-
槟榔为棕榈科植物槟榔的干燥成熟种子,居“四大南药”之首,入药最早记录在《李当之药录》中[1],具有行气利水,消积杀虫,截疟等功效,用于治疗寄生虫病、关节炎、青光眼、水肿、脚气、疟疾等疾病[2]。槟榔主要含生物碱、多酚、多糖、脂肪酸、鞣质、氨基酸、三萜类、矿物质、槟榔红色素、粗纤维、油脂、维生素等多种物质[3-4]。药理研究表明其具有抗氧化、抗抑郁、抗炎、抗寄生虫、抗老化、清除自由基、修护神经系统、抗疲劳、改善胃肠功能、治疗糖尿病、抑菌等作用[5],文献报道槟榔的抗氧化作用与其含有的多酚类物质有关[6-12]。
课题组前期的研究发现,槟榔醇提取物能显著增强H9c2细胞的耐缺氧能力[13],进行高原实地研究发现,槟榔多酚能够显著改善高原实地缺氧大鼠的血气指标,能提高其肝、肺、心组织中谷胱甘肽、超氧化物歧化酶活性,降低其肝、肺、心组织中丙二醛的含量,槟榔多酚提取物的抗缺氧作用与消除过量的氧自由基,减轻脂质过氧化和氧化应激损伤有关[14-15]。同时,课题组进一步研究还发现,槟榔多酚提取物能预防高原肺水肿的发生,该作用与其减轻肺水肿、维持肺泡毛细血管通透性、改善氧化应激损伤及病理损伤有关[16]。由此可见,将槟榔多酚提取物开发为新的抗高原缺氧药物具有很大的潜力。槟榔多酚成分复杂,文献报道槟榔多酚中含有儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸、没食子酸等,另外药理研究表明,儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸具有抗氧化、抗炎等作用[17-21],基于此,本研究采用紫外分光光度法对槟榔多酚提取物中总多酚的含量进行测定;并建立槟榔多酚提取物中儿茶素类成分的HPLC测定方法,以期为槟榔多酚提取物的质量控制和标准制定提供实验依据。
-
槟榔由联勤保障部队第九四〇医院药剂科中药房提供,没食子酸(上海源叶生物科技有限公司,批号Y19M8C36143,质量分数≥98%)、儿茶素(中国食品药品检定研究院,批号110877-201604,质量分数99.2%)、表儿茶素(上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,批号K2009336,质量分数≥98%)、原儿茶酸(成都曼思特生物科技有限公司,批号MUST-20110310,质量分数99.78%),甲醇、乙腈均为色谱纯;酒石酸钠钾、七水合硫酸亚铁、磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠、无水乙醇、甲酸均为分析纯。
-
Ultimate 3000DGLC高效液相色谱仪(赛默飞世尔科技)、超微量分光光度计NP80(德国IMPLEN公司),电子分析天平(上海梅特勒-托利多有限公司),超声波清洗器(上海科导超声仪器有限公司),多功能动态热回流提取浓缩机(上海天巨源设备有限公司),电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(上海跃进医疗器械厂)。
-
取槟榔药材20 kg,粉碎后过3号筛,分别加入10倍、8倍、6倍量的80%乙醇,80 ℃加热回流提取3次,时间分别为2、1.5、1.5 h,合并提取液,过滤,滤液减压回收乙醇,得浸膏。浸膏加入等体积水悬浮,加入到已经处理好的AB-8大孔吸附树脂柱上,纯水洗脱除杂,20%乙醇洗脱,收集20%洗脱液,减压回收乙醇得浸膏,真空60 ℃干燥,制得干燥槟榔多酚提取物1,命名为:BLDF202001。大孔吸附树脂经80%乙醇洗脱,收集洗脱液,减压回收乙醇得浸膏,真空60 ℃干燥,制得干燥槟榔多酚提取物2,命名为:BLDF202002。提取物2加水悬浮,加入到已经处理好的聚酰胺层析柱上,纯水洗脱除杂,80%乙醇洗脱,收集80%洗脱液,减压回收乙醇得浸膏,真空60 ℃干燥,制得干燥槟榔多酚提取物3,命名为:BLDF202003。
-
精密称取没食子酸对照品5 mg,置于5 ml容量瓶中,加蒸馏水超声使其充分溶解,定容,配制成1 mg/ml的对照品溶液。
-
分别精密称取各对照品适量,加甲醇制成含儿茶素1.92 mg/ml、表儿茶素2.46 mg/ml和原儿茶酸1.12 mg/ml的单一对照品储备液。
-
精密称取槟榔多酚提取物10 mg,置于10 ml容量瓶中,加乙醇超声,使其充分溶解,定容,配制成1 mg/ml的供试品溶液。
-
精密称取槟榔提取物50 mg,置于10 ml棕色容量瓶中,用甲醇超声使其充分溶解,定容,配制成浓度为5 mg/ml的供试品储备液。精密吸取供试品储备液2 ml,置于5 ml容量瓶中,用50%的甲醇定容至刻度,摇匀,临用前过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,取续滤液,即得。
-
采用酒石酸亚铁法测定槟榔多酚的含量[14],精密吸取“2.2.1”项下的没食子酸对照品溶液各0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.25、0.30 ml,置于5 ml容量瓶中,加蒸馏水至1 ml,再加入酒石酸亚铁溶液1 ml,用pH 7.5的磷酸缓冲溶液定容,混匀,静置15 min,以蒸馏水为空白参照,在540 nm处测定吸光度值。以吸光度值(A)为纵坐标,浓度(X,μg/ml)为横坐标,绘制标准曲线,得没食子酸对照品的线性回归方程:A=12.44X+0.0731,r=0.999 4,表明没食子酸对照品溶液在9.8~58.8 μg/ml范围内线性关系良好。
-
精密吸取没食子酸对照品溶液0.1 ml,按“2.3.1”项下方法测定吸光度,重复测定6次,没食子酸对照品溶液的吸光度RSD值为0.40%,表明该方法精密度良好。
-
取同一供试品溶液(BLDF202001)6份,按“2.3.1”项下方法测定吸光度,槟榔提取物中总多酚的吸光度RSD值为1.1%,表明该方法重复性良好。
-
取同一供试品(BLDF202001)10 mg,精密称定,按“2.2.3”项下方法制备供试品溶液,分别在0、5、10、15、30 min和1、2、4、8、12、24 h后,按“2.3.1”项下方法测定吸光度,槟榔提取物中总多酚吸光度的RSD值为2.8%,表明该供试品在24 h内稳定性良好。
取同一供试品溶液(BLDF202001)0.1 ml,按“2.3.1”项下方法分别于7、9、11、13、15、17、21 min测定吸光度,槟榔提取物中总多酚吸光度的RSD值为0.93%。表明该供试品溶液在21 min内显色稳定,提示总多酚含量测定应等待7 min之后,在21 min之前完成。
-
取同一批(BLDF202001)已知含量的槟榔多酚提取物,平行6份,按“2.2.3”项下方法制备供试品溶液,取供试品溶液0.1 ml,置于5 ml棕色容量瓶中,加入没食子酸对照品溶液0.1 ml,按“2.3.1”项下方法测定吸光度,没食子酸的加样回收率为98.44%,RSD值为1.4%。。
-
吸取0.3 ml的供试品溶液,按“2.3.1”项下方法测定吸光度,平行测定3次,计算总多酚的含量。3批槟榔提取物中总多酚的含量见表1。
批号 总多酚含量(%) BLDF202001 51.45 BLDF202002 51.82 BLDF202003 52.70 -
色谱柱:AcclaimRSLC120 C18柱(3 mm×150 mm,3 µm);流动相为:乙腈(A)-0.3%甲酸溶液(B),梯度洗脱程序见表2;检测波长:280 nm;流速:1.0 ml/min;柱温:35 ℃;进样量:5 μl。
时间(t/min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0~5 5~10 95~90 5~7 10~15 90~85 7~9 15~20 85~80 9~12 20~5 80~95 -
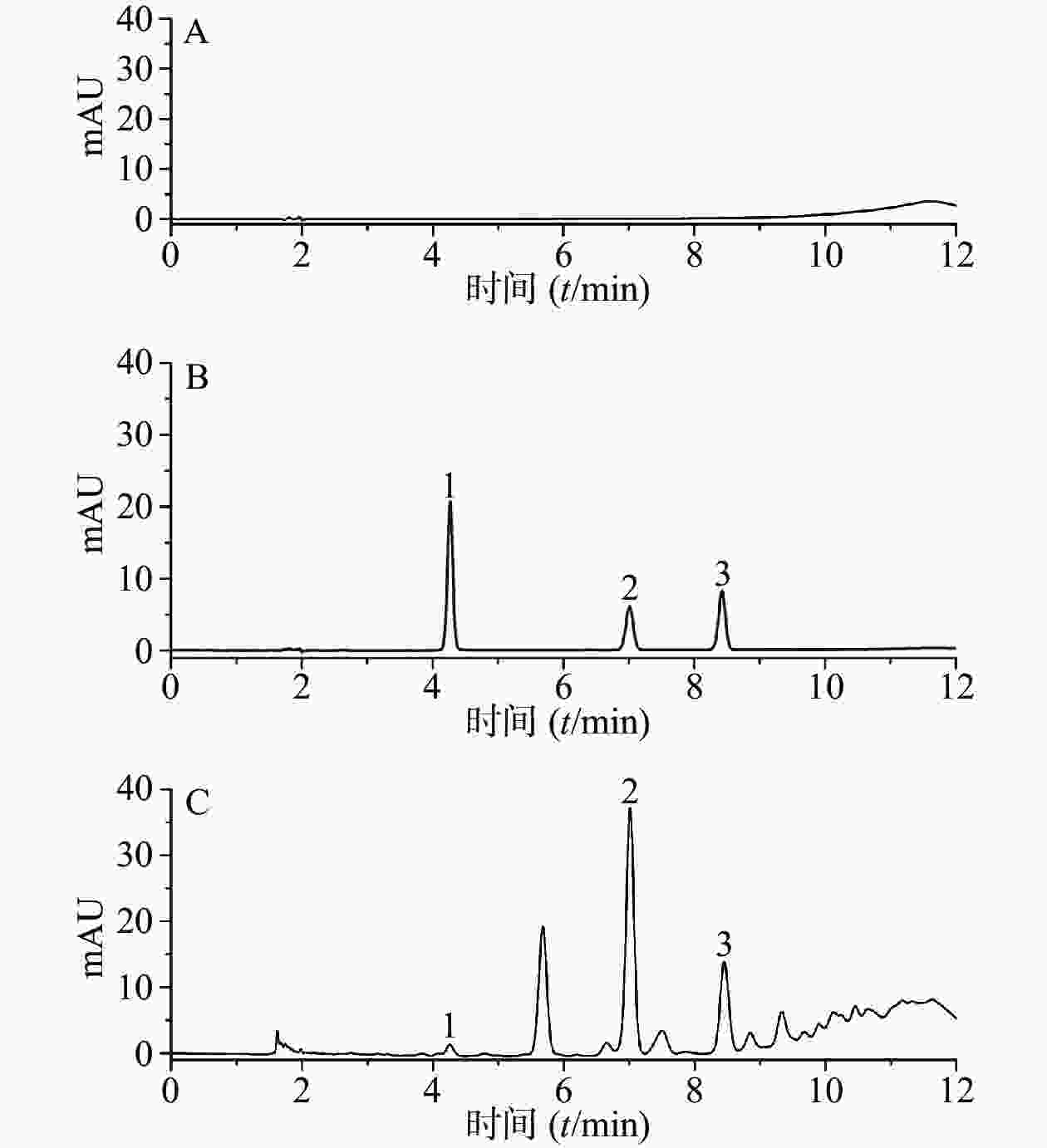
分别精密吸取50%的甲醇,混合对照品溶液,供试品溶液各5 μl,按“2.4.1”项下色谱条件进样分析,记录色谱图。结果表明,各峰分离度均较好,各组分的分离度大于1.5,符合定量分析要求,理论板数以儿茶素计,不低于6 000。其中原儿茶酸、儿茶素、表儿茶素的保留时间分别为4.273、7.017和8.433 min,色谱图见图1。
-
分别精密吸取“2.2.2”项下儿茶素对照品储备液0.010、0.025、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8 ml;表儿茶素储备液0.010、0.025、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.6 ml;原儿茶酸储备液0.005、0.010、0.025、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4 ml,用50%的甲醇定容于5 ml容量瓶中,配制成不同浓度的对照品溶液,按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件进样,以对照品的浓度(X,μg/ml)为横坐标,峰面积(Y)为纵坐标进行线性回归,结果见表3,表明儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸分别在相应的线性范围内线性关系良好。
成分 回归方程 r 线性范围(μg/ml) 儿茶素 Y=0.0436X−0.0201 0.999 7 3.84~307.2 表儿茶素 Y=0.0415X+0.0395 0.999 8 4.92~295.2 原儿茶酸 Y=0.0833X+0.0113 0.997 7 1.12~89.6 -
取各成分浓度约为20 μg/ml的混合对照品溶液,按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件连续进样6次,记录峰面积。儿茶素、表儿茶素和原儿茶酸峰面积的RSD值分别为0.65%、0.96%、2.3%,表明仪器精密度良好。
-
取同一供试品溶液(BLDF202001)按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件分别于0、4、8、12、18 h进样分析,记录峰面积。儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸峰面积的RSD值分别为1.1%、1.6%、1.1%,表明供试品溶液在18 h内稳定。
-
取槟榔多酚提取物(BLDF202001)约50 mg,精密称定,平行6份,分别按“2.2.4”项下方法制备供试品溶液,按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件测定,计算供试品中儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸的质量分数分别为5.9%、2.4%、0.10%,RSD值分别为1.0%、2.1%、2.1%,表明该方法的重复性良好。
-
精密称取已知含量的槟榔多酚提取物(BLDF202001)25 mg,置于5 ml容量瓶中,共6份,分别精密加入一定量的儿茶素、表儿茶、原儿茶酸对照品溶液,分别按“2.2.4”项下方法制备供试品溶液,按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件测定,计算回收率和RSD值。儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸的平均回收率为99.17%、101.67%、101.18%;RSD值分别为2.5%、1.2%、1.8%,表明该方法准确度良好。
-
取3批按“2.2.4”项下方法制备的供试品溶液,按“2.4.1”项下的色谱条件分别测定。3个批号的供试品中儿茶素、表儿茶素、原儿茶酸的含量见表4。
批号 儿茶素 表儿茶素 原儿茶酸含量 BLDF202001 5.90 2.40 0.10 BLDF202002 0.52 0.43 / BLDF202003 1.30 0.77 /
Determination of total polyphenols and catechins in betel nut polyphenol extract
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106013
- Received Date: 2021-06-03
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-04-26
- Available Online: 2023-11-06
- Publish Date: 2022-05-25
-
Key words:
- betelnut total polyphenols /
- catechins /
- HPLC /
- UV spectrophotometry
Abstract:
| Citation: | MA Jianghong, WANG Rong, DU Xing, ZHAO Anpeng, WANG Zihan, ZHANG Haobo. Determination of total polyphenols and catechins in betel nut polyphenol extract[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(3): 243-247. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106013 |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: