-
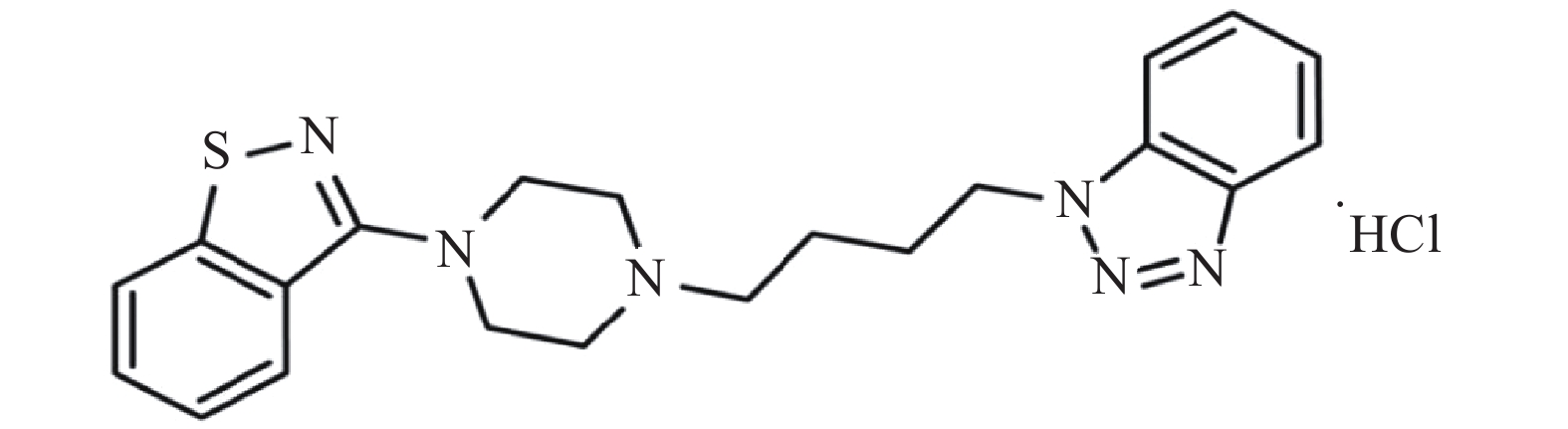
动脉粥样硬化是指动脉壁上形成的纤维脂肪病变,是导致心脏病和中风的主要原因[1]。高血压或血脂异常是触发动脉粥样硬化的独立风险因素,许多高血压患者也患有动脉粥样硬化。因此,降压药物对动脉粥样硬化的作用非常值得关注[2]。MT-1207是一种新开发的多靶标治疗高血压的药物,于2018年进入中国临床试验,它的化学名称为3-(4-(4-(1H-苯并三唑-1-基)丁基)哌嗪-1-基)苯并异噻唑盐酸盐,分子式为C21H25ClN6S,化学结构式如图1所示[3-4]。课题组前期在动物模型上的研究结果表明,MT-1207能够有效地降低血压,改善压力反射敏感性,并且降低高血压器官损伤、减少卒中后病死率[3]。前期研究表明,高血压导致的压力反射性受损能加重动脉粥样硬化,而MT-1207能治疗高血压并改善压力反射敏感性,有可能延缓或改善动脉粥样硬化[5]。目前,对MT-1207的药理性质和作用的评价较少,评价MT-1207对动脉粥样硬化的作用,对临床高血压伴动脉粥样硬化疾病的治疗具有重要的参考价值。因此,本研究评估长期应用MT-1207治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用,并分析其对血糖和血脂等基础研究指标的作用。
-
采用CRISPR/Cas9技术构建的ApoE-/-小鼠(雄性30只、雌性16只),小鼠购于赛业(苏州)生物科技有限公司;8周龄雄性C57小鼠24只,购于上海必凯科翼生物技术有限公司;动物自由饮水和进食,在明暗交替、温度(25±1)℃、相对湿度40%~60%、噪音≤60 dB的环境中饲养。本实验研究严格遵守实验动物福利等伦理原则。
-
MT-1207原料药,批号为20181201,购于辽宁格林生物药业集团股份有限公司,避光密封保存于4℃冰箱。
氯沙坦钾,批号为LOSB-4-06210326,购于宁波美诺华药业股份有限公司,避光密封保存于4℃冰箱。
-
含药饲料的制备:①计算含药饲料中的药物浓度,即饲料含药量,饲料含药量(mg/kg)=给药剂量(mg/kg)/小鼠平均进食量(g/kg)×1 000。②分别称量一定质量的原料药(MT-1207或氯沙坦)和普通饲料粉,将原料药与普通饲料粉在饲料混合器中混合1 h,使药物均匀分布在饲料粉中。③向混匀的药物饲料中加少量的水,将遇水形成的团块搓开后放入饲料搅拌机中再次混合0.5 h。④使用颗粒饲料机将混匀的饲料粉压制成药物饲料,置于50℃烘箱烘干。⑤最后,将含药饲料置于4℃冰箱中避光密封保存。
高脂饲料,购于上海普路腾生物科技有限公司,配方为繁殖鼠料60%、猪油16.4%、蔗糖10%、酪蛋白8.5%、胆固醇1.3%、胆盐0.3%、预混料1.6%和麦芽糊精1.9%。
-
每天分别称取MT-1207和氯沙坦原料药10 mg,加双蒸水3.3 ml,超声溶解,分别制成3 mg/ml的药物溶液。空白对照溶液为双蒸水。
-
将雄性和雌性ApoE-/-小鼠随机分为3组,即普通饲料对照(模型)组(n=15),氯沙坦给药(氯沙坦)组(n=14)和MT-1207给药(MT-1207)组(n=17),分别给予普通饲料、氯沙坦含药饲料和MT-1207含药饲料,给药剂量为30 mg/kg,给药周期为4个月。
-
将C57小鼠随机分为3组,即空白对照(模型)组(n=7)、氯沙坦组(n=7)和MT-1207组(n=7),进食高脂饲料,并分别于每天灌胃双蒸水、氯沙坦溶液和MT-1207溶液,给药剂量为30 mg/kg,给药周期为1个月。
-
每2周称量ApoE-/-小鼠的体质量;每周称量C57小鼠的体质量。
-
长期饲料给药的ApoE-/-小鼠,每2~4周称重每笼小鼠3 d前、后的饲料重量,计算小鼠平均进食量。平均进食量(g/kg)=饲料重量差(g)/每笼小鼠数量/天数/平均体质量(g)×1 000。
灌胃给药的高脂饮食的C57小鼠,每周称每笼小鼠1 d前、后的饲料重量,计算小鼠平均进食量。平均进食量(g/kg)=饲料重量差(g)/小鼠数量/平均体质量(g)×1 000。
-
长期饲料给药的ApoE-/-小鼠,每4周检测小鼠禁食后的血糖水平;灌胃给药的C57小鼠,每周检测小鼠禁食后的血糖水平,具体血糖测定方法如下:血糖检测前将实验小鼠禁食不禁水,禁食时间为晚上20:00至次日8:00(禁食12 h)。次日清晨先将小鼠单只单笼放于安静无打扰的环境中40 min,小鼠自由活动。早上8:00检测小鼠血糖,剪去小鼠尾巴末端1~2 mm,尾巴末端血滴弃去第1滴后滴于GA-3型血糖仪试纸条上,测定血糖。
-
1%戊巴比妥钠溶液的配制:称取0.500 6 g戊巴比妥钠,加水50 ml溶解、混匀即得。
小鼠称重,1%戊巴比妥钠(100 mg/kg)腹腔麻醉,打开胸腔,暴露心脏,用1 ml注射器自上下腔静脉汇合处抽取血液至离心管中并室温静置2 h,离心取血清并储存于−80℃超低温冰箱。使用微量灌流泵以4℃预冷的1×PBS缓冲液灌流小鼠心脏后,解剖肝脏、心脏并称重。
-
在显微镜下逐层分离主动脉至髂总动脉,分离除去附着在血管上的多余脂肪组织,观察主动脉的斑块情况并拍照。将主动脉纵向切开、展开并用钢针固定于特殊处理的培养皿中,主动脉内腔面平铺朝上。整个过程中轻柔,避免过多牵拉损伤动脉内膜。
-
0.5%油红O储备液的配制:称取油红O粉末0.254 2 g,加入50 ml异丙醇充分溶解,滤纸过滤2次后使用0.2 μm的滤膜再次过滤,室温避光密封储存。
将0.5%油红O储备液与水按3∶2比例配制油红O工作液,现配现用。使用油红O工作液浸没主动脉内腔面染色15 min,倒掉油红O溶液,加入75%乙醇浸没主动脉分色10~15 min,倒掉75%乙醇,加入PBS缓冲液,用数码相机拍摄图像。使用Image-J软件分别测量整个主动脉内腔面的面积和斑块面积。主动脉粥样硬化斑块面积比=斑块总面积/主动脉内腔总面积×100%。
-
由武汉赛维尔生物科技有限公司检测血清中三酰甘油(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)和游离脂肪酸(NEFA)水平。
-
使用GraphPad Prism-6软件对数据进行统计分析。所有数据的计量均以平均数±标准误(
$ \bar{x} $ ±s)表示,两样本均数的比较采用 t 检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 -
氯沙坦组:雄鼠平均进食量为133 g/kg,饲料平均含药量为206 mg/kg,实际药物剂量为27 mg/kg;雌鼠平均进食量为159 g/kg,饲料平均含药量为209 mg/kg,实际药物剂量为33 mg/kg,如图2所示。
MT-1207组:雄鼠平均进食量为127 g/kg,饲料平均含药量为217 mg/kg,实际药物剂量为27 mg/kg;雌鼠平均进食量为152 g/kg,饲料平均含药量为216 mg/kg,实际药物剂量为33 mg/kg,如图2所示。
综上,氯沙坦组和MT-1207组小鼠实际药物剂量与理论药物剂量一致。
-
长期饲料给药过程中,3组小鼠的体质量无显著性差异。与模型组小鼠相比,MT-1207组小鼠从第6周开始体质量增长得更快,氯沙坦组小鼠从第2周开始体质量增长得更快,如图3所示。
-
长期饲料给药过程中,第4、12、18周ApoE-/-小鼠的血糖数据如图4所示。第4周和第18周给药组小鼠血糖与模型组相比无差异;第12周氯沙坦组和MT-1207组小鼠血糖水平比模型组小鼠血糖低。
-
长期饲料给药4个月后,ApoE-/-小鼠未禁食条件血脂检测结果见图5。高水平的LDL-C被认为是动脉粥样硬化的致病性风险因素,本研究中动脉粥样硬化ApoE-/-小鼠的LDL-C水平均远高于正常水平。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组小鼠的HDL-C的水平上升且具有显著性差异,TC、LDL-C和TG水平有上升趋势,但无显著性差异;与模型组相比,MT-1207组小鼠的TC、LDL-C、HDL-C、TG和NEFA的水平无显著性差异;与氯沙坦组相比,MT-1207组小鼠TC、LDL-C、HDL-C、TG和NEFA的水平有降低的趋势,但无显著性差异。
-
长期饲料给药4个月后,ApoE-/-小鼠取材时的体质量、肝脏重、肝脏体质量比、心脏重、心脏体质量比结果如图6所示。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组小鼠的肝脏重量增加,肝脏体质量比有增加的趋势;MT-1207组小鼠的肝脏重量有增加的趋势,肝脏体质量比增加。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组和MT-1207组小鼠的心脏重量和心脏体质量比均无明显差异。
-
长期饲料给药4个月后,与模型组相比,MT-1207组和氯沙坦组小鼠主动脉粥样硬化斑块面积比均无显著差异,如图7所示,表明MT-1207和氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化斑块面积无改善作用。
-
不同时间点测定的小鼠的平均进食量如图8所示。给药过程中高脂饲料饮食的小鼠平均进食量要低于给药前普通饲料饮食的小鼠的平均进食量。
-
每组C57小鼠每天分别灌胃双蒸水、MT-1207和氯沙坦溶液,连续4周后,3组小鼠的体质量和体质量增长百分比结果如图9所示。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组和MT-1207组的小鼠体质量无显著性差异;与模型组相比,氯沙坦组小鼠的体质量增长百分比与模型组无明显差异,而MT-1207组小鼠的体质量增长百分比明显低于模型组小鼠。
-
给药前与给药后1周、2周、3周、4周测定的小鼠血糖结果如图10所示。实验结果表明,高脂饲料喂养后,小鼠的血糖水平整体升高。MT-1207组小鼠给药后1周、2周、4周时的血糖水平比模型组的高;氯沙坦组小鼠给药后4周时的血糖水平高于模型组,其他时间点与模型组相比均无显著性差异。在该实验条件下,MT-1207对血糖有升高的作用,而氯沙坦有升高血糖的趋势,两者均不能降低血糖水平。
-
30 mg/kg的剂量灌胃给药4周后,小鼠未禁食条件的血脂检测结果见图11。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组小鼠TC、LDL-C和TG水平增高,HDL-C和NEFA水平则无显著差异;与模型组相比,MT-1207组小鼠的LDL-C水平提高,TC、HDL-C、TG和NEFA的水平则无显著性差异;与氯沙坦相比,MT-1207组小鼠的TC、LDL-C、HDL-C、TG和NEFA的水平有降低的趋势,但无显著性差异。
-
30 mg/kg的剂量连续灌胃给药4周后,与模型组相比,氯沙坦组小鼠的肝脏重量有增加的趋势,肝脏体质量比增加,MT-1207组小鼠肝脏重量和肝脏体质量比有增加的趋势,无显著性差异。与模型组相比,氯沙坦组和MT-1207组小鼠的心脏重量和心脏体质量比均无明显变化,结果如图12。
-
MT-1207是一种新开发的多靶标治疗高血压的药物,目前对其药理性质和作用的研究还比较少,本实验研究了MT-1207对血糖、血脂和动脉粥样硬化的作用,研究结果表明,30 mg/kg剂量的MT-1207不能改善ApoE-/-小鼠或高脂饮食小鼠的血糖和血脂水平,对ApoE-/-小鼠的动脉粥样硬化情况也无改善作用。在两种不同模型小鼠的研究中发现,MT-1207表现出对血糖的不同作用,30 mg/kg剂量的MT-1207提高了高脂饮食的C57小鼠的血糖,而基本不改变ApoE-/-小鼠的血糖水平,结合实验现象分析,可能是由于该剂量的MT-1207灌胃给药后,小鼠立即表现出活动量的减少,影响了小鼠的进食和血糖水平。因此,本实验的下一步研究需要改进的是控制药物的剂量和给药时间,减少药物对小鼠活动和进食的影响。
氯沙坦是经典的常用抗高血压药物,临床试验表明,氯沙坦能显著降低糖尿病、高血压和左心室肥大患者的心血管发病率和病死率[6]。还有临床研究结果表明,氯沙坦能够降低患有血脂异常的高血压患者的血糖、血脂水平[7]。临床前研究的文献报道表明,氯沙坦能够改善动脉粥样硬化,但对血脂水平无明显作用[8-10]。一项研究表明,氯沙坦能降低高脂饮食新西兰兔的内膜增厚和内膜/中膜比率,降低脂质面积[8];另一项研究结果也表明,氯沙坦对高脂饮食的ApoE-/-小鼠的体质量和血脂水平没有影响,但可以改善动脉粥样硬化的斑块面积[9];氯沙坦治疗ApoE-/-小鼠显著减少了油红O染色的动脉粥样硬化病变区域,但对TC、LDL-C等血脂水平无改善作用[10]。本实验进一步探究了氯沙坦对动脉粥样的作用,实验结果表明,氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠的斑块面积没有直接的改善作用,也没有降低血脂LDL-C的水平。本实验中氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化的作用与文献报道的不一致的原因可能是研究模型的不同,本实验采用的动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠为自发形成动脉粥样硬化的ApoE-/-小鼠,其导致的动脉粥样硬化的进程可能与文献中高脂饲料饮食后的小鼠动脉粥样硬化的进程不一致,从而在本实验条件下氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化的作用不明显。因此,本实验也补充了氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化的作用的基础研究数据,为进一步探究氯沙坦对动脉粥样硬化作用的研究提供参考。
总的来说,本实验表明,MT-1207和氯沙坦不会改善血糖、血脂水平,且不加重动脉粥样硬化情况,为临床高血压伴动脉粥样硬化病患的治疗提供了参考。
Effects of MT-1207 on blood glucose, blood lipids and atherosclerosis in mice
-
摘要:
目的 研究MT-1207对小鼠血糖、血脂和动脉粥样硬化的作用。 方法 载脂蛋白E (ApoE)基因敲除(ApoE-/-)小鼠分别给予普通饲料、氯沙坦含药饲料和MT-1207含药饲料,给药剂量为30 mg/kg,测定小鼠的体质量、血糖和血脂指标,并评价动脉粥样硬化的斑块面积。对8周龄的雄性C57小鼠给予高脂饲料,每天以30 mg/kg的剂量灌胃MT-1207和氯沙坦,考察小鼠的体质量、血糖和血脂的水平,进一步评价MT-1207对血糖、血脂的作用。 结果 长期MT-1207饲料给药和氯沙坦饲料给药的ApoE-/-小鼠体质量增长更快,但血糖和血脂的水平没有显著改善,动脉粥样硬化的斑块面积也无明显变化。MT-1207和氯沙坦对高脂饮食的C57小鼠血糖、血脂均无明显改善作用。 结论 MT-1207和氯沙坦对血糖、血脂以及动脉粥样硬化没有改善作用,不会加重动脉粥样硬化。 Abstract:Objective To study the effect of MT-1207 on blood glucose, blood lipids and atherosclerosis in mice. Methods The apolipoprotein E knockout (ApoE-/-) mice were fed with normal feed, drug feed containing losartan and drug feed containing MT-1207 at a dosage of 30 mg/kg. The body weight, blood glucose and blood lipids were detected, and the plaque area of atherosclerotic was evaluated. 8-week-old male C57 mice were fed a high fat diet and given intragastric administration of MT-1207 and losartan at a dose of 30 mg/kg per day. The body weight, blood glucose and lipids levels were also examined to further evaluate the effects of MT-1207 on blood glucose and lipids levels. Results ApoE-/- mice treated with MT-1207 and losartan gained weight faster. There was no significant improvement in blood glucose and lipid levels, and no significant change in atherosclerotic plaque area. MT-1207 and losartan had no significant improvement effect on blood glucose and blood lipids of C57 mice. Conclusion MT-1207 and losartan couldn’t improve the levels of blood glucose, blood lipids and atherosclerosis, and couldn’t aggravate atherosclerosis. -
Key words:
- MT-1207 /
- losartan /
- atherosclerosis /
- blood glucose /
- blood lipids
-
[1] LIBBY P, BURING J E, BADIMON L, et al. Atherosclerosis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5(1):56. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0106-z [2] HURTUBISE J, MCLELLAN K, DURR K, et al. The different facets of dyslipidemia and hypertension in atherosclerosis[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2016, 18(12):1-12. [3] XU T Y, WANG P, TIAN J S, et al. Pharmacological characterization of MT-1207, a novel multitarget antihypertensive agent[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2021, 42(6):885-897. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00636-1 [4] ZHANG H, WU M, HU Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MT-1207, a novel multitarget blocker of α1 receptor, 5-HT2A receptor, and calcium channel, in healthy subjects[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2021, 30(3):271-278. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1887137 [5] CAI G J, MIAO C Y, XIE H H, et al. Arterial baroreflex dysfunction promotes atherosclerosis in rats[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2005, 183(1):41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.03.037 [6] LINDHOLM L H, IBSEN H, DAHLOF B. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes in the Losartan intervention for Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol[J]. Lancet, 2002, 359(9311):1004-1010. [7] SIVASUBRAMANIAM S,KUMARASAMY B. Pleiotropic effects of Losartan in hypertensive patients with dyslipidemia[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2017, 11(9):FC05-FC08. [8] ZHANG Y H, HAO Q Q, WANG X Y, et al. ACE2 activity was increased in atherosclerotic plaque by losartan: possible relation to anti-atherosclerosis[J]. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, 2015, 16(2):292-300. doi: 10.1177/1470320314542829 [9] YANG J M, SUN Y, DONG M, et al. Comparison of angiotensin-(1-7), losartan and their combination on atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 240(2):544-549. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.02.055 [10] LEE B S, CHOI J Y, KIM J Y, et al. Simvastatin and losartan differentially and synergistically inhibit atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e (-/-) mice[J]. Korean Circ J, 2012, 42(8):543-550. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.8.543 -





 下载:
下载: