-
山楂为蔷薇科植物山里红Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N. E. Br. 或山楂 Crataegus pinnati- fida Bge. 的干燥成熟果实,焦山楂为其炒制品[1]。现代药理研究证明,焦山楂抑菌作用强于生山楂,而某些特定菌群与消化功能密切相关[2]。而山楂炒焦后产生新的物质—类黑素,类黑素是在食品热处理过程中形成的。目前,类黑素的抗菌活性已得到证实。大多数类黑素对微生物作用的研究都是在特定的微生物生长培养基中进行的,这些研究表明类黑素可以刺激微生物生长[3],也可以抑制微生物生长[4-5]。肠道菌群与人体健康密切相关,药物和功能食品可能通过调节肠道微生物来改善胃肠功能,帮助消化[6-7]。双歧杆菌和大肠杆菌是典型的有益菌和有害菌,双歧杆菌常被加入酸奶饮品中帮助消化。乙酸是双歧杆菌的主要代谢物质,随着乙酸的增多,pH值降低从而抑制大肠杆菌的生长繁殖。本实验通过研究山楂,焦山楂以及焦山楂炒制过程中产生的类黑素对大肠杆菌、双歧杆菌以及其代谢物乙酸的影响,探究“山楂炒焦长于消食导滞”的作用机制。
-
低温培养箱(美墨尔特有限公司,德国),生物安全柜(赛默飞世尔科技公司,美国),高压灭菌锅(三洋公司,日本),纯水机(密理博公司,美国),厌氧罐(北京陆桥技术股份有限公司,北京);紫外可见分光光度计(上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司,上海);7890B型气相色谱仪(安捷伦科技有限公司,美国);HP-FFAP型毛细管柱(货号:19091F-413,安捷伦科技有限公司,美国);GM900型非接触红外测温仪(深圳聚茂源科技有限公司,深圳)。
-
MRS固体培养基、PYG液体培养基、厌氧产气袋和厌氧指示剂(北京陆桥技术股份有限公司);蛋白胨、酵母粉(英国OXOID公司);乙酸(98.85%,国药集团化学试剂有限公司,中国);其余试剂均为分析纯。
-
净山楂饮片(四川同善堂中药饮片有限责任公司,批号:180501);双歧杆菌(GDMCC1.1258)、大肠杆菌(ATCC25922)(中国科学院微生物研究所)。
-
参照2015版《中国药典》一部山楂项下制备焦山楂。取生山楂150 g,中火(380~420)℃炒制10 min,至药材表面呈焦黄或焦褐色,内部颜色加深,并具有焦香气味,取出,常温封存,即得。
-
(1)生山楂和焦山楂浸膏的制备
取生山楂和焦山楂各100 g进行水浸提,料液比为1:15,浸提8 h,浸提2次。生山楂和焦山楂浸提液分别在4 ℃下以3 600 r/min离心10 min,取上层清液各1 000 ml。将500 ml上层清液进行蒸发浓缩至胶状,停止加热,余温使其自然干燥,得生山楂浸膏13.75 g,焦山楂浸膏14.02 g。
(2)焦山楂中类黑素的提取
取焦山楂100 g,按照“1.2.2”项中⑴的方法提取得到1 000 ml上层清液。取500 ml上层清液蒸发浓缩得棕褐色浓缩液50 ml,进行大孔树脂吸附,室温吸附流速1.5 ml/min,60%乙醇作为洗脱剂,洗脱至色谱柱上无棕色为止,收集洗脱液500 ml。洗脱液蒸发浓缩至胶状,停止加热,余温使其自然干燥,得焦山楂类黑素浸膏13.12 g。
(3)类黑素的紫外检测
取类黑素浸膏1 g,蒸馏水溶解定容至100 ml,取10 ml溶液,分别定容至50 ml;因波长420 nm处是类黑素的特征吸收波长,测其特征吸收下的吸光度值,焦山楂类黑素浸膏吸光度值为0.492,说明焦山楂中类黑素提取成功。
-
(1)双歧杆菌测试菌菌液的制备
以接种环自双歧杆菌标准菌种管挑取菌种,划线接种至MRS固体培养基,36 ℃厌氧培养48 h,挑取单菌落接种至PYG液体培养基,36 ℃厌氧培养48 h,以生理盐水调整浓度至1.0麦氏浓度,作为受试菌初始菌液,按10:1浓度加入试验体系。
(2)大肠杆菌测试菌液的制备
以接种环自大肠杆菌标准菌种管挑取菌种,划线接种至LB固体培养基(配方:蛋白胨10 g,酵母粉5 g,氯化钠10 g,琼脂粉15 g,加入1 L蒸馏水,以5 mol/L氢氧化钠调节pH至7.0,121 ℃高压灭菌15 min备用),36 ℃有氧培养24 h,挑取单菌落接种至LB液体培养基(配方:蛋白胨10 g,酵母粉5 g,氯化钠10 g,加入1 L蒸馏水,以5 mol/L氢氧化钠调节pH至7.0,121 ℃高压灭菌15 min备用),36 ℃有氧培养6 h,以生理盐水调整浓度至0.5麦氏浓度,作为受试菌初始菌液,按10:1浓度加入试验体系。
(3)样本药液的处理
准确称取生山楂,焦山楂和类黑素浸膏各10 g,加入100 ml去离子水,超声振荡处理,期间手动震摇数次,直至样本完全溶解,配制10%母液,并经115 ℃高压灭菌处理15 min后4 ℃保存备用。
(4)乙酸含量测定
①样本前处理:将经过微生物培养的溶液1 ml,经过高速离心机4 000 r/min离心,之后再过0.2 µm有机相滤头于进样瓶,样品量大于0.5 ml,或者使用内插管,上机测定。
②标准溶液及标准曲线:称取60.05 g乙酸于100 ml容量瓶,用一级水定容至刻度,摇匀,作为储备标准溶液,浓度为101.33 mmol/L。将标准储备溶液依次稀释1、3、10、20、100、200倍得标准工作溶液。
③色谱条件:洗针液为甲醇,进样量0.5 µl,进样口温度240 ℃;压力6.1219 psi;分流比10:1,流量为1.0 ml;升温程序:初始温度:100 ℃,保持0 min;梯度一:以5 ℃/min升到120 ℃,保持0 min;梯度二:以20 ℃/min升到200 ℃,保持10 min;总运行时间:18 min;检测器(FID)温度:240 ℃;空气流量:300 ml/min;氢气流量:33 ml/min;尾吹氮气流量:20 ml/min;数据采集频率/峰宽:20 Hz/0.01 min。
-
使用SPSS 22.0进行独立样本t检验,数据以平均数±标准差(
$\bar x \pm s$ )表示,P<0.05认为存在显著性差异。 -
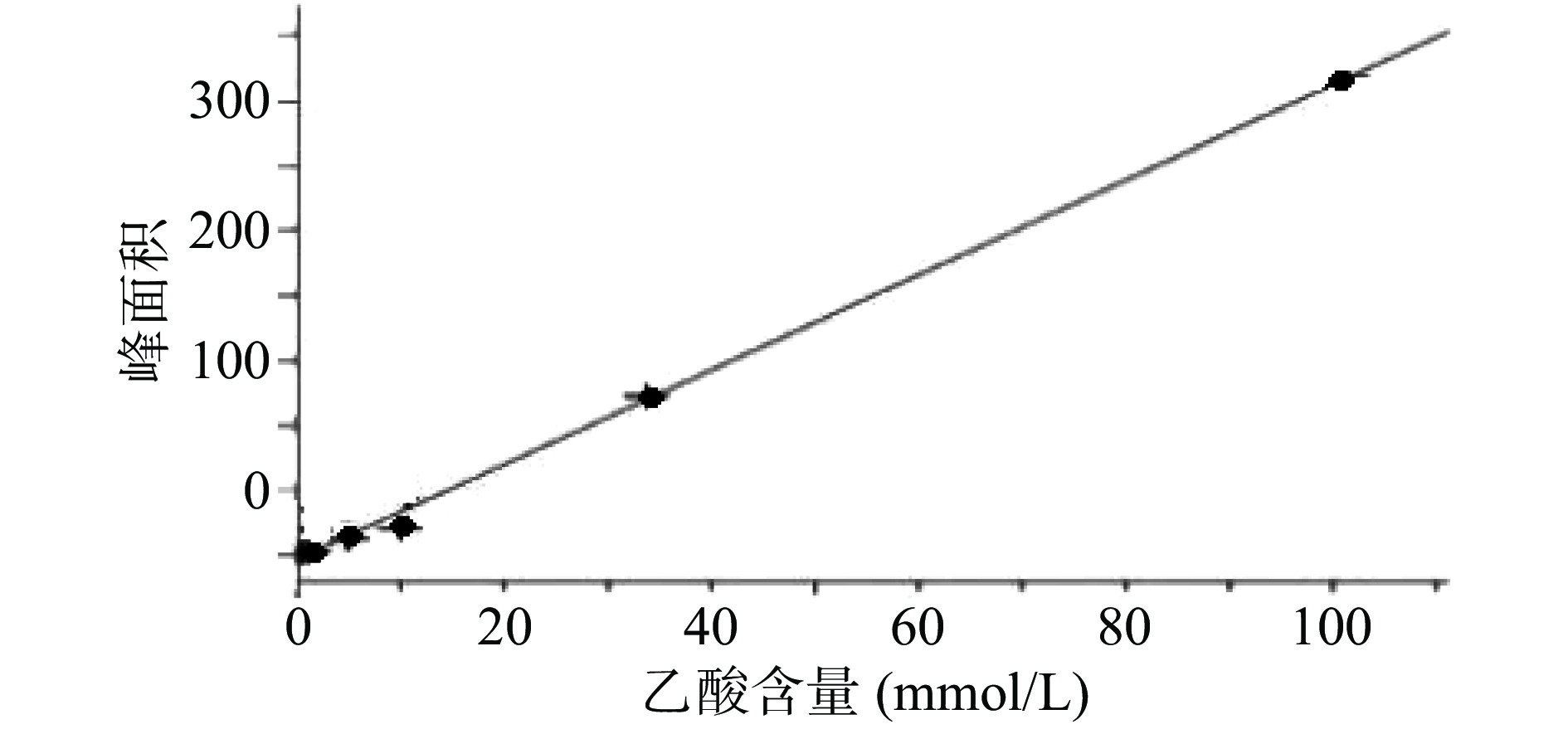
乙酸浓度在0.51~101.33 mmol/L线性关系良好。以乙酸峰面积(Y)为纵坐标,乙酸含量(X)为横坐标,绘制标准曲线,得到线性回归方程为Y=3.670 5X−4.300 8,r=0.999 0,残留标准误差为6.644 2,如图1所示。
-
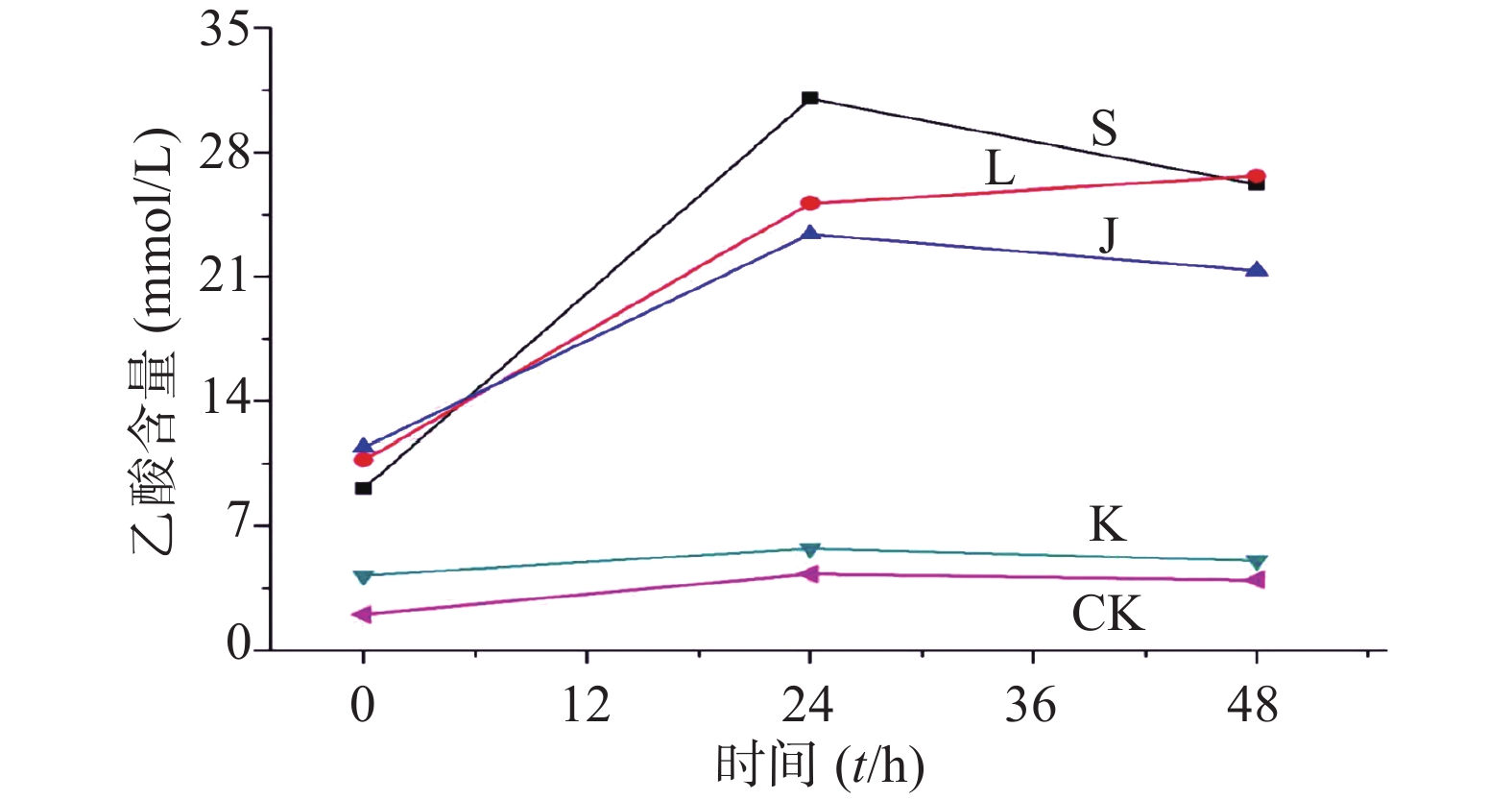
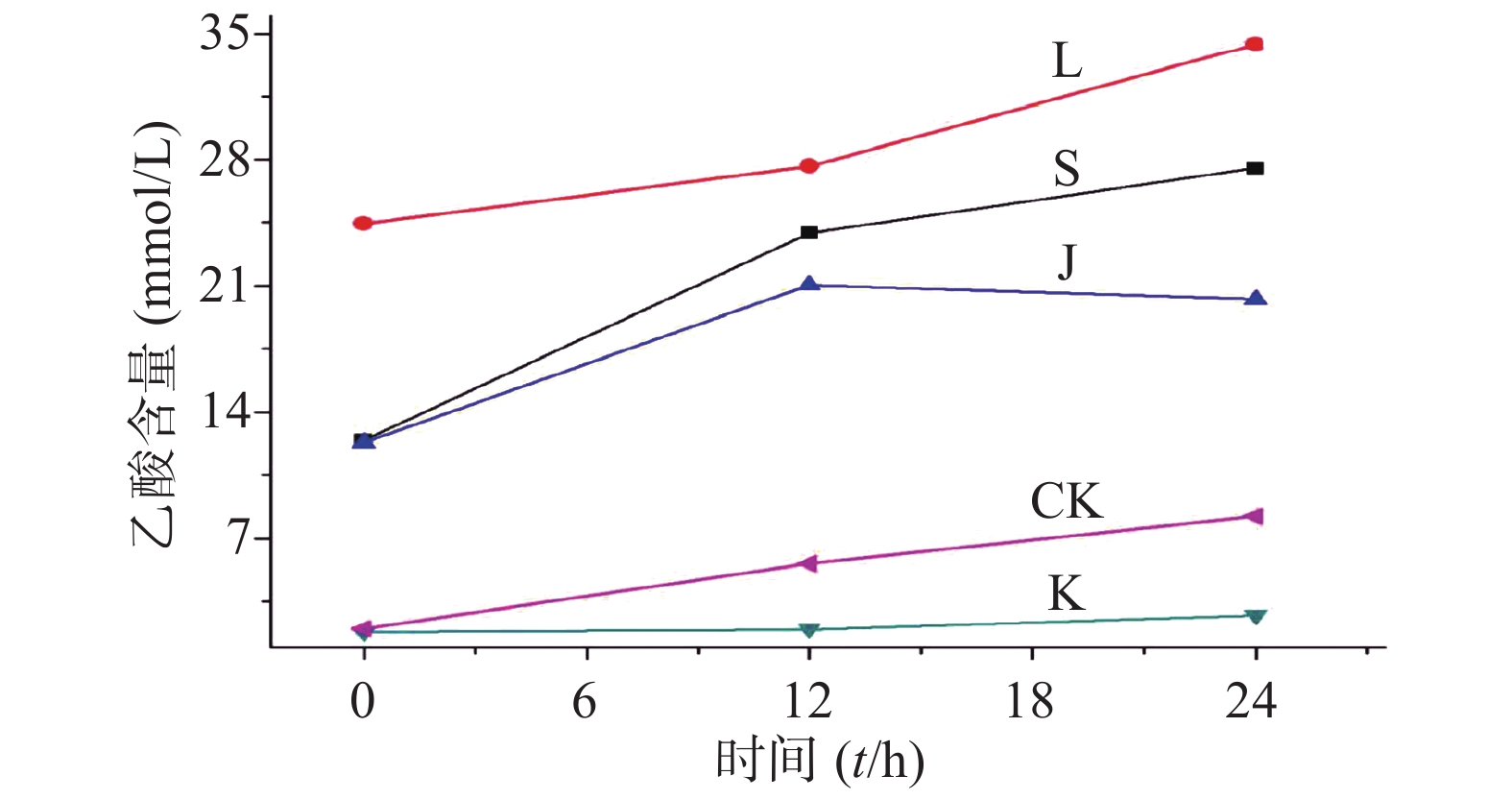
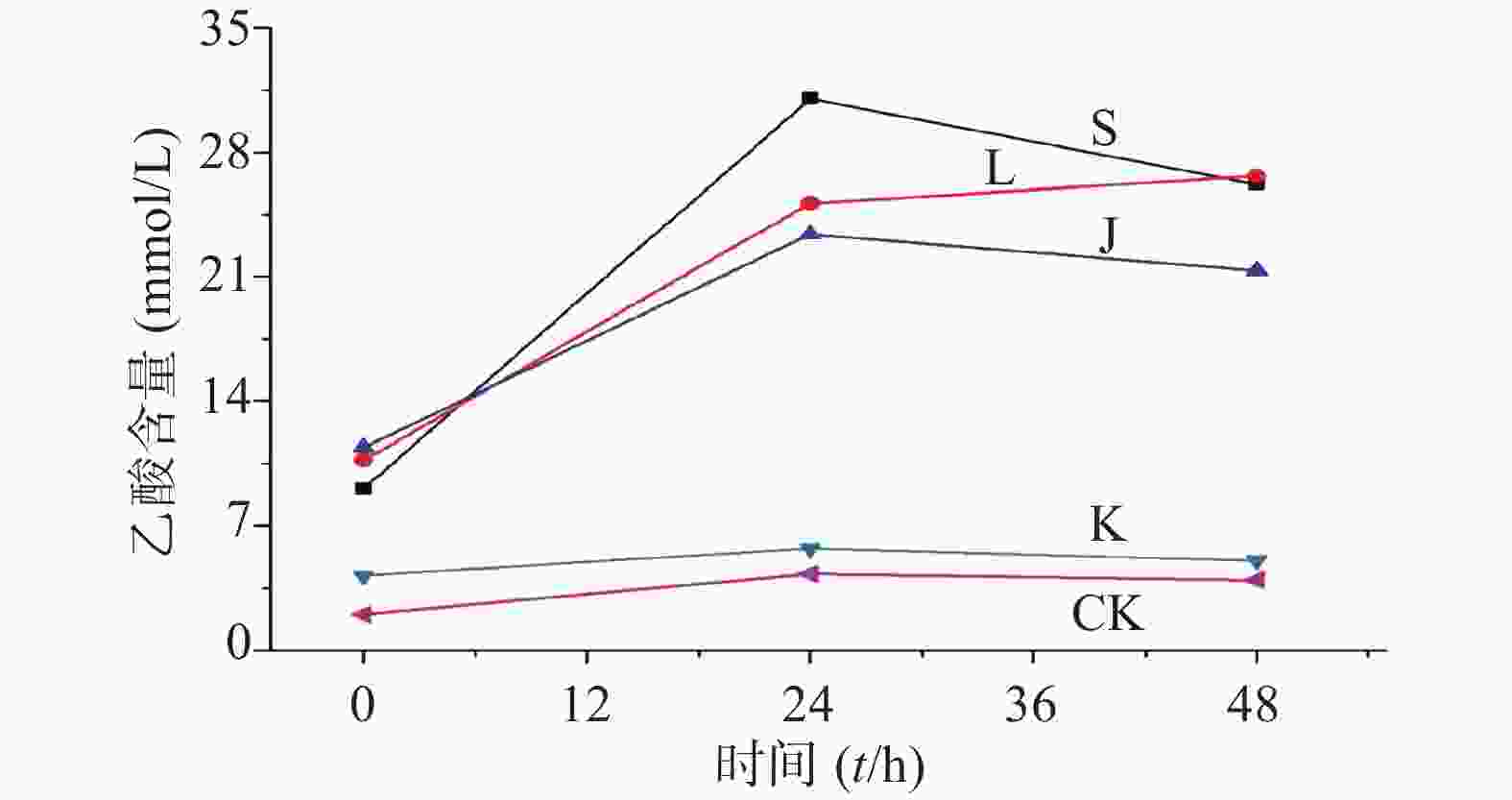
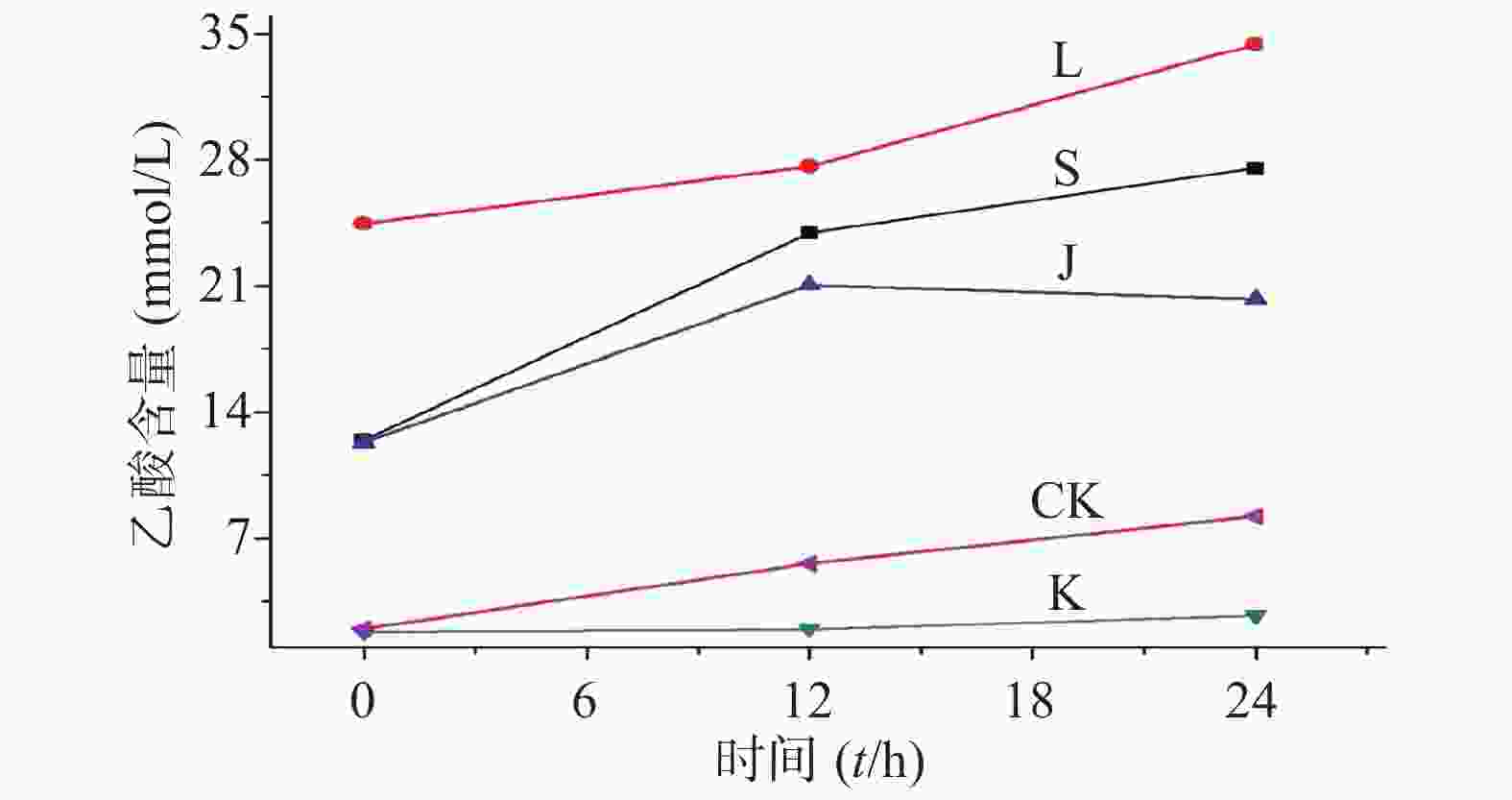
生山楂和焦山楂加速生长期双歧杆菌的生长繁殖,达稳定期后,由于生山楂中多种物质被分解,菌群产生大量代谢废物,于衰亡期加速双歧杆菌的衰亡;由于焦山楂中多种物质被分解,菌群产生大量代谢废物,于衰亡期加速双歧杆菌的衰亡;但因焦山楂中存在类黑素且其他物质较少,衰亡速率慢于生山楂组;类黑素加速生长期双歧杆菌的生长繁殖,但由于无其他物质,其生长速率慢于生山楂组,但在衰亡期中明显改变双歧杆菌生长规律,使生长期延长(生长速率变缓),双歧杆菌衰亡延后,如图2。
-
生山楂促进大肠杆菌生长期前期的生长繁殖,但由于代谢废物的逐渐增加,乙酸堆积,使生长速率逐渐变缓;焦山楂促进大肠杆菌生长期前期的生长繁殖,但由于类黑素及代谢废物的影响使生长期变短,稳定期提前;类黑素对大肠杆菌生长期前期无明显影响,但生长期后期明显促进大肠杆菌的生长繁殖,如图3所示。
-
《中国药典》一部中对焦山楂炮制方法为:取净山楂,中火条件下炒至药材表面焦褐色,内部焦黄色,并具有焦香气味。因无可控工艺参数,焦山楂炮制过程中易出现饮片表面以及内部颜色不均一,山楂炒制成品质量不稳定等情况。结合课题组前期实验,采用分别100、150、200和250 g净山楂为炮制对象,中火条件为(340~380)℃、(380~420)℃和(420~460)℃,炮制时间为8、10、12和14 min;不同质量同一批号的净山楂在不同的中火条件下炮制不同的时间,采用非接触式红外测温仪检测炒制温度,并以炒锅初温和山楂药材炒制末温辅助控温。实验筛选出150 g净山楂中火条件(380~420)℃下炒制10 min,可得到质量稳定,颜色均一的焦山楂。
-
类黑素的提取方法主要是水浸提法,Borrelli等[8]在90 ℃条件下,采用1:6料液比,对咖啡中的类黑素进行水提;Langner等[9]在室温条件下采用1:12料液比,水浸提1 h,提取到土豆类黑素粗制品。类黑素成分复杂,提纯困难。目前,主要的纯化方法有大孔树脂、超滤和凝胶层析等方法。何健[10]等发现X-5大孔树脂是曲霉型豆豉类黑素的最佳吸附树脂。秦礼康等[11]利用S-8树脂分离得到豆豉两个类黑素组分。本实验在水浸提法的基础上进行改良,最终获得最优提取工艺。结果显示类黑色素在420 nm处有较强吸收[12]。
-
实验采用气相色谱法检测菌群代谢物乙酸的含量。参照文献[13-14],结果显示其色谱条件对于本样品分析效果不佳;在柱温选择中,恒温法对乙酸检测效果不理想,峰形不稳定,因此实验采取梯度升温。经反复试验,最终获得正文中的检测参数,分离效果好,可作为本实验乙酸检测条件。
Effects of hawthorn and melanoidins on the in-vitro growth of Bifidobacterium and E.coli
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.201904129
- Received Date: 2019-04-25
- Rev Recd Date: 2020-02-18
- Available Online: 2020-04-23
- Publish Date: 2020-03-01
-
Key words:
- melanoidins /
- charred hawthorn /
- gas chromatography /
- Bifidobacterium /
- E.coli
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Yun, LU Min, LIANG Jie, SUN Hua, ZHANG Mengqi, LAN Zelun, WAN Jun, ZHOU Xia. Effects of hawthorn and melanoidins on the in-vitro growth of Bifidobacterium and E.coli[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2020, 38(2): 135-137, 165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.201904129 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: