿瘤作用[5-9]。据报道,EGCG在乳腺癌、胃癌、白血病、膀胱癌治疗中均显示有抗肿瘤作用[10-13]。本实验旨在探讨曲妥珠单抗与EGCG对HER2过表达细胞株是否具有协同增殖抑制作用,为HER2高表达乳腺癌的治疗提供新的思路。
-
EGCG(MedChemExpress公司),CCK-8检测试剂盒(美国bimake生物科技有限公司);GAPDH一抗、AKT一抗、p-AKT一抗、MAPK一抗、p-MAPK一抗、EGFR一抗、p-EGFR一抗、HER2一抗、p-HER2一抗、抗兔IgG一抗、抗鼠IgG一抗、HRP抗体二抗(美国Cell Signaling Technology公司),凝胶过滤层析标准品(美国BIO-RAD公司),二抗Goat pAb to Human IgG(英国Abcam公司)。
-
人乳腺癌细胞系BT474、SK-BR-3(购自中国科学院细胞库并保存于本实验室)。
-
AKTA Avant 25蛋白纯化仪、Imager 600超灵敏多功能成像仪(美国Cytiva公司); Agilent 1200 series高效液相色谱仪(美国Agilent公司);Spark多功能酶标仪(瑞士TECAN); Intellicyt® iQue3 高通量流式细胞仪(德国赛多利斯)。
-
用含有曲妥珠单抗重链和轻链表达载体的质粒共转染Expi293F细胞7 d后收集培养上清液,用Protein A亲和层析法进行纯化。SEC-HPLC对抗体的纯度进行检测,并用流式细胞术检测曲妥珠单抗抗体与HER2过表达细胞株SK-BR-3、BT474的结合活性。
-
细胞按3×104个细胞/孔铺于V型底96孔板中,每孔30 μl。曲妥珠单抗按100 nmol/L的起始浓度,3倍比稀释,分成11个浓度梯度,末孔为PBS作为阴性对照,加入铺有细胞的96孔板中,每孔30 μl。曲妥珠单抗与细胞4℃共孵育1~2 h,用含0.1% BSA的PBS洗1遍,加入二抗Goat pAb to Human IgG,1∶200稀释,每孔30 μl,4℃孵育30 min。二抗孵育结束,用含0.1% BSA的PBS洗2遍,每孔加入30 μl 含0.1% BSA的PBS,用 Intellicyt® iQue3 高通量流式细胞仪进行检测。
-
采用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基培养SK-BR-3细胞,用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基培养BT474细胞,培养条件为5% CO2,37℃。当细胞密度达到80%~90%时进行传代,每周2~3次。取对数生长期的细胞进行实验。
-
将细胞按1×104个细胞/孔的数量接种于96孔板中,在37℃、5% CO2条件下培养24 h。每孔加入100 μl含设定浓度药物的培养基,培养48 h后,弃去孔内培养基,每孔加入100 μl含10%CCK8试剂的培养基,继续培养1~3 h,用酶标仪在450 nm测定光密度值(A),并计算细胞的增殖抑制率。增殖抑制率=(A对照−A实验)/(A对照−A背景)。联合给药组用CompuSyn软件计算CI值(药物联合指数),通过CI值的数值可以定量判断药物间相互作用的强度以及性质(CI>1为拮抗作用;CI=1为相加作用;CI<1为协同作用)。
-
根据分组将细胞按5×105个细胞/孔的数量接种于6孔板培养24 h。弃去原培养基,加入含设定浓度药物的培养基继续培养24 h。采用细胞裂解液试剂盒提取各组细胞总蛋白,用BCA试剂盒测定蛋白浓度。按每泳道30 μg蛋白样品的上样量进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳后,转移至PVDF膜。用5%脱脂奶粉在摇床上室温封闭1 h,加入一抗4 ℃孵育过夜,加入二抗室温孵育1 h。一抗、二抗均按照抗体使用说明书稀释。洗膜后,加ECL发光液,用超灵敏多功能成像仪进行显影,并用ImageJ软件对条带进行灰度值分析。目的蛋白相对表达量=目的蛋白灰度值/内参GAPDH灰度值 。
-
采用 GraphPad prism 8.0软件(Version X,USA)进行统计学分析和作图,用compuSyn软件计算联合指数。两组数据之间比较采用t检验,多组数据之间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
-
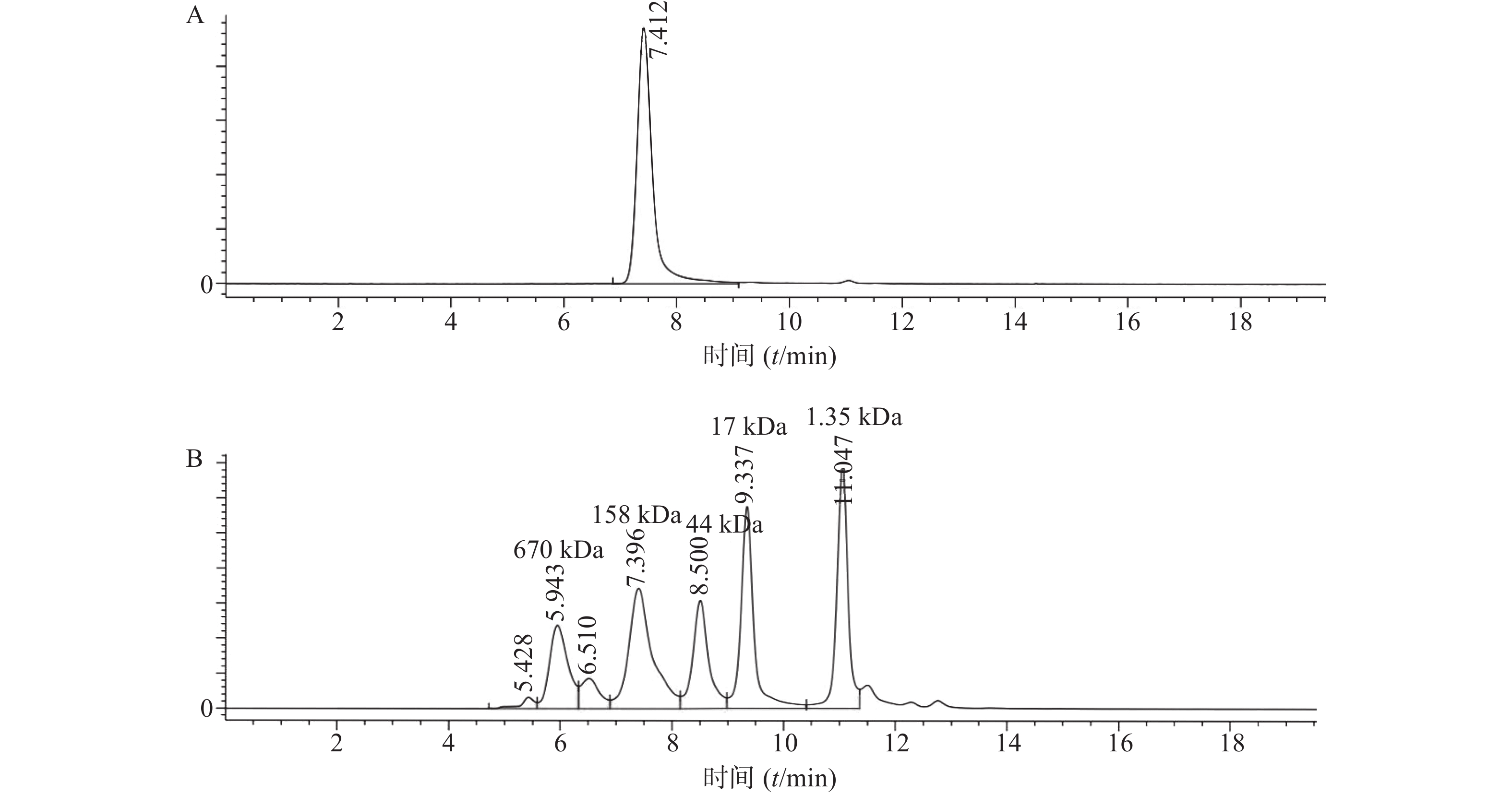
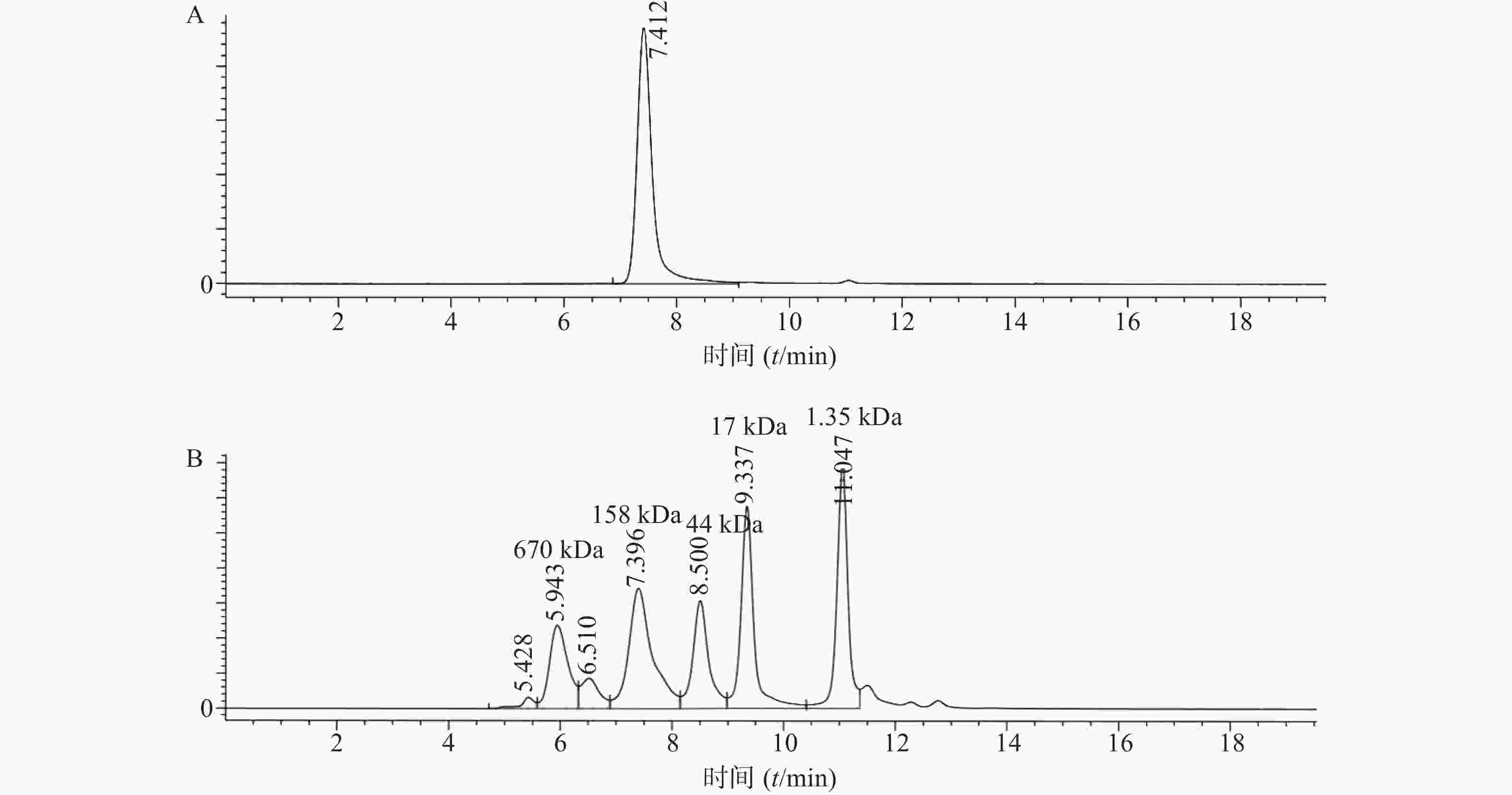
将表达纯化后的曲妥珠单抗用SEC-HPLC进行检测,结果显示曲妥珠单抗的纯度为100%,且分子量大小在150 kDa(1kDa=1×103)左右(图1)。
-
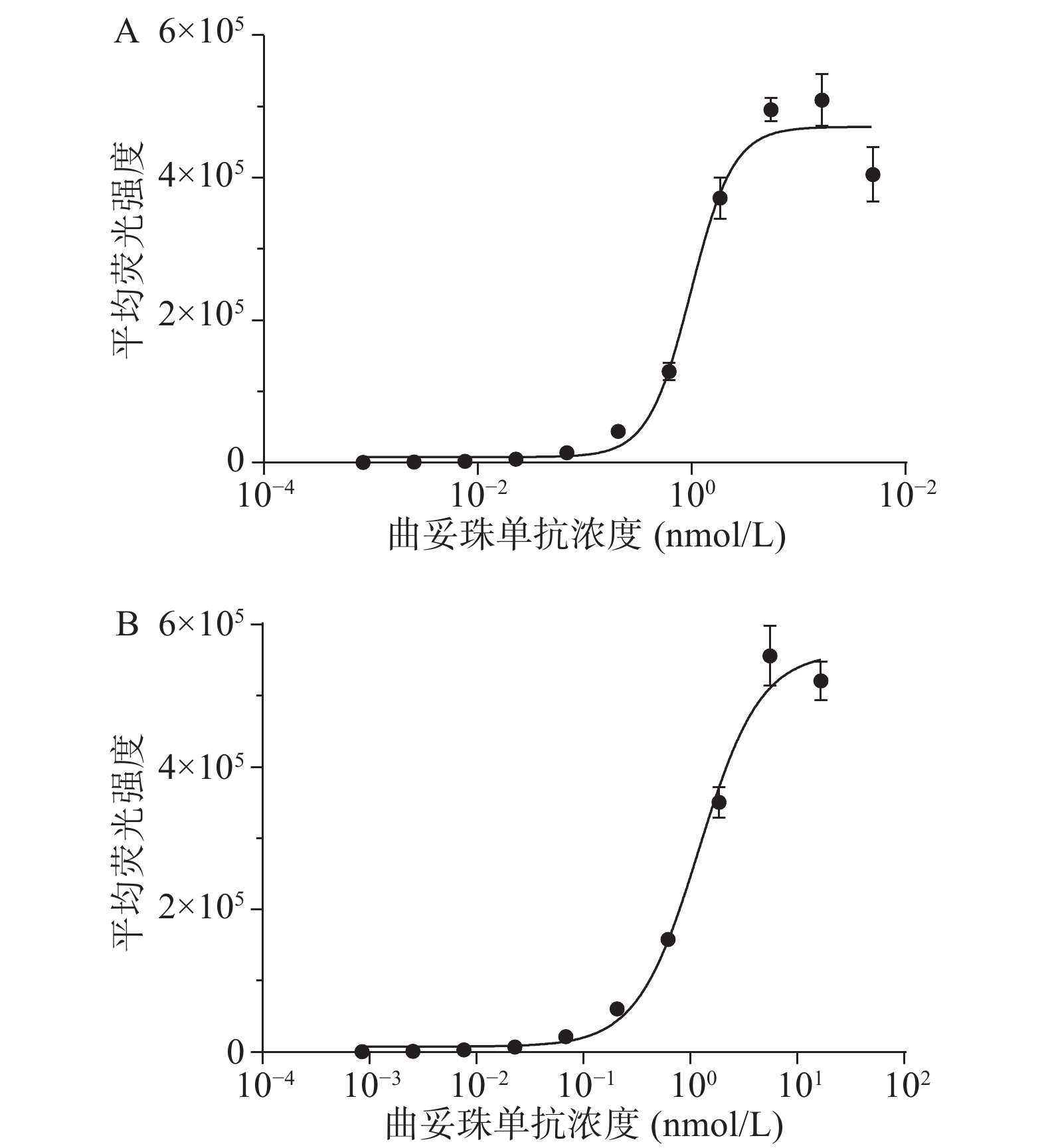
采用流式细胞术测定曲妥珠单抗与HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞株SK-BR-3和BT474的结合活性。结果显示,曲妥珠单抗以浓度依赖性的方式结合SK-BR-3和BT474细胞,其中,曲妥珠单抗与SK-BR-3细胞株结合的EC50值为1.128 nmol/L,与BT474细胞株结合的EC50值为1.203 nmol/L,两者EC50值大约一致(图2)。
-
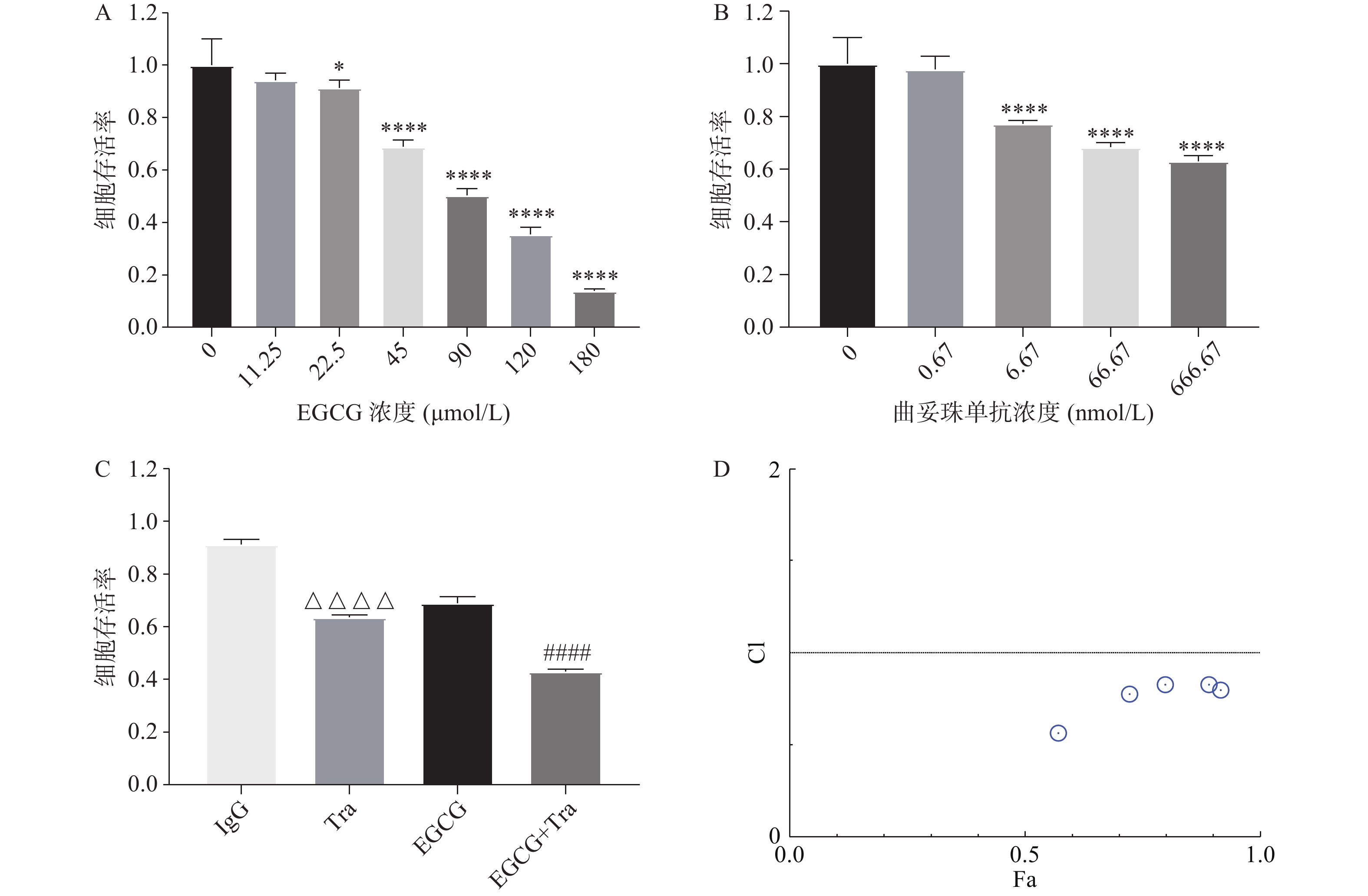
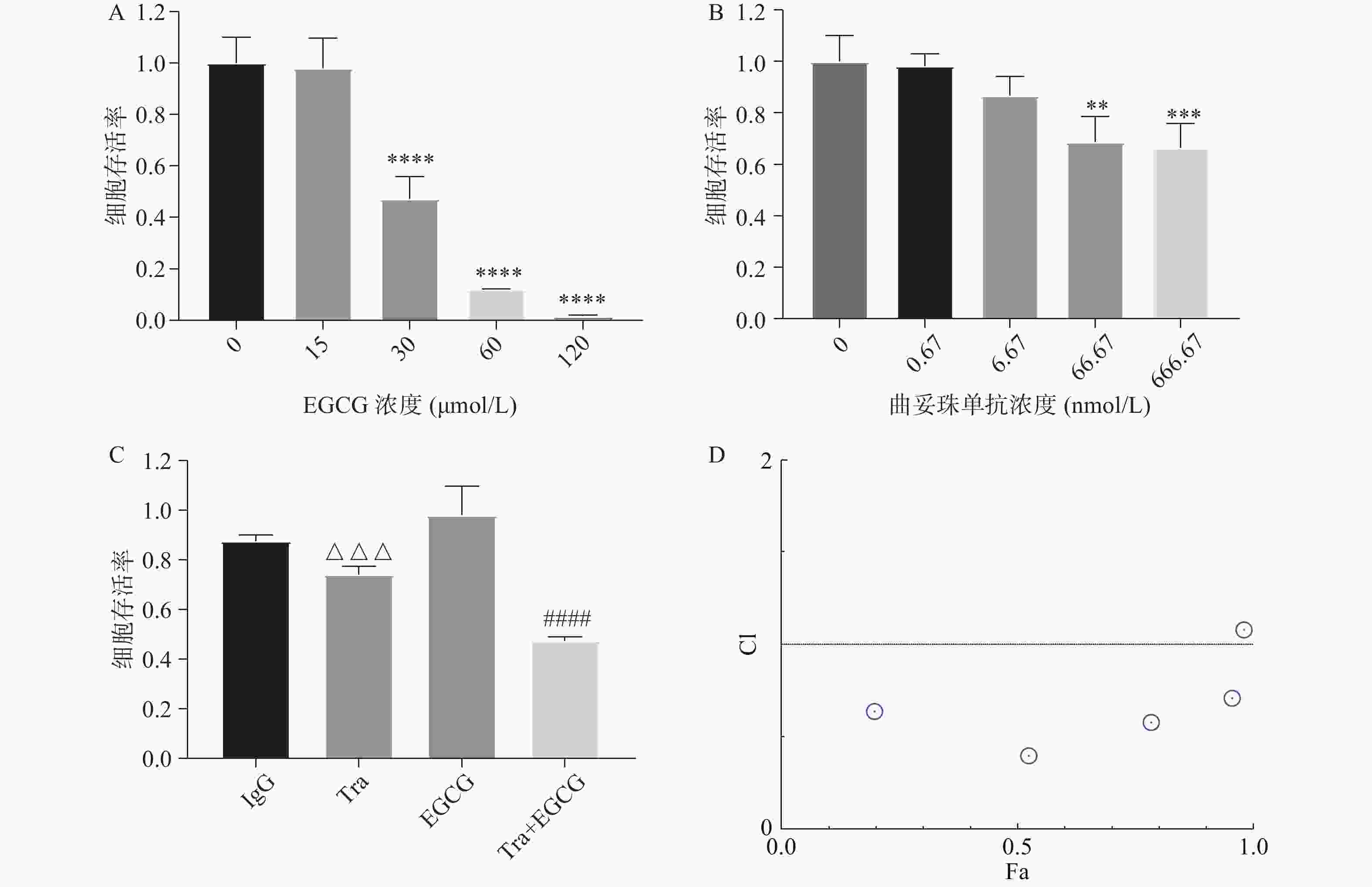
采用CCK8法测定EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联合对BT474的增殖抑制作用。图3A和图3B结果显示, EGCG和曲妥珠单抗对BT474细胞均显示出浓度依赖性的增殖抑制作用。图3C结果显示EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合给药组的增殖抑制作用显著强于单药组。图3D结果显示EGCG在一定浓度范围内(45~200 μmol/L)与16.67 nmol/L 曲妥珠单抗联用时显示有协同抗肿瘤作用(CI<1)。
-
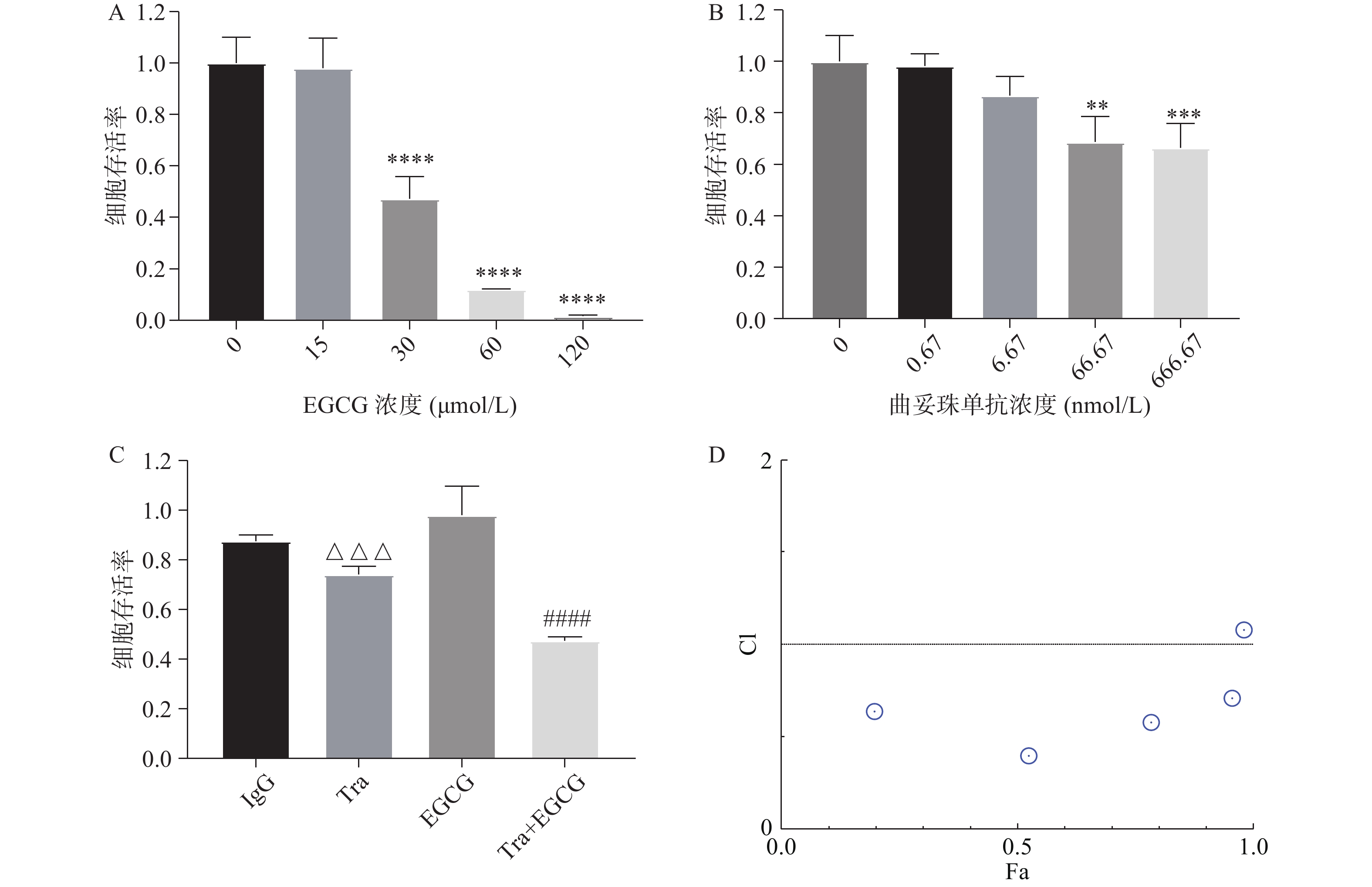
采用CCK8法测定EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联合对SK-BR-3的增殖抑制作用。图4A和图4B结果显示,EGCG和曲妥珠单抗均对SK-BR-3细胞显示出浓度依赖性的增殖抑制作用。图4C结果显示,EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合给药组的增殖抑制作用显著强于单药组。图4D结果显示,EGCG在一定浓度范围内(7.5~120 μmol/L)与16.67 nmol/L曲妥珠单抗联用时有协同抗肿瘤作用(CI<1)。
-
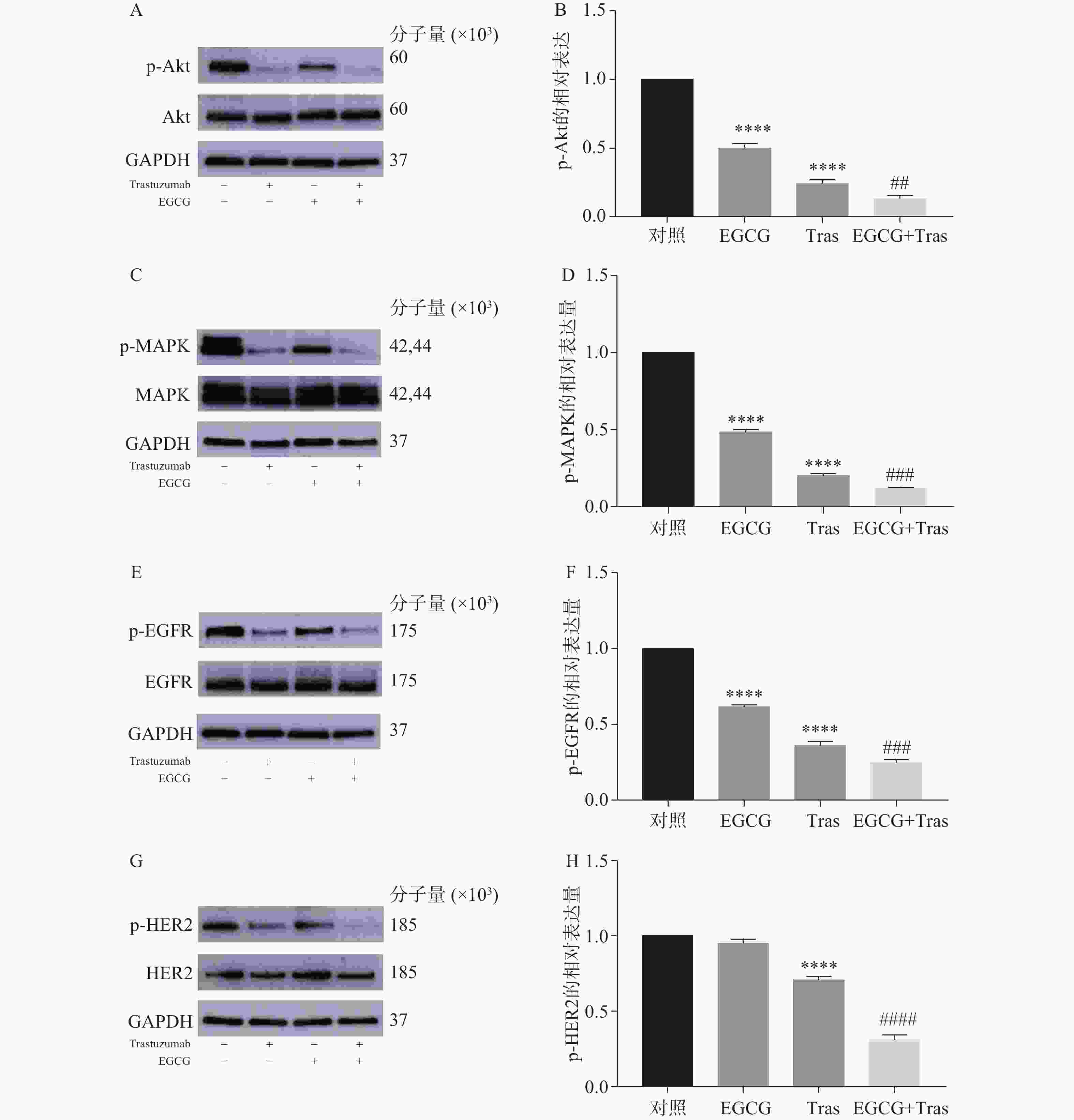
图5A-F结果显示,EGCG单药、曲妥珠单抗单药及两者联用组均能显著降低BT474细胞中p-Akt、p-MAPK、p-EGFR的表达。图5G-H结果显示,曲妥珠单抗单药组能显著降低BT474细胞p-HER2的表达,EGCG单药组虽然无显著性差异(P>0.05),但对p-HER2的表达有一定抑制作用。与EGCG和曲妥珠单抗单药组相比,EGCG与曲妥珠单抗联用可进一步显著降低BT474细胞p-Akt、p-MAPK、p-EGFR、p-HER2蛋白的表达。
-
ErbB-2(HER-2/neu)是一种分子量为1.85×105的穿膜受体络氨酸激酶,属于表皮生长因子受体家族[14]。该家族由4个紧密相关的络氨酸激酶(TK)受体组成:HER1(EGFR)、HER2、HER3和HER4。HER2主要是通过与家族中的其他成员形成同源或异源二聚体,激活下游的RAS/MAPK和磷脂酰肌醇-3/激酶(PI3K)/ATK信号通路,进而促进细胞增殖、迁移、血管生成以及抑制细胞的凋亡[15-16]。ERK/MAPK通路是参与细胞增殖控制的主要细胞内信号通路之一。 PI3K/ATK信号通路在控制Her-2/neu过表达细胞的生长和转化表型中起重要作用[17-18]。HER2过表达的癌症表现出较强的转移能力和浸润能力,对化疗敏感性差,且易复发。
曲妥珠单抗是一株靶向HER2的人源化单克隆抗体。1998年,被美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准应用于治疗HER2阳性的转移性乳腺癌[19]。曲妥珠单抗可能通过下调HER2受体在细胞膜上的表达,阻断HER2和HER3形成异源二聚体从而抑制下游通路,导致细胞周期阻滞,以及抗体依赖的细胞介导的细胞毒性活性[20]等。虽然曲妥珠单抗单药治疗起到了一定的效果, 但大部分HER2过表达的乳腺癌患者对曲妥珠单抗治疗不产生反应,初次治疗有效率大约在30%, 即使对曲妥珠单抗产生反应的患者也有约50%会在1年内发生耐药。
茶多酚可以抑制多种与细胞增殖和肿瘤进展相关的酶活性。EGCG是茶多酚中的主要成分之一。研究显示,在人A431表皮样癌细胞中,EGCG可能通过阻断EGF与其受体的结合进而抑制EGFR活性[21]。EGCG能抑制结肠癌细胞中EGFR、HER2、HER3的激活,并抑制细胞生长[22]。
为了进一步提高HER2靶向治疗疗效,在本研究中我们探讨了曲妥珠单抗和EGCG在乳腺癌细胞的联合抗肿瘤作用。实验结果发现EGCG与曲妥珠单抗在一定浓度范围内可以协同抑制HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞的生长,提示临床治疗中如果利用EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合治疗则需重点关注两者各自的剂量。可以先利用乳腺癌荷瘤小鼠模型对不同剂量的EGCG和曲妥珠单抗的联合抗肿瘤作用进行评价,并参考动物体内药效实验的结果进行EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联合用药临床试验的设计,通过临床试验的结果确定临床治疗时最佳的联合用药剂量。
本研究还对EGCG和曲妥珠单抗的联合抗肿瘤作用机制进行了阐明:与EGCG和曲妥珠单抗单药组相比,EGCG与曲妥珠单抗联用可进一步显著降低BT474细胞中p-EGFR、p-HER2和p-Akt、p-MAPK的表达,提示EGCG和曲妥珠单抗联用对HER2过表达乳腺癌细胞的协同增殖抑制活性可能与其显著增强的对Akt和MAPK信号通路的抑制作用有关。本研究为EGCG与曲妥珠单抗的联合应用提供了理论支持,并为HER2过表达乳腺癌的治疗提供新的思路。
The effect and mechanism of epigallocatechol gallate combined with trastuzumab on the proliferation of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202112035
- Received Date: 2021-12-11
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-02-28
- Available Online: 2022-03-29
- Publish Date: 2022-03-25
-
Key words:
- EGCG /
- trastuzumab /
- HER2 overexpression /
- breast cancer /
- synergy /
- proliferation inhibition
Abstract:
| Citation: | LEI Bixia, ZHANG Mengyao, CHEN Xiaorui, LIANG Beibei, XIE Wei, WANG Huajing, LI Bohua. The effect and mechanism of epigallocatechol gallate combined with trastuzumab on the proliferation of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(2): 136-142. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202112035 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: