-
河豚毒素是一种钠通道阻滞剂,可以导致人类中毒和死亡[1]。河豚毒素不仅存在于河豚科的河豚中,而且在海洋和陆地环境的多种生物中均有发现[2-4]。河豚毒素作用时具有选择性,其与心肌NaV通道缺乏亲和力,且无法穿透血脑屏障,这些特性使其成为麻醉和镇痛药物设计的有吸引力的候选者[5]。河豚毒素的毒理作用在神经性、急性和炎症性疼痛模型中得到证实[6-8]。在远低于半数致死剂量(LD50)的浓度下,河豚毒素对神经系统的急性和瞬时作用使其在最低浓度时即可达到预期结果[9]。然而,河豚毒素的高毒性引发人们对其安全性问题的关注,本文利用斑马鱼模型研究河豚毒素的急性毒性,旨在为评价河豚毒素的安全性提供依据。
-
河豚毒素[中洋生物科技(上海)股份有限公司,批号:2020102307],用醋酸盐缓冲液配制成10.0 mmol/L母液,冷藏避光储存。斑马鱼饲养于28 ℃的养鱼用水中(水质:每1 L反渗透水中加入200 mg速溶海盐,电导率为450~550 μS/cm,pH为6.5~8.5,硬度为50~100 mg/L CaCO3),由杭州环特生物科技股份有限公司养鱼中心繁殖提供,实验动物使用许可证号为:SYXK(浙)2012-0171,饲养管理符合国际AAALAC认证(编号:001458)的要求。野生型AB品系斑马鱼,以自然成对交配繁殖方式进行,年龄为受精后2 d(2 dpf)。
-
随机选取2 dpf野生型AB品系斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔(实验组)均处理30尾斑马鱼。分别水溶给予河豚毒素(浓度为0.125、0.250、0.500、1.00、2.00、4.00、8.00、16.0、32.0、64.0 µmol/L),同时设置正常对照组和溶剂对照组,每孔容量为3 ml。28 ℃处理72 h,每天统计各实验组的斑马鱼死亡数量并及时移除。
-
实验结束后,在解剖显微镜下观察并记录斑马鱼心脏、循环系统、出血及血栓、脑、下颌、眼睛、肝脏、肾脏、肠道、躯干/尾/脊索、肌肉/体节、身体着色、体长等变化情况,采集典型毒性器官照片。以各器官的毒性发生率评价河豚毒素样品对斑马鱼的急性毒性,并鉴别毒性靶器官。
-
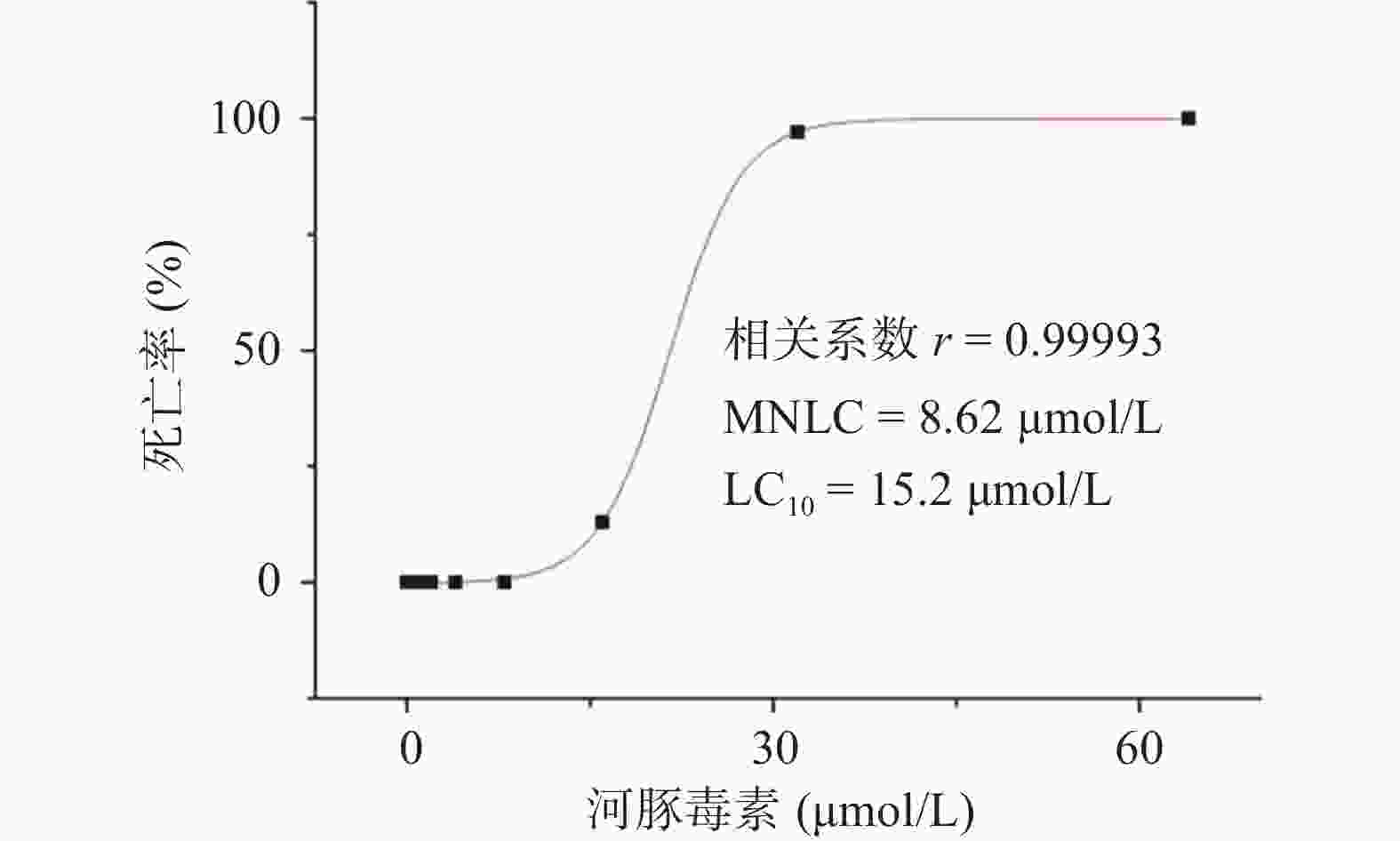
用Origin 8.0统计学软件绘制“浓度-死亡率”效应曲线,并计算河豚毒素对斑马鱼的MNLC和LC10。
-
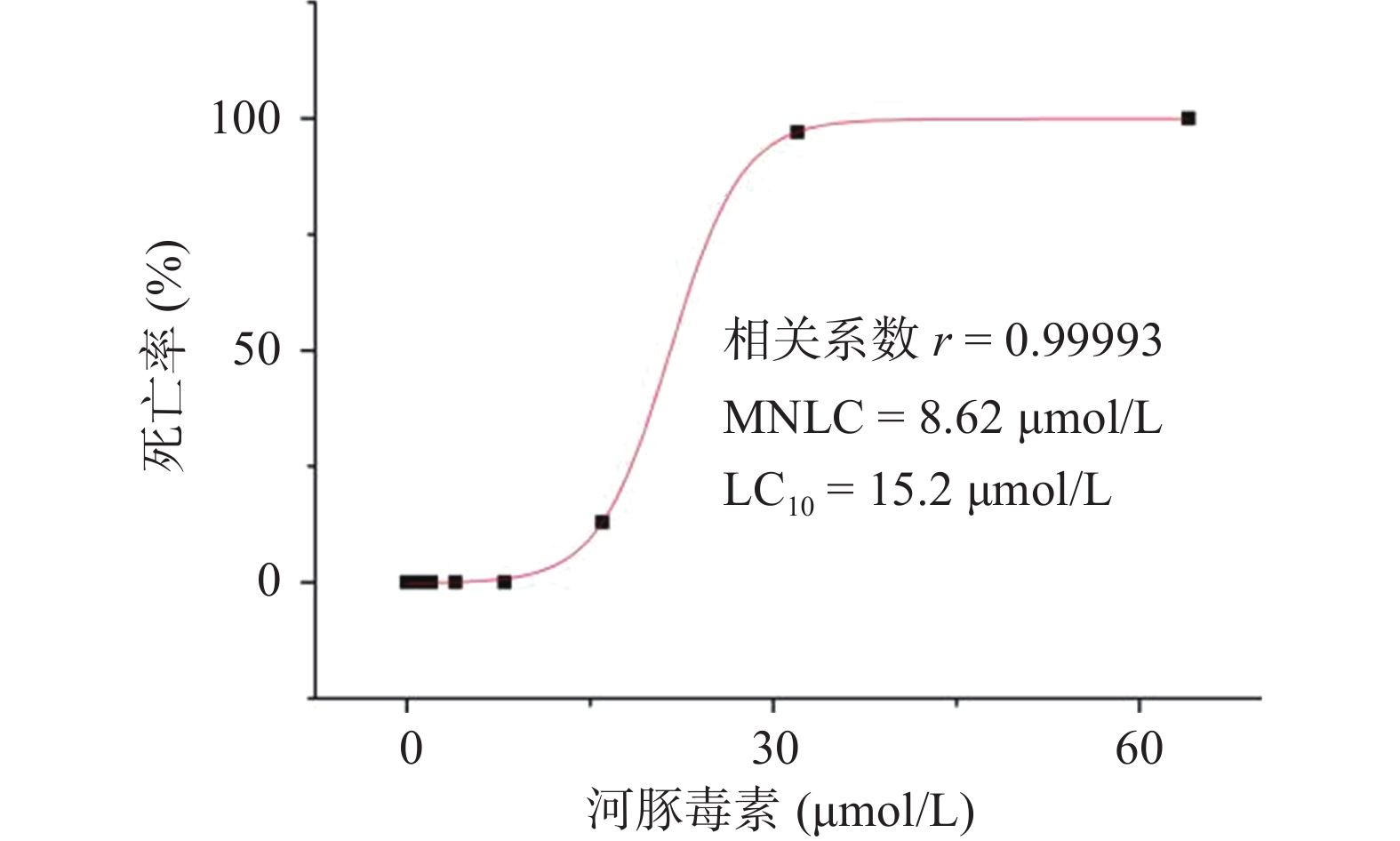
研究结果显示,正常对照组和溶剂对照组斑马鱼的死亡率均为0;0.125~8.00 µmol/L的河豚毒素处理后斑马鱼的死亡率均为0;当河豚毒素的浓度达到16.0 µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡4尾,死亡率为13%,当河豚毒素的浓度达到32.0 µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡29尾,死亡率为97%,而当河豚毒素的浓度达到64.0µmol/L时,斑马鱼死亡30尾,死亡率为100%。经Origin 8.0软件模拟得出河豚毒素对斑马鱼急性毒性MNLC为8.62 μmol/L,LC10为15.2 µmol/L,详见图1。
-
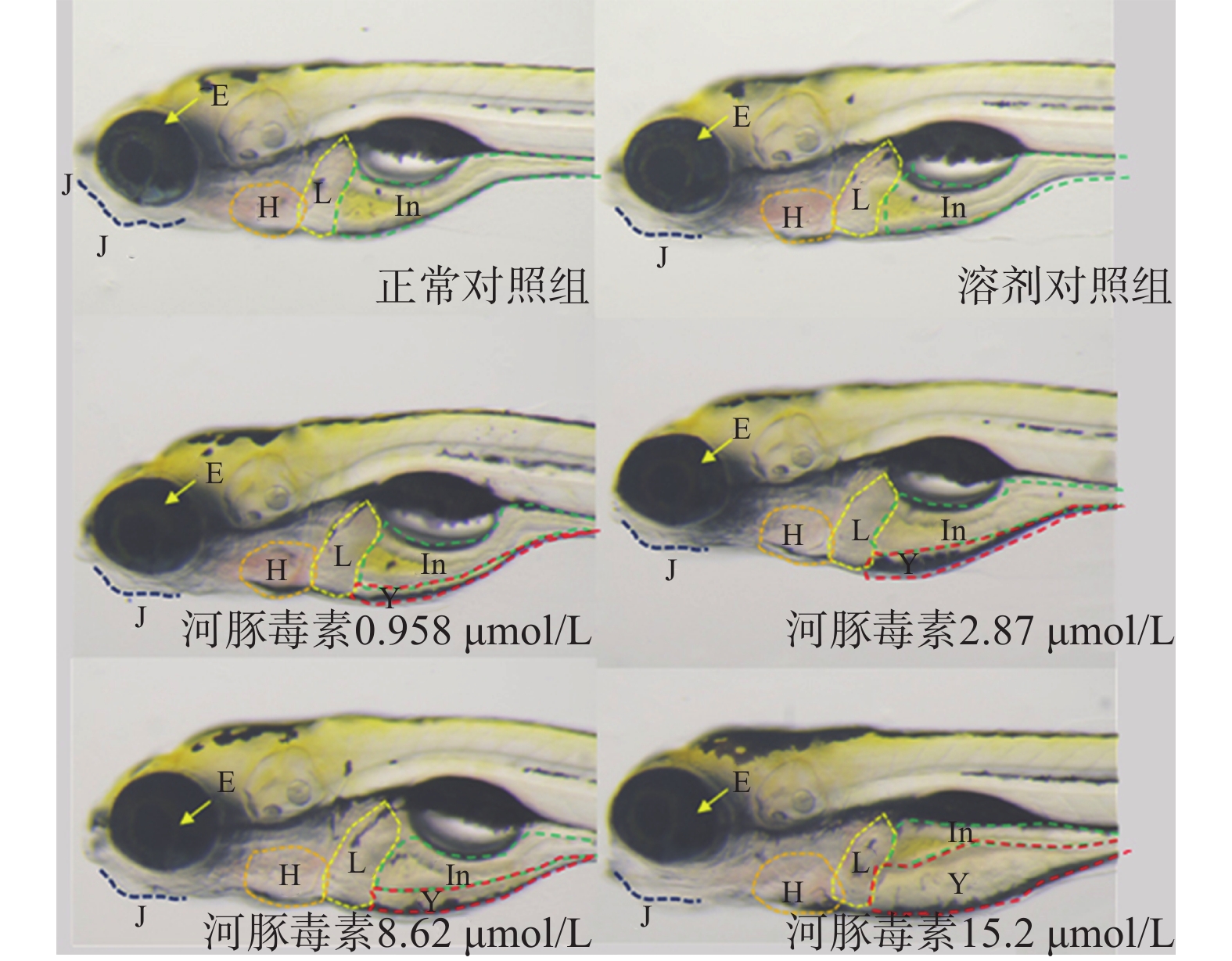
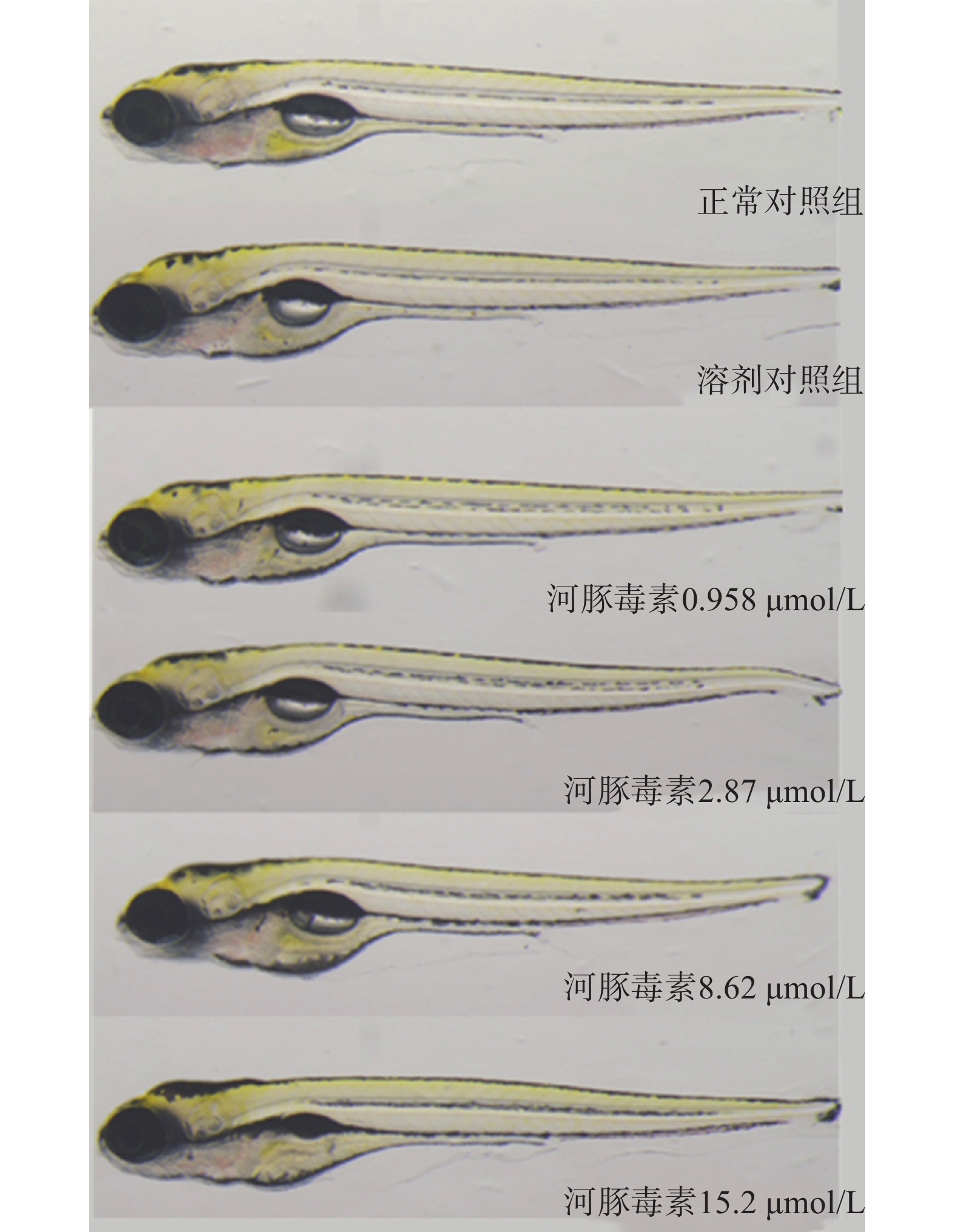
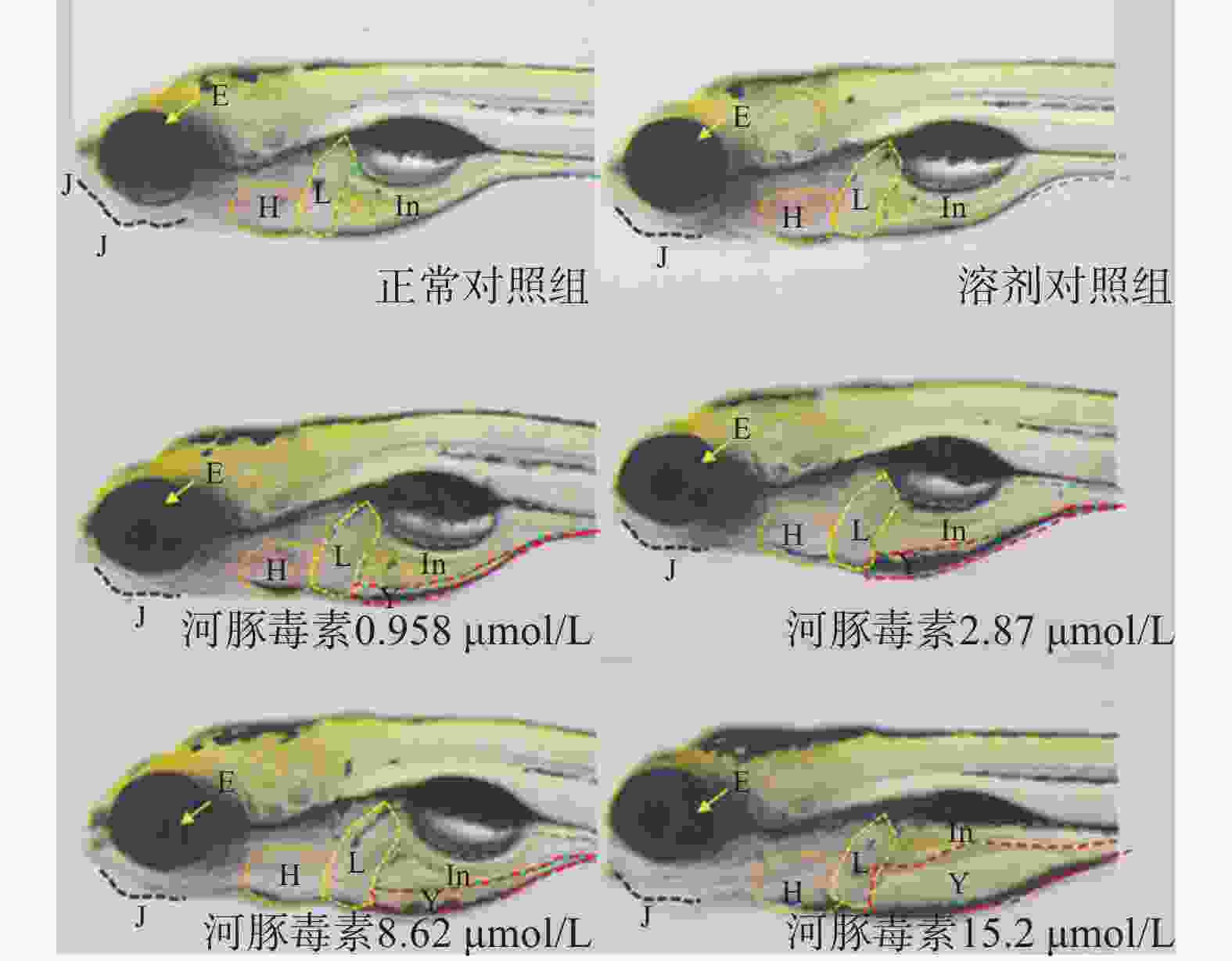
在本实验条件下浓度摸索过程中,16.0 μmol/L及以上浓度诱发心包水肿和心律异常,河豚毒素处理后72 h出现部分或全部死亡。如表1和图2、图3所示,河豚毒素急性毒性靶器官是心脏和肝脏,当河豚毒素的浓度达到0.958 µmol/L及以上时,斑马鱼表现出卵黄囊吸收延迟。当河豚毒素的浓度达到2.87 µmol/L及以上时斑马鱼表现出心律异常和肠腔异常。当河豚毒素浓度达到8.62 µmol/L及以上时斑马鱼表现出心包水肿。不同浓度的河豚毒素均未发现躯干/尾/脊索、肌肉/体节、身体着色以及体长生长等异常。
毒性类型 正常对照组 溶剂对照组 河豚毒素浓度(μmol/L) 0.958 2.87 8.62 15.2 心脏 心包水肿 - - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 房室缺失 - - - - - - 心律异常 - - - 7(2/30) 7(2/30) 17(5/30) 循环系统 血流变慢 - - - - - - 循环缺失 - - - - - - 出血及血栓 - - - - - - 脑 畸形 - - - - - - 下颌 短小 - - - - - - 眼睛 眼变小 - - - - - - 肝脏 缺失 - - - - - - 肝肿大 - - - - - - 肝变性 - - - - - - 卵黄囊吸收延迟 - - 80(24/30) 80(24/30) 87(26/30) 93(28/30) 肾脏 水肿 - - - - - - 肠道 肠腔异常 - - - 7(2/30) 13(4/30) 13(4/30) 躯干/尾/脊索 弯曲 - - - - - - 肌肉/体节 肌肉变性 - - - - - - 身体着色 异常 - - - - - - 体长变短 - - - - - 死亡 - - - - - 注:“-”表示未见明显异常 -
河豚毒素是一种致命的神经毒素,作为一种选择性Na+通道阻滞剂,其在生物医学中的应用引起了广泛关注[10]。日本传统医学中曾使用河豚鱼来治疗麻风病患者的神经痛,后来河豚毒素被发现、提取和纯化,并用于抑制破伤风患者的痉挛[11]。近年来,在双壳贝类中也发现了河豚毒素。例如,2011年在新西兰发现一种蛤类中的河豚毒素(0.8 mg/kg)[12],2014年英国学者发现贻贝和太平洋牡蛎样本中的河豚毒素(0.003~0.12 mg/kg)[13]。这些证据表明,河豚毒素对于食品安全来说具有一定的威胁,因此,国际食品和药品监管机构将河豚毒素作为一种新的风险。
在本研究中我们通过使用MNLC和LC10这两个指标,以评估河豚毒素对斑马鱼的急性毒性。研究发现,当河豚毒素的浓度达到16.0 μmol/L时,斑马鱼出现了心包水肿和心律异常,导致部分或者全部的斑马鱼死亡。有研究证实,选择性激活河豚毒素敏感的神经元钠通道可以安全地增加心脏收缩力[14]。还有研究结果显示,河豚毒素的肌肉内给药改变了肝脏中参与各种信号通路的肝脏基因的表达[15]。由此可见,河豚毒素对斑马鱼具有明显的心脏和肝脏毒性,且其毒性随着河豚毒素浓度的升高而增强。
目前,尚无针对河豚毒素的解毒剂,一旦摄入河豚毒素,严重中毒者可发生心力衰竭甚至死亡[16]。多年前有研究者收治了5例河豚毒素中毒者,患者出现了肾脏损害,表现为多尿,经过治疗后仍有患者死亡[17]。在日本,监管规定了河豚毒素的摄入浓度不得超过2 mg/kg[11]。目前,关于河豚毒素急性毒性的可用数据非常少,而且现有的大部分数据都缺乏足够的实验细节。有研究者发现,在昆明小鼠腹膜内(ip)、皮下(sc)和胃内(ig)注射的中位致死剂量(LD50)分别为10.7、12.5、532 μg/kg[18]。我们在斑马鱼模型中研究发现,河豚毒素对斑马鱼急性毒性MNLC为8.62 μmol/L,LC10为15.2 µmol/L,急性毒性靶器官是心脏和肝脏,主要表现为心包水肿、心律异常和卵黄囊吸收延迟,毒性出现浓度为0.958 µmol/L。
本研究还存在一定的不足。作为一种常用于药物毒性评价的模式生物,斑马鱼具有易养殖、繁殖快、成本低等优势,但斑马鱼被用于药物毒性检测时易存在假阳性和假阴性。因此,本研究的结论还需要在其他动物模型中进一步研究。
The acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin to zebra fish
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202202083
- Received Date: 2022-02-28
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-06-22
- Available Online: 2022-11-28
- Publish Date: 2022-11-25
-
Key words:
- tetrodotoxin /
- zebra fish /
- acute toxicity
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Haoneng, ZHANGJI Qianzhu, LI Jingfeng, JIA Rui, ZHU Yuping, ZHU Jiangbo, CHEN Jikuai, YAN Lang. The acute toxicity of tetrodotoxin to zebra fish[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(6): 536-539. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202202083 |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: