-
肝纤维化(HF)是一种创伤愈合反应,其特征是细胞外基质(ECM)在肝内的过度沉积,导致肝功能丧失和肝脏结构破坏[1]。在正常肝脏中,肝星状细胞(HSC)是位于肝脏窦状隙的DISE腔内,负责储存维生素A。当肝脏受到损伤刺激时,HSC从静止状态转化为具有增殖、类维生素A消失、趋化性、收缩性、纤维生成等特性的肌成纤维细胞(MFs),参与肝纤维化进程[2-4]。
核糖体蛋白S5(RPS5)是核糖体40S小亚基的组成成分,是核糖体生物发生所必需的。越来越多的证据表明,一些核糖体蛋白除了参与蛋白质加工合成之外,还具有许多核糖体外功能[5-6]。例如,RPS5基因对于胚胎干细胞的分化和类胚体的形成至关重要[7];RPS5的β-发夹结构能够与HCV IRES相互作用,并介导HCV的翻译过程[8];RPS5在结肠癌中异常表达,并可能在癌变过程中作为检查点发挥重要作用[9]。此外,RPS5还参与小鼠红白血病细胞分化,其表达下调会影响细胞周期蛋白依赖激酶-2、-4和-6的蛋白水平,并延迟体外红细胞成熟,引起G1/G0细胞周期停滞[10-11]。
本课题组前期研究发现,在肝纤维化过程中,RPS5在静息和激活的HSC内存在差异表达[12-13]。体外实验证实RPS5参与HSC活化,体内研究表明,RPS5基因敲减可加重肝纤维化,RPS5过表达则减轻肝纤维化[13]。但是,我们并没有研究特异性敲减HSC内RPS5的表达对肝纤维化的影响[14-17]。为此,我们构建了GFa2(GFAP启动子)-驱动shRPS5腺病毒,并研究其靶向敲减HSC的RPS5表达对肝纤维化进展的影响。
-
高糖DMEM培养基(Gibco);Western及IP细胞裂解液液(Beyotime);BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Thermo Fisher Scientific);RPS5抗体(Santa Cruz)、ALB、GAPDH抗体(Cell Signaling Technology)、GFAP、α-SMA、胶原蛋白 I抗体(Abcam);山羊(多克隆)抗兔 IgG(H+L)、山羊(多克隆)抗小鼠 IgG(H+L)(LI-COR Biosciences);Odyssey成像系统(LI-COR Biotechnology);SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM PCR 试剂盒(Takara)。
-
雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠,清洁级,重约200 g,购于上海SLAC实验动物有限公司。
-
原代HSC和肝细胞从雄性SD大鼠分离,通过蛋白酶-胶原酶消化,单步Nycodenz梯度纯化[13]。分离的HSC和肝细胞在含有10%胎牛血清(FBS)DMEM培养基,5% CO2、37 ℃培养箱中培养。每隔1天更换1次培养基。通过GFAP免疫染色评估,HSC的纯度为90%~95%。本实验于分离后第3天在转分化的HSC上进行。HSC以感染复数(MOI)50感染腺病毒48 h。
-
根据AdEasy™ Adenoviral Vector System(AgilentStratagene, USA)的说明制备质粒 pShuttle-GFa2-shRPS5。将GFAP基因启动子(GFa2)、shRPS5序列和必需元件克隆到无启动子穿梭载体pShuttle中,穿梭载体pShuttle-GFa2驱动shRPS5的表达。重组AdGFa2-shRPS5和AdGFa2-shNC腺病毒在293细胞中扩增,通过氯化铯梯度超速离心纯化。使293细胞通过噬斑测定病毒原液的滴度。shRPS5和shNC序列见表1。
名称 序列 shRPS5 5′-GCTCATGACTGTACGAATTCTCGAGAATTCGTACAGTCAT GAGC-3′ shNC 5′-GCGCGCTTTGTAGGATTCGCTCGAGCGAATCCTACAAA GCGCGC-3′ -
将HSC细胞中的培养基吸弃,用PBS洗涤1次,加入Western及IP细胞裂解液冰上裂解20 min。通过BCA法测量蛋白浓度后将蛋白样品在95 ℃下加热5 min。制胶上样,将20 μg样品进行10% SDS-PAGE电泳,结束后将蛋白质转移到NC膜上。5%脱脂奶粉封闭1 h。分别加入RPS5、ALB、GAPDH、GFAP、α-SMA和I型胶原的单克隆抗体4 ℃孵育过夜,用PBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。山羊(多克隆)抗兔IgG(H+L)或山羊(多克隆)抗小鼠IgG(H+L)室温孵育2 h,PBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。Odyssey红外扫描成像系统对NC膜扫描,观察相关蛋白的表达情况。
-
用Trizol试剂盒提取总RNA。用SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM PCR试剂盒,合成cDNA,定量PCR检测基因mRNA表达。以管家基因β-肌动蛋白(β-actin)作为内部对照,并将基因特异性mRNA表达与β-actin表达进行归一化。引物序列见表2。
名称 正向引物序列 反向引物序列 β-actin 5′-CCAT TGAACACGGCATTGTC-3′ 5′-TCATAGATGGGCACAC AGTG-3′ RPS5 5′-AAATGTGCAGGTGTTGACCA-3′ 5′-CACGCTCCTCCTGAAGAATC-3′ α-SMA 5′-CCGAGATCTCACCGACTACC-3′ 5′-TCCA GAGCGACATAGCACAG-3′ collagen I 5′-CCGTGACCTCAAGATG TGCC-3′ 5′-GCTCATACCTTCGCTT CCAA-3′ -
用二甲基亚硝胺(DMN)和胆管结扎术(BDL)的方法建立大鼠肝纤维化模型[13],尾静脉注射腺病毒(4×109pfu)特异性敲减肝内HSC的RPS5水平。
-
肝组织切片HE染色分析病理改变情况;羟脯氨酸(羟脯氨酸检测试剂盒)含量测定、切片天狼星红和 Masson染色评价胶原沉积情况;免疫组织化学染色检测α-SMA和RPS5的表达情况。
-
数据分析通过SPSS 21统计软件进行,采用t检验分析,实验结果用均数±标准差(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示。与对照组比较,P<0.05 则认为差异具有统计学意义。 -
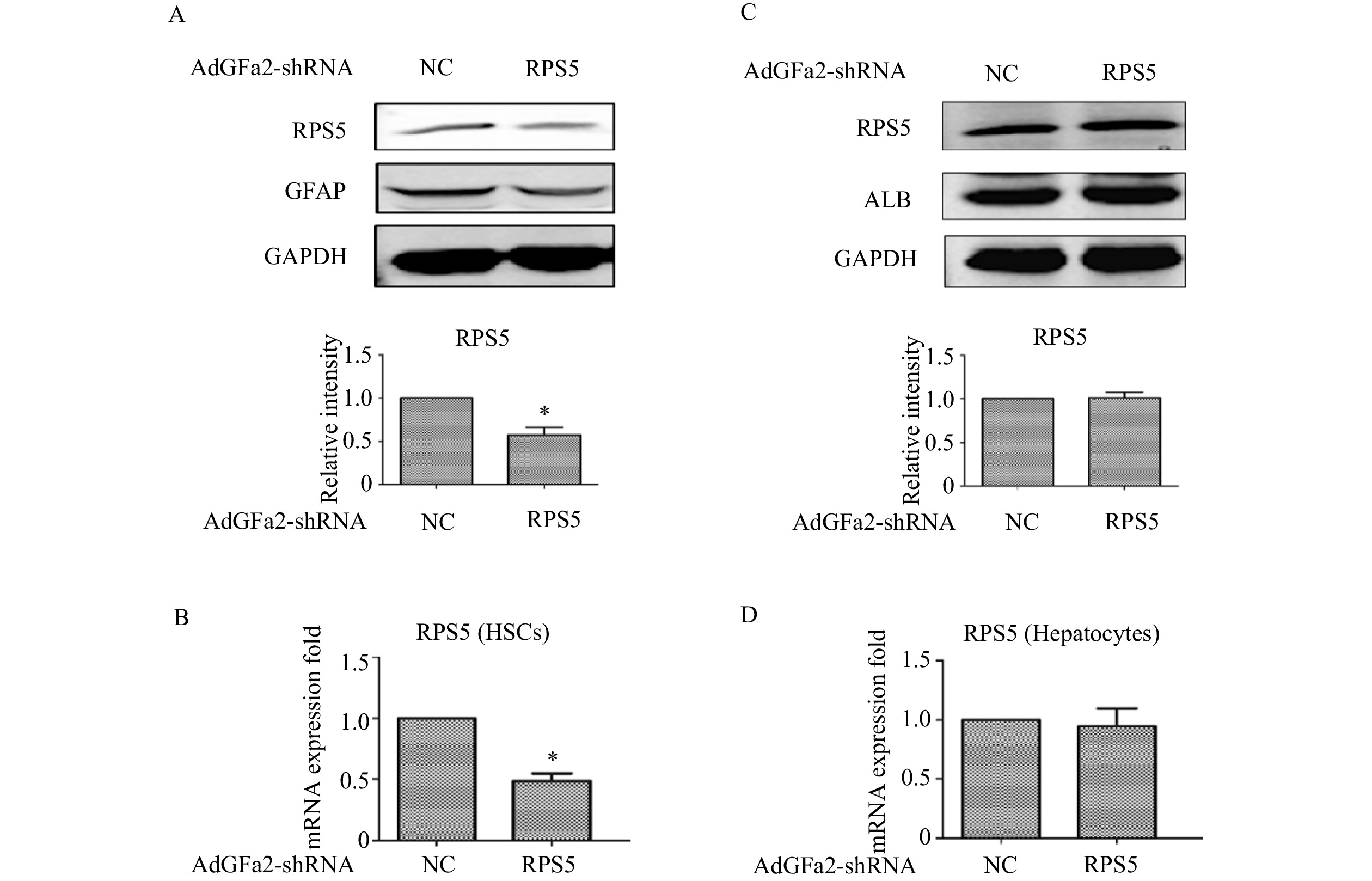
为了确定AdGFa2-shRPS5对RPS5表达的影响及对HSC的特异性,我们分别用AdGFa2-shRPS5和AdGFa2 shNC转染大鼠的原代HSC和肝细胞48 h,蛋白印迹法和实时PCR测定RPS5的表达情况。结果显示,RPS5 mRNA和蛋白质水平仅在原代HSC中降低(图1A、1B),在肝细胞中没有明显变化(图1C、1D)。
-
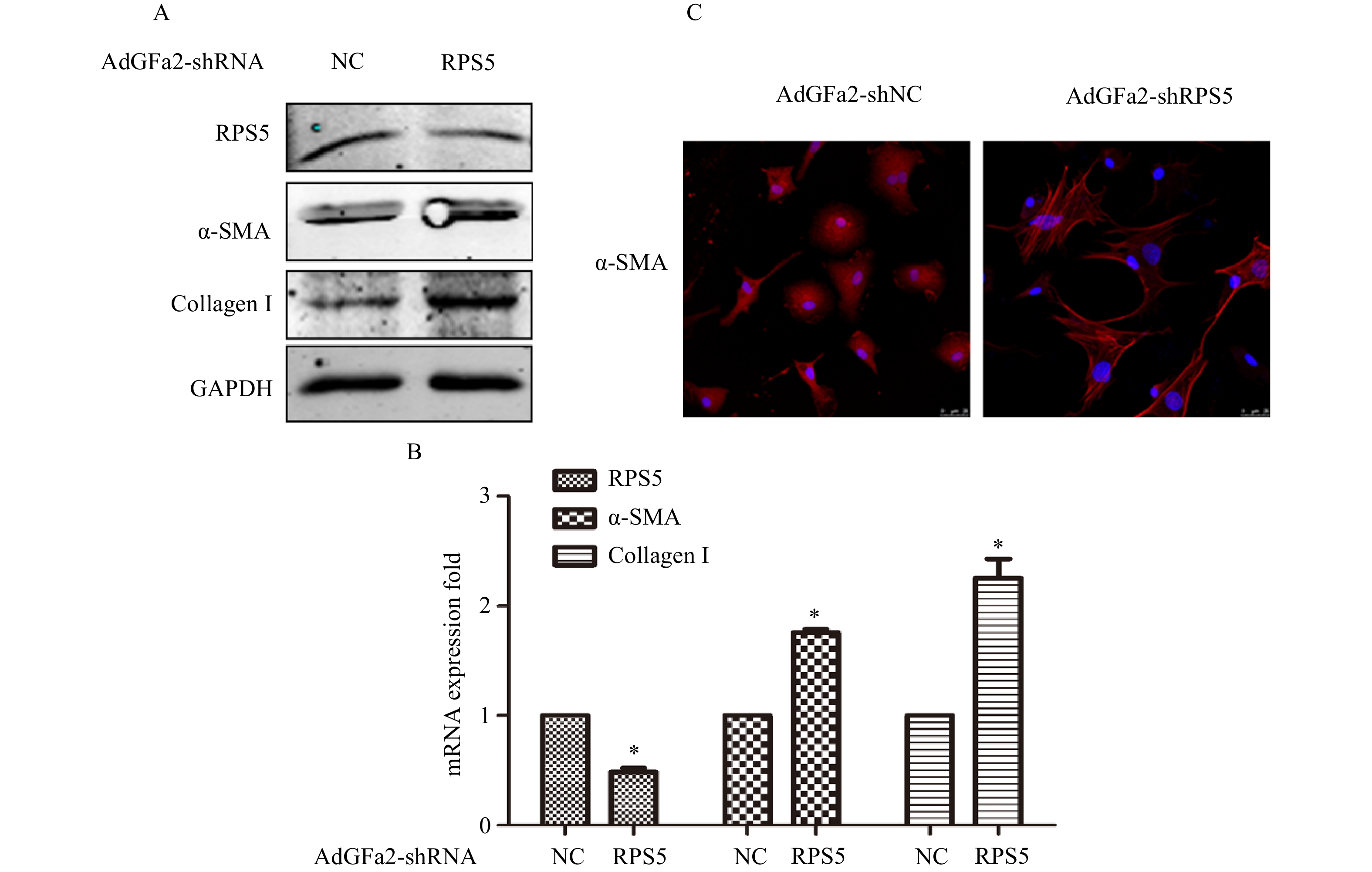
AdGFa2-shRPS5转染原代培养的HSC,蛋白印迹法和实时PCR分析α-SMA和I型胶原表达变化。结果表明,AdGFa2-shRPS5感染HSC后,α-SMA和I型胶原mRNA和蛋白质的表达显著增加(图2A、2B)。免疫荧光结果显示,转染AdGFa2-shRPS5的HSC形态明显改变,细胞更加扁平而延展(图2C)。以上结果表明RPS5敲减促进了HSC的活化。
-
为了考察AdGFa2-shRPS5体内对肝纤维化的影响,我们构建了BDL肝纤维化模型。BDL手术前2 d和手术后5 d由尾静脉注射AdGFa2-shRPS5,2周后处死所有大鼠(图3A),评价肝纤维化情况。免疫组织化学染色结果所示,与AdGFa2-shNC组相比,AdGFa2-shRPS5降低了小鼠体内RPS5的表达,促进HSC的活化,α-SMA表达相应增加,表明肝纤维化程度加重。HE染色结果表明,在AdGFa2-shRPS5组中,反应性胆管周围有更广泛的胆管增生和有害的肝实质塌陷,α-SMA阳性表达增加。此外,天狼星红和Masson染色结果显示AdGFa2-shRPS5增加了胶原沉积(图3B)。天狼星染色半定量分析表明,AdGFa2-shRPS5处理的BDL大鼠纤维化面积增加了161%(P<0.05,图3C)。羟脯氨酸含量AdGFa2-shRPS5组明显高于AdGFa2 shNC组(P<0.05,图3D)。并且α-SMA和I型胶原mRNA的表达也与其蛋白质水平结果表达相一致(图3E)。
-
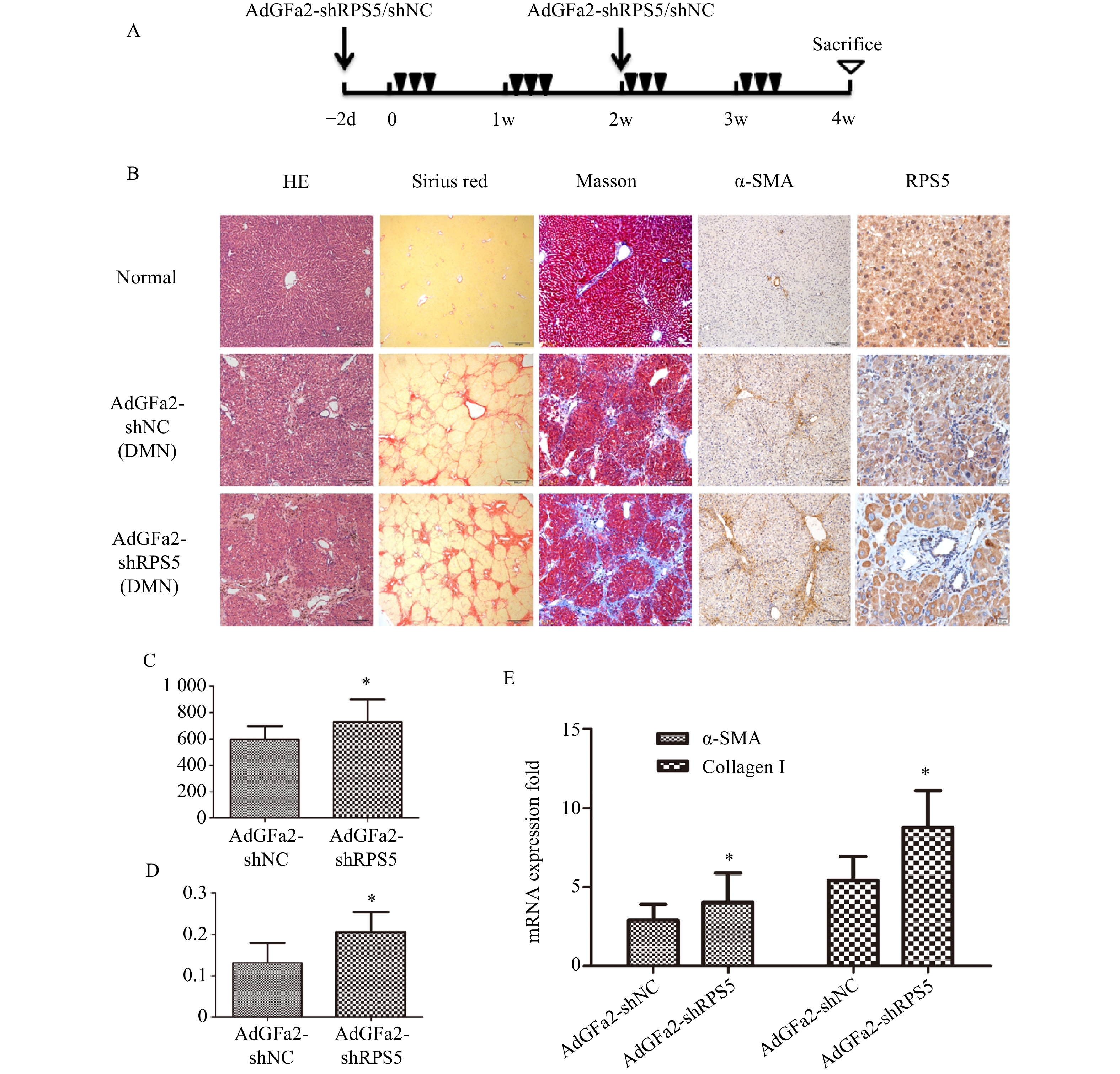
为了进一步证实AdGFa2-shRPS5对肝纤维化的作用,腹腔注射DMN制备纤维化模型。分别在第一次DMN注射前2天和后2周通过尾静脉向大鼠注射AdGFa2-shRPS5,在4周后处死所有大鼠(图4A)。AdGFa2-shRPS5抑制大鼠体内RPS5的表达,α-SMA在肝脏中的表达增加(图4B)。与BDL模型一致,HE、天狼星红、Masson、α-SMA染色及α-SMA RT-PCR分析证实(图4B,4E),AdGFa2-shRPS5也促进了DMN诱导的肝纤维化的发展。在DMN模型中,AdGFa2-shRPS5组的羟脯氨酸含量高于AdGFa2 shNC组(P<0.05,图4C)。天狼星红染色的半定量分析结果显示,AdGFa2-shRPS5使纤维化面积显著增加约157%(P<0.05,图4D)。综上结果证实特异性敲减HSC内的RPS5加剧了纤维化的进展。
-
肝纤维化是一个动态过程,其特征是慢性肝损伤导致ECM的过度沉积,当肝损伤发生时,HSC活化以获得成纤维能力,因此HSC是肝纤维化的主要生成细胞。文献表明,在转分化的HSC和人类肝硬化肝脏中RPS5显著降低[13]。RPS5的过表达使得体内肝纤维化得到改善,而RPS5的敲减促进了肝纤维化[13]。但究竟是哪一种细胞在这一过程中起主要作用仍值得进一步研究。因此,有必要仅针对肝脏中一个或有限细胞群进行研究。胶质纤维酸性蛋白GFAP是成熟星形胶质细胞中的主要中间丝状蛋白,但也在肝脏的HSCs中表达。因此,使用GFAP启动子GFa2来驱动RPS5敲减可能是靶向HSC的方法。在此研究中,我们使用GFAP启动子驱动shRNA系统来研究RPS5靶向HSCs对大鼠肝纤维化进展的影响。
本研究构建重组腺病毒AdGFa2-shRPS5,并证实AdGFa2-shRPS5可以特异性地将HSCs中RPS5的表达降低约50%,对肝细胞没有明显作用。研究证明RPS5的敲减促进HSCs的活化。体内研究结果表明,两种慢性肝损伤动物模型中纤维化的发展随着RPS5的特异性敲减而加重,并伴有显著的细胞外基质沉积。综上结果表明,RPS5的下调有助于HSC的激活,从而促进体内肝纤维化,表明RPS5可能是HSC激活的分子开关。
RPS5是核糖体40S小亚基的组成成分,是核糖体生物发生所必需的,并且具有许多核糖体外功能,如促进细胞的凋亡、DNA修复、细胞增殖和分化[5-6,10-11]。文献证实RPS5可抑制LPS诱导的巨噬细胞中的IL-6和NO释放,表明RPS5也参与炎症过程[18]。本研究结果表明,RPS5在调节HSC活化中起着重要作用,揭示了RPS5的新功能。由于GFa2启动子的活性较弱,我们没有研究过表达HSC中的RPS5对体内肝纤维化的影响。
本研究为敲减HSC中的RPS5对肝纤维化有促进作用提供了证据。使用AdGFa2-shRPS5的一个关键优势是靶向HSC,并且对正常肝细胞没有影响。结果表明,RPS5对肝纤维化的发生发展至关重要,可能是治疗肝纤维化的一个有前景的靶点。
Effects of specific knockdown of ribosomal protein S5 in hepatic stellate cells on liver fibrosis
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202209007
- Received Date: 2022-09-04
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-01-30
- Publish Date: 2023-04-25
-
Key words:
- ribosomal protein S5 /
- hepatic stellate cells /
- glial fibrillary acidic protein /
- HSC activation /
- hepatic fibrosis
Abstract:
| Citation: | TANG Yuzhen, ZHANG Junping. Effects of specific knockdown of ribosomal protein S5 in hepatic stellate cells on liver fibrosis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(4): 227-233. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202209007 |












 DownLoad:
DownLoad: