-
随着腹腔镜技术在普外科、妇科、泌尿外科等领域的广泛应用,在一些外科疾病如胆囊结石,阑尾炎,子宫肌瘤的治疗上,腹腔镜手术正在逐渐取代传统开腹手术。较传统手术而言,腹腔镜手术具有较高诊断准确率和治疗能力[1],且具有手术出血量少、肠蠕动恢复早、术后疼痛轻、术后恢复快、下床活动时间早、住院时间短、手术口美观、术后并发症降低等优势[1-2]。然而,无论是传统手术和腹腔镜手术,术后感染依然是影响患者预后的重要并发症。对于腹腔镜手术如何直接改变腹腔微生物群落种类及数量,目前还没有相关报道。
通过DNA测序对微生物种群进行鉴定(菌种鉴定)是比传统生化鉴定更为先进、更为准确的鉴定方法。16S rDNA是编码原核生物(主要为细菌)核糖体小亚基rRNA(16S rDNA)的DNA序列,长度约为1540~bp,存在于所有细菌染色体基因组中。16S rDNA分子大小适中,突变率小,目前是细菌系统分类学研究中最常用的基准序列。16S rDNA测序不依赖菌种本身的性质,使得它对所有菌种均可使用。通过对16S rDNA的测序,可以快速、直观地明确细菌群落多样性的变化。
本研究通过制作新西兰兔腹腔镜探查术模型,对术后动物腹腔积液进行细菌16S rDNA测序,对比分析腹腔积液中的微生物多态性,探索腹腔镜术后的微生物变化情况,可为腹腔镜手术的术后感染提供有效防治依据。
-
雄性2月龄新西兰兔6只(上海甲干生物科技有限公司),体重约为2 kg,分别设置模型组(n = 3)和对照组(n = 3)。
-
ABI GeneAmp® 9700 型PCR仪;NanoDrop2000型分光光度计;CQZ2000720型便携一体式电子腹腔镜,腹腔镜镜头型号为J1000B型、J1030B型(上海卓外医疗电子科技有限公司);手提式高压蒸汽灭菌器DSX-24L-I(上海申安医疗器械厂)。
-
2%戊巴比妥钠溶液(0.4 g戊巴比妥钠粉末溶于20 ml 0.9%氯化钠注射液);碘伏溶液;液氮;0.9%氯化钠注射液;手术器械(打孔器、手术刀、组织剪、血管钳、镊子、布巾钳、圆针三角针、手术单)。
-
随机将6只新西兰兔分成两组,分别设置模型组(n = 3)和对照组(n = 3),模型组麻醉后给予腹腔镜探查术,术后关闭腹腔;对照组麻醉后开腹,然后关闭腹腔。
-
对模型组新西兰兔称重,耳缘静脉注射2%戊巴比妥钠(剂量1 ml/kg),麻醉成功后(呼吸平稳,角膜反射消失,身体肌肉松软),脱毛备皮,固定,生理盐水清洗皮肤,碘伏溶液消毒皮肤3次(范围为伤口周围15 cm)。铺手术巾,铺巾钳固定。沿腹正中线上切开皮肤,向下分离肌肉筋膜,切开腹膜,腹腔镜打孔器深入腹腔,插入腹腔镜套筒。将腹腔镜沿腹膜伸进去,到达肝脏表面,探查肝脏及胆囊约2 min。取出腹腔镜及套筒,消毒手术区域,关闭腹腔,缝合手术切口,敷料固定。对对照组进行相同操作,但不进行腹腔镜探查术。待新西兰兔麻醉苏醒后,送回动物饲养中心饲养。
-
腹腔镜术后模型制备一周后,动物取材。新西兰兔称重,备皮,分别对模型组动物和对照组动物固定、消毒、铺巾,沿腹正中线行5 cm切口,打开腹膜腔,用无菌注射器深入到腹腔后部最低处,吸取约1.5 ml腹腔液体,放入相应编号的EP管中(并备份),液氮冷藏,随后进行16S rDNA测序。
-
根据 E.Z.N.A.® soil DNA kit (美国Omega Bio-tek公司)进行腹腔液体微生物群落的DNA抽提,使用338F(5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′)和806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′)对 16S rDNA基因V3-V4 可变区进行 PCR 扩增。在Miseq PE300/NovaSeq PE250平台(美国Illumina公司)进行测序(上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)。使用Fastp软件对原始测序序列进行质控,使用Flash软件进行拼接后,在美吉生物的I-Sanger平台上进行生物信息学分析。
-
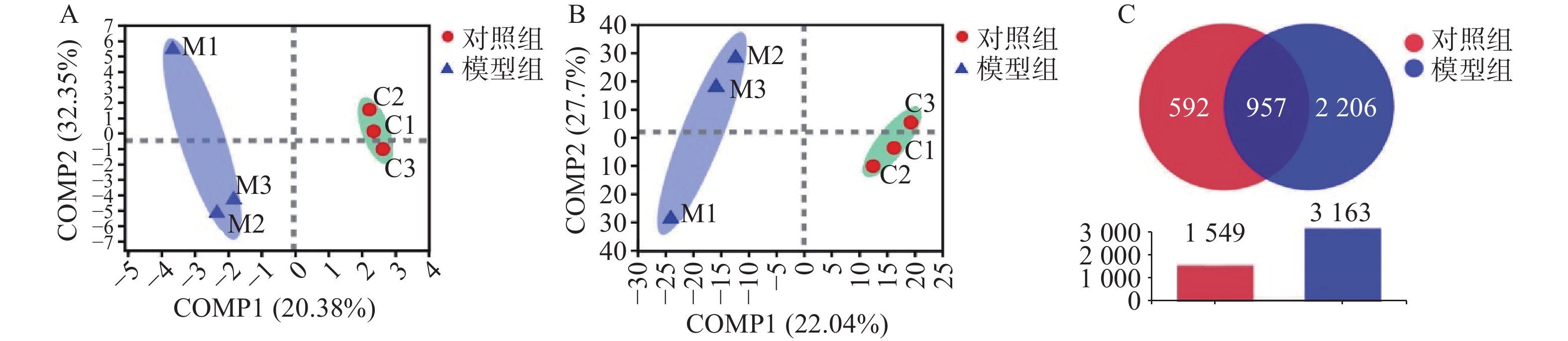
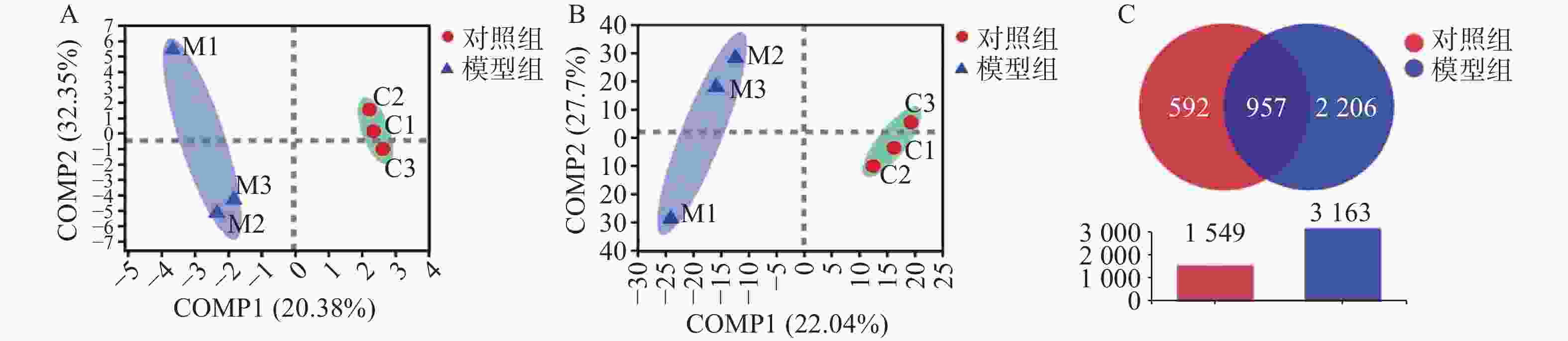
以最小二乘法对样本做判别分析(PLS-DA),寻找物种丰度矩阵和样品分布/分组信息的最大协方差,在门水平和种水平上,模型组样本与对照组样本组内聚合良好、组间区分明显(图1A、图1B)。结果显示为两组样本细菌的种类均一度良好。对两组样本数据做Venn图分析,显示两者共有的OTU数目为957,模型组OTU数目为2206,对照组OTU数目为592。模型组腹水OTU含量高于对照组,表明模型组细菌种类较对照组明显升高(图1C)。
-
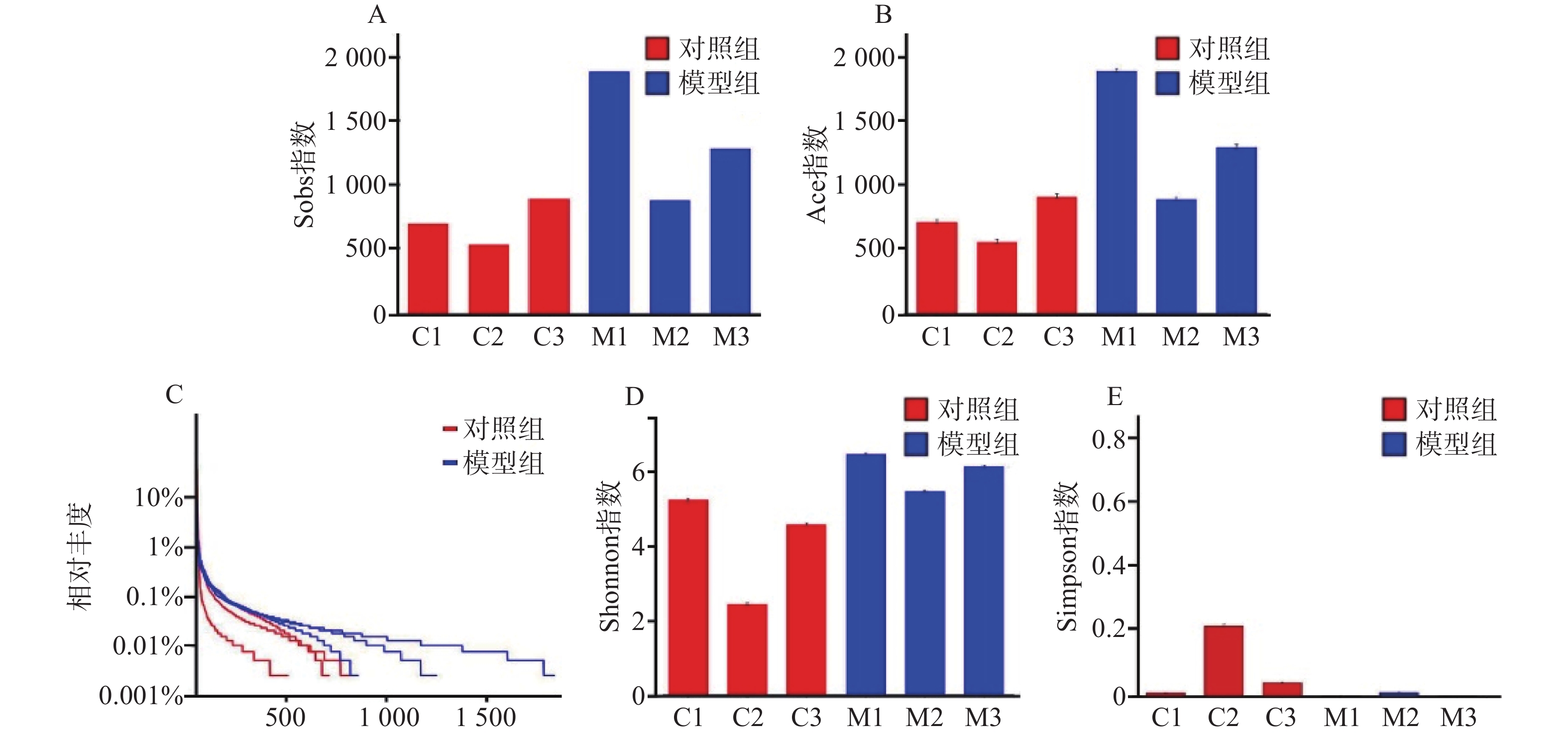
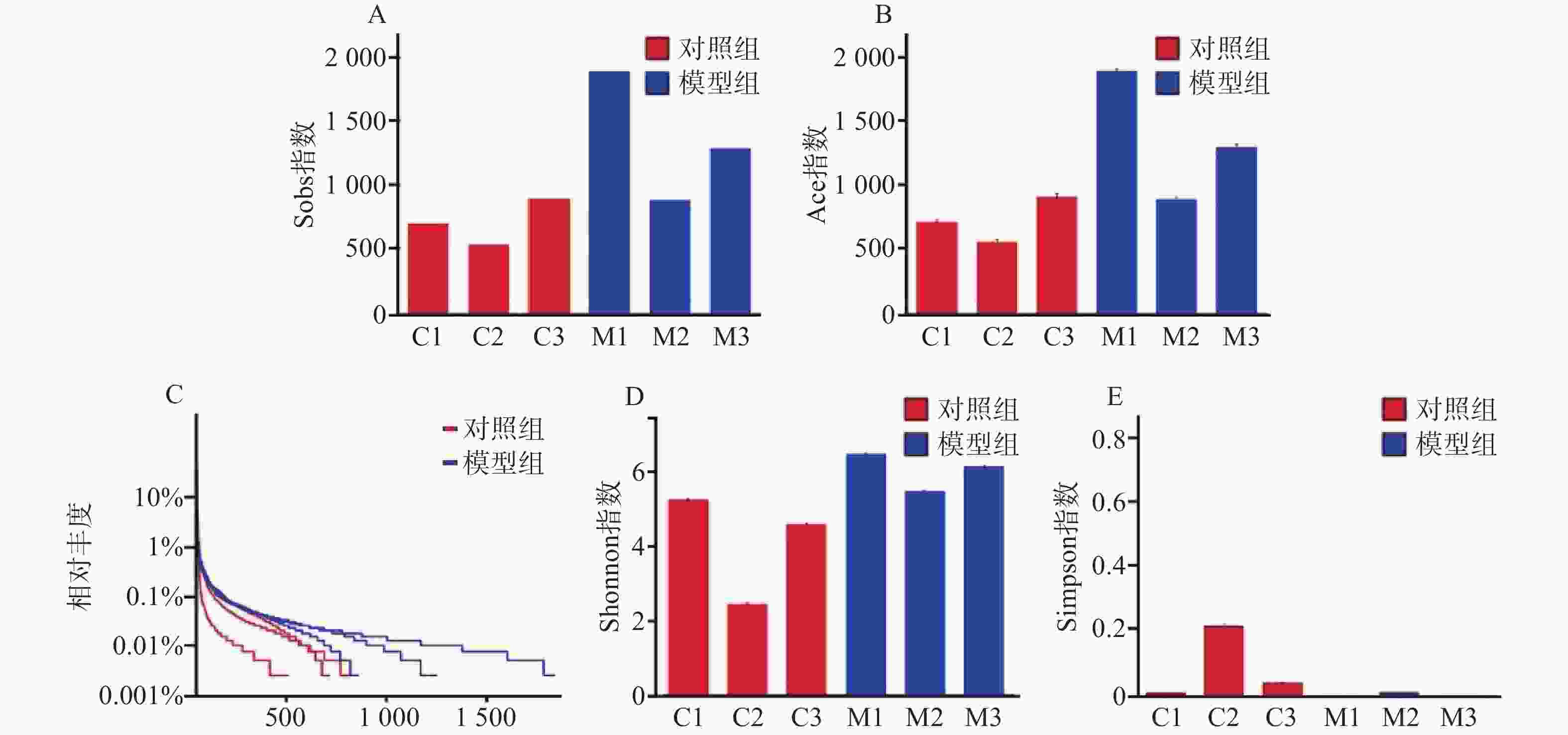
对样本数据进行α多样性分析,菌落丰富度Sobs及Ace值越高提示微生物群落丰度越高,结果显示模型组比对照组微生物群落丰度更高(图2A、图2B)。在微生物群落多样性分析中,Shannon指数提示,数值越高多样性越大;Simpson指数提示,数据越小多样性越大。得出模型组在微生物群落丰度和多样性方面均高于对照组(图2C、图2D)。从Alpha多样性指数表中可得出同样的结论(表1)。
组别 Sobs指数 Ace指数 Shannon指数 Simpson指数 对照组C1 701 712.782842 5.213487 0.016805 对照组C2 535 555.895755 2.418362 0.263764 对照组C3 894 912.018376 4.549837 0.054558 模型组M1 1885 1899.991681 6.43408 0.005768 模型组M2 882 892.237411 5.444351 0.018387 模型组M3 1284 1301.268936 6.109346 0.005465 通过对样本的OTU分类学分析,对样本测序结果中的菌种、菌属等进行聚类,通过对97%相似水平的OTU代表序列进行分类学分析,在丰度-均匀度曲线中,水平方向是物种丰度,曲线在横轴上的宽度越大,提示丰度越高。曲线的形状反映了物种的均匀度,曲线越平缓,物种越丰富。模型组相对于对照组曲线宽度更宽,更平缓。提示模型组细菌种类数量以及含量高于对照组(图2E)。
-
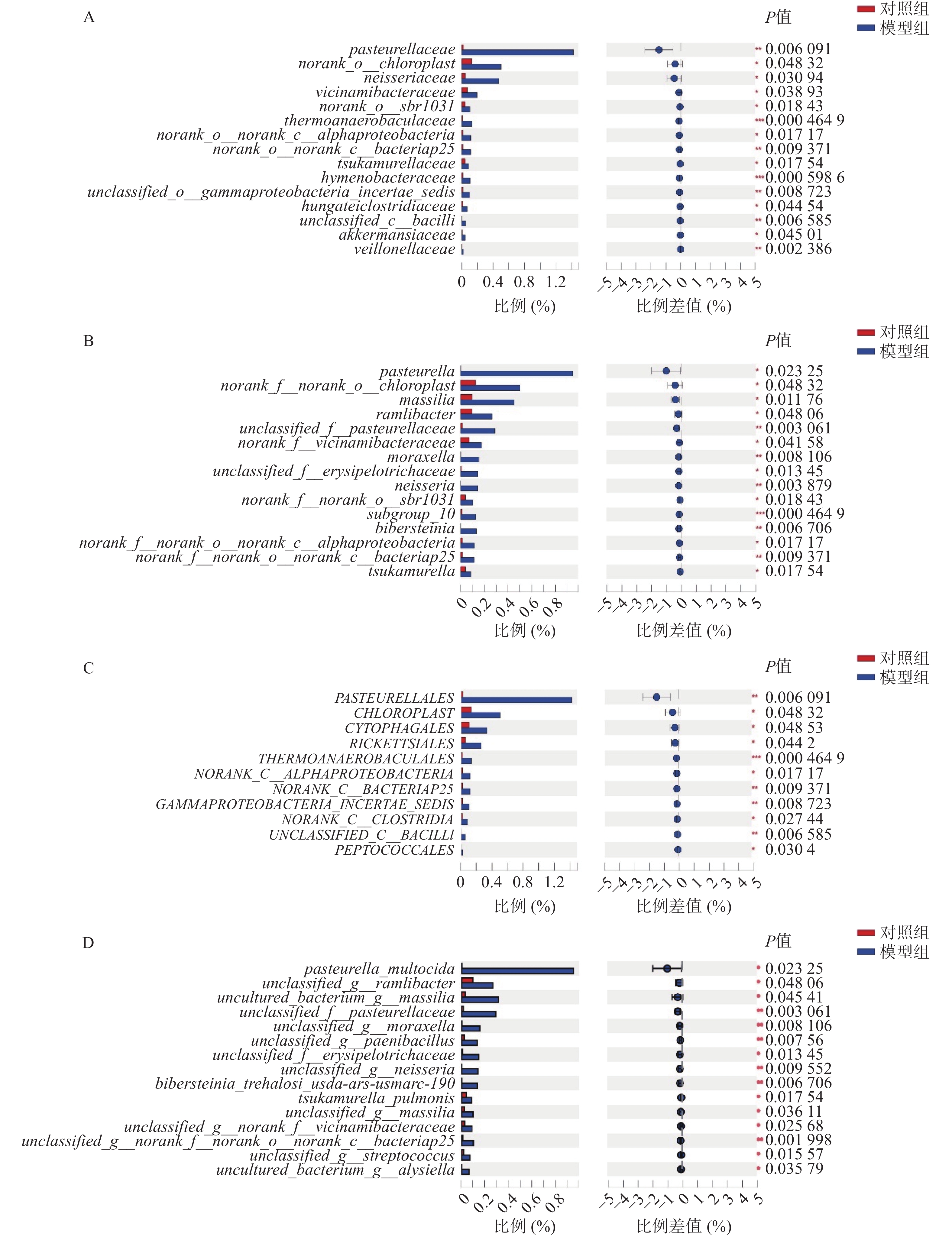
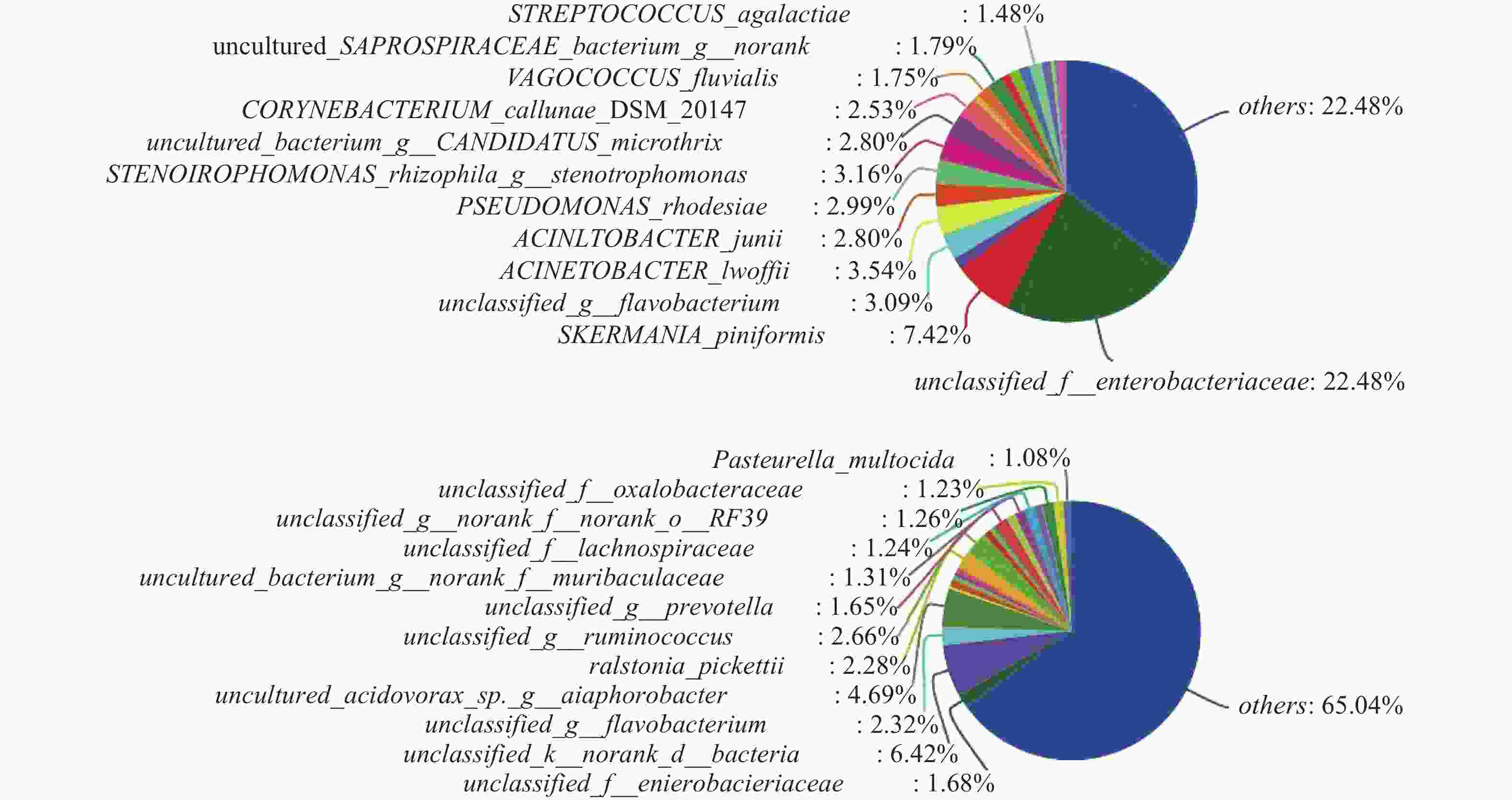
对样本数据进行微生物组成成分分析,在对照组中其他菌群数量占整体菌群数量的35.08%(图3A),而模型组其他菌群数量占整体菌群数量的65.04%(图3B),说明经过腹腔镜手术后,不明原因的其他菌群数量升高。模型组较对照组菌群占比升高的菌群有出血败血性巴斯德菌、草酸桿菌科、普雷沃菌、瘤胃球菌、正皮氏罗尔斯顿菌等。由此得出结论:腹腔镜手术后杂菌的数量显著增加,且以出血败血性巴斯德菌、草酸桿菌科、普雷沃菌、瘤胃球菌、 正皮氏罗尔斯顿菌等升高为主。
-
微生物组在目、科、属、种水平上进行物种差异性分析。在目水平上,得出以下微生物群落升高:巴斯德菌目、马赛菌目、沙壤土杆菌目、莫拉菌目、奈瑟菌目、山羊海藻百伯史坦菌目、冢村氏菌目; 在科水平上,发现以下微生物群落升高:巴斯德菌科、奈瑟菌科、紫杉霉菌科、热苜蓿菌科、冢村氏菌科、膜杆菌科、虎蛆科、Akk菌科 、韦荣氏球菌科;在属水平上,发现以下微生物群落升高:巴斯德菌属、马赛菌属、莫拉菌属、奈瑟菌属、山羊海藻百伯史坦菌属、冢村氏菌属;在种水平上,发现以下微生物群落升高: 巴斯德菌、类芽孢杆菌、奈瑟菌、拉姆利杆菌、马赛菌、赤藓科菌、冢村氏菌、马赛菌、链球菌属。通过分析,发现在目、科、属、种上模型组均有增长且增长较为明显的菌种为巴斯德菌(图4A~图4D)。
-
随着腹腔镜手术大量应用于临床,相比于传统手术而言,术后感染虽有所下降[3],但由于植入材料的应用,腹腔术后感染发生率依然很高。有研究表明,在腹腔镜术后患者的术后感染中革兰阴性菌占半数以上,以大肠埃希菌、铜绿假单胞菌、鲍氏不动杆菌、肺炎克雷伯杆菌、嗜血菌属为主;革兰阳性菌以溶血葡萄球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌、粪肠球菌为主;真菌以念球菌属、光滑假丝酵母菌、白假丝酵母菌为主[3-5]。在这些术后感染的病人中,感染的部位主要集中在肺部、腹部和尿道[5],从而引起相应术后并发症。
本研究通过对新西兰兔进行腹腔镜探查手术,发现模型组与对照组在样本菌群的聚合度良好,并且在模型组中,菌群的多样性和丰度比对照组高。在进行两组样本微生物群落对比分析中发现,在属水平上模型组的其他菌群占比由35%上升至65%。表明菌群群落数量在腹腔镜手术术后显著升高,且以草酸杆菌科、有益杆菌、巴斯德菌、瘤胃球菌、黄杆菌升高为主,其中巴斯德菌、瘤胃球菌、正皮氏罗尔斯顿菌、黄杆菌导致人感染疾病。研究发现,巴斯德菌是一种来源于动物的革兰阴性球菌,可引起蜂窝织炎、腹膜炎、菌血症、心内膜炎、脑膜炎和化脓性关节炎等疾病[6],严重者病死率可达到31%[7]。瘤胃球菌是一种革兰阳性厌氧菌,是人类正常肠道菌群的一员[8],可以导致炎症性肠病[9]。正皮氏罗尔斯顿菌是革兰阴性杆菌,容易侵袭免疫功能低下的患者,可导致严重的菌血症和肾盂肾炎[10]。有研究表明,在195名呼吸功能衰竭患者中有黄杆菌定植,但均未出现相应的并发症。微生物菌群物种差异性分析发现,在科、目、种、属水平上,模型组较对照组在巴斯德菌、奈瑟菌、冢村氏菌、热苜蓿菌、叶绿体、噬纤维菌等均有不同程度上升,而其中巴斯德菌、奈瑟菌、冢村氏菌可导致人类发病。据相关研究显示。冢村氏菌是一种革兰阳性、专性需氧、弱抗酸细菌,可导致人体肺部感染[11]。奈瑟菌可导致人体感染尿道炎、脑膜炎[12]。
本研究发现巴斯德菌、瘤胃球菌、正皮氏罗尔斯顿菌、黄杆菌、奈瑟菌、冢村氏菌在模型组呈现显著上升趋势,这些菌种可引起腹腔、尿道、肺部感染,出现严重的腹膜炎、肠梗阻,尿道炎以及脑膜炎,甚至导致病人死亡,对腹腔镜腹腔感染控制有一定的指导意义。由于本次为动物实验,可能存在手术室条件有限,手术者操作不规范等将细菌带入腹腔情况,能否在临床病人身上得出同样的结论,还需要做进一步的研究。
Study on polymorphism of peritoneal microbial community after laparoscopic exploration in New Zealand rabbits based on 16S rDNA sequencing
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202201016
- Received Date: 2022-01-07
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-07-05
- Available Online: 2022-11-28
- Publish Date: 2022-11-25
-
Key words:
- 16S rDNA sequencing /
- laparoscope /
- microbial community polymorphism
Abstract:
| Citation: | ZHANG Pingping, WU Wenbin, CAO Qi, QU Zhuo, WANG Pei. Study on polymorphism of peritoneal microbial community after laparoscopic exploration in New Zealand rabbits based on 16S rDNA sequencing[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(6): 494-498, 504. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202201016 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: