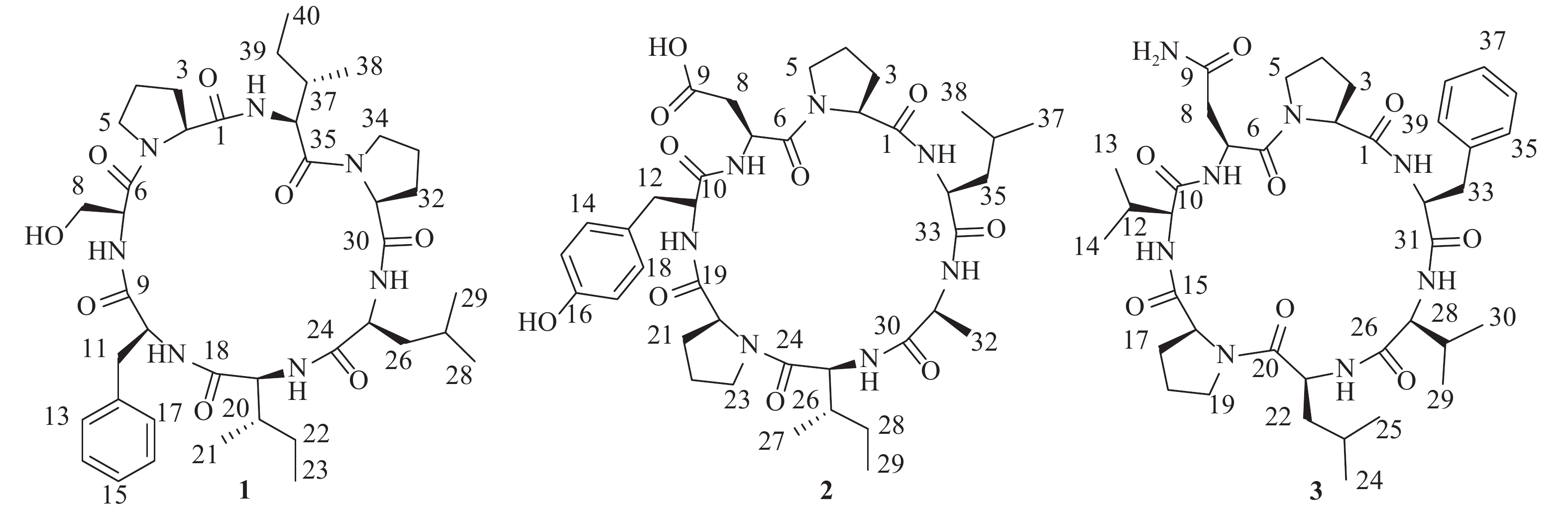
-
肾指海绵属(Reniochalina)海绵为寻常海绵纲(Demospongiae)软海绵目(Halichondrida)小轴海绵科(Axinellidae)的海洋多细胞动物。目前,针对该属海绵进行的化学成分研究主要包括甾类[1]、低极性化合物(如脂肪酸类、邻苯二甲酸类、烃类)[2]、炔醇[3]和环肽[4]等类型。其中,环肽reniochalistatins A-E由我们课题组获得,而环八肽reniochalistatin E因对人骨髓瘤细胞RPMI-8226的IC50值为4.90 μmol/L,已有两个团队采用不同策略对其完成全合成[5-6]。
为进一步高效挖掘肾指海绵中的潜在新型活性环肽,课题组基于环肽类化合物质谱响应度好,灵敏度高,二级质谱中存在明显的氨基酸单元碎裂的b和y特征离子,以质谱为导向,继续追踪分离该属海绵中的环肽类成分。最终,分离鉴定了3个环七肽(图1),并对它们进行了初步细胞毒活性评价。
-
600、700 MHz核磁共振波谱仪(德国Bruker公司);Xevo G2-XS QTOF质谱仪(美国Waters公司);质谱引导的自动纯化系统(美国Waters公司);Acquity UPLC高效液相色谱仪(美国Waters公司);Interchim PuriFlash 450中压色谱仪(法国Interchim公司);SK5200H型超声仪(上海科导超声仪器有限公司);BT224S电子天平(德国Sartorius公司);EYELAN-1000型旋转蒸发仪(日本东京理化公司);低温高速离心机(美国Thermo Fisher公司);XBridge C18半制备型液相色谱柱(10 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm,美国Waters公司);ODS柱色谱填料(日本YMC公司);Sephadex-LH20柱色谱填料(瑞典Pharmacia公司);色谱级试剂(德国Merck公司);分析纯试剂(上海化学试剂公司);氘代试剂(美国Cambridge Isotope公司)。
-
海绵样本由课题组颜益珍老师于2021年4月采集自中国南海永乐群岛附近海域(25~30 m深度)。样本呈橙黄色,质地较硬。经课题组杨琪博士鉴定为Reniochalina属海绵。凭证标本(编号:212604)现保存于上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院海洋药物实验室。
-
将干重78.5 g的海绵剪碎成块,先后加入等体积甲醇、二氯甲烷-甲醇(V/V = 1∶1)分别超声提取3~5次,每次30 min,合并提取液经减压浓缩得粗提物23.7 g。先将粗提物混悬于90%的甲醇水中,用等体积石油醚萃取3~5次,再将90%的甲醇水层加水稀释至60%,用等体积二氯甲烷萃取3~5次,合并萃取液经减压浓缩得二氯甲烷层浸膏1.2 g,其经LC-MS分析确认富含潜在的大分子量环肽。而60%的甲醇水层稀释至30%后再用乙酸乙酯萃取,经LC-MS检测已无大分子量环肽。故通过质谱导向的分步萃取,潜在的大分子量环肽主要分布于二氯甲烷层。
-
基于环肽类化合物分子量大的特点,通过两次Sephadex LH-20凝胶柱色谱分离,并采用质谱定位追踪的方式将潜在环肽富集。第一次以二氯甲烷-甲醇(V/V = 1∶1)为洗脱剂,二氯甲烷层浸膏经凝胶柱色谱分离得到组分Fr.A ~ Fr.C。第二次以正己烷-二氯甲烷-甲醇(V/V/V = 4∶5∶1)为洗脱剂,富含潜在大分子量环肽的Fr.B经凝胶柱色谱分离得到亚组分Fr.B1 ~ Fr.B5。其中,Fr.B2 ~ Fr.B4先后经中压ODS柱色谱分离(紫外监测波长设为210 nm,以甲醇-水为流动相,以流速15 ml/min在10 h内梯度洗脱10% ~ 100%),通过质谱定位追踪分别获得一系列精细组分。
上述精细组分经质谱引导的自动纯化系统制备获得环肽单体。质谱条件:质量扫描范围m/z 100~1250,锥孔电压 15 V,ES+模式下扫描采集数据。色谱条件:以半制备型C18柱为固定相,以乙腈-水(含0.1% 甲酸)为流动相,以流速6 ml/min进行梯度洗脱。其中,Fr.B2-27在32 min内线性梯度洗脱40%~48%获得化合物1(2.7 mg, tR=21 min);Fr.B4-5在52 min内线性梯度洗脱20%~23%获得化合物2(3.3 mg, tR=36 min);Fr.B2-11在32 min内线性梯度洗脱30%~40%获得化合物3(3.4 mg, tR=18 min)。
-
化合物1:无色结晶固体,茚三酮显色阴性。HRESIMS给出准分子离子峰m/z 768.4661 [M+H]+ (calcd 768.4660),确定其分子量为767。结合1H和13C-NMR谱确定其分子式为C40H61N7O8,计算不饱和度为14。1D NMR谱图给出典型的肽类化合物特征信号。其中,1H NMR谱显示有5个低场区的酰胺氨基质子信号(δH 9.45, 8.90, 8.71, 7.23, 7.16),7个α-次甲基质子信号(δH 4.69, 4.32, 4.16, 4.12, 4.03, 3.89, 3.51)。13C NMR谱提示有7个酰胺羰基碳信号(δC 171.6, 171.1, 170.9, 170.8, 170.6, 169.6, 168.5),7个α-次甲基碳信号(δC 60.7, 60.6, 59.2, 55.4, 55.1, 55.0, 54.1)。由此推断该化合物可能为七肽。结合2D NMR谱图,确定该七肽由两个脯氨酸残基、一个亮氨酸残基、两个异亮氨酸残基、一个苯丙氨酸残基和一个丝氨酸残基组成。残基连接顺序由HMBC、ROESY相关信号和ESI-MS/MS质谱数据确定,绝对构型由高级Marfey法确定[7-8]。综上,该化合物结构为cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Ser-L-Phe-L-Ile-L-Leu-L-Pro-L-Ile)。将核磁共振数据归属如下:1H NMR (700 MHz, DMSO-d6) δH 9.45 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, 36-NH), 8.90 (1H, br s, 7-NH), 8.71 (1H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, 25-NH), 7.23 (1H, d, J = 10.3 Hz, 19-NH), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz, 10-NH), 7.31 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, H-13, H-17), 7.25 (2H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-14, H-16), 7.20 (1H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-15), 4.69 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-2), 4.39 (1H, m, H-34a), 4.32 (1H, dd, J = 11.0, 8.4 Hz, H-36), 4.16 (1H, m, H-10), 4.12 (1H, t, J = 10.5 Hz, H-19), 4.03 (1H, t, J = 7.8 Hz, H-31), 3.89 (1H, t, J = 7.1 Hz, H-7), 3.57 (1H, m, H-34b), 3.51 (1H, m, H-25), 3.50 (1H, m, H-5a), 3.49 (1H, m, H-8a), 3.47 (1H, m, H-8b), 3.36 (1H, m, H-5b), 3.13 (1H, dd, J = 13.1, 2.8 Hz, H-11a), 2.84 (1H, dd, J = 13.0, 9.5 Hz, H-11b), 2.38 (1H, m, H-3a), 2.18 (1H, td, J = 12.7, 4.3 Hz, H-26a), 2.08 (1H, m, H-32a), 2.05 (1H, m, H-37), 2.01 (1H, m, H-33a), 1.92 (1H, m, H-3b), 1.90 (1H, m, H-4a), 1.79 (1H, m, H-33b), 1.73 (1H, m, H-32b), 1.55 (1H, m, H-26b), 1.53 (1H, m, H-39a), 1.52 (1H, m, H-4b), 1.43 (1H, m, H-20), 1.42 (2H, m, H-22a, H-27), 1.15 (1H, m, H-39b), 1.09 (1H, m, H-22b), 0.87 (3H, m, H-21), 0.85 (3H, m, H-29), 0.83 (6H, m, H-23, H-38), 0.82 (3H, m, H-28), 0.75 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-40);13C NMR (175 MHz, DMSO-d6) δC 171.6 (C-30), 171.1 (C-35), 170.9 (C-9), 170.8 (C-1), 170.6 (C-24), 169.6 (C-18), 168.5 (C-6), 136.9 (C-12), 129.9 (C-13, C-17), 127.9 (C-14, C-16), 126.4 (C-15), 60.7 (C-31), 60.6 (C-2, C-8), 59.2 (C-19), 55.4 (C-7), 55.1 (C-10), 55.0 (C-36), 54.1 (C-25), 48.2 (C-34), 46.3 (C-5), 37.0 (C-11, C-26), 36.7 (C-20), 34.8 (C-37), 30.8 (C-3), 29.4 (C-32), 24.7 (C-27, C-33), 24.2 (C-22), 23.9 (C-39), 23.2 (C-29), 22.2 (C-4), 20.8 (C-28), 14.9 (C-40), 14.5 (C-23), 10.1 (C-38), 9.5 (C-21)。以上数据与文献[9]基本一致,故将化合物1鉴定为stylopeptide 1。
化合物2:无色无定形粉末,茚三酮显色阴性。HRESIMS给出准分子离子峰m/z 770.4102 [M+H]+ (calcd 770.4089),确定其分子量为769。结合1H和13C-NMR谱确定其分子式为C38H55N7O10,计算不饱和度为15。1D NMR谱图给出典型的肽类化合物特征信号。其中,1H NMR谱显示有5个低场区的酰胺氨基质子信号(δH 8.77, 8.43, 8.33, 8.03, 7.55),7个α-次甲基质子信号(δH 4.53, 4.38, 4.34, 4.28, 4.05, 4.03, 3.99)。13C NMR谱提示有7个酰胺羰基碳信号(δC 172.6, 172.4, 170.6, 170.5, 170.3, 170.0, 169.9),7个α-次甲基碳信号(δC 62.5, 60.4, 57.5, 56.9, 51.6, 49.9, 47.4)。据此推断该化合物可能为七肽。结合2D NMR谱图,确定该七肽由两个脯氨酸残基、一个亮氨酸残基、一个酪氨酸残基、一个天冬氨酸残基、一个丙氨酸残基和一个异亮氨酸残基组成。残基连接顺序由HMBC、ROESY相关信号和ESI-MS/MS质谱数据确定,绝对构型由高级Marfey法确定。综上,该化合物结构为cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Asp-L-Tyr-L-Pro-L-Ile-L-Ala-L-Leu)。将核磁共振数据归属如下:1H NMR (700 MHz, DMSO-d6) δH 8.77 (1H, br s, 31-NH), 8.43 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 11-NH), 8.33 (1H, br s, 25-NH), 8.03 (1H, s, 7-NH), 7.55 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, 34-NH), 6.97 (2H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, H-14, H-18), 6.66 (2H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, H-15, H-17), 4.53 (1H, m, H-7), 4.38 (1H, m, H-31), 4.34 (1H, m, H-20), 4.28 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, H-34), 4.05 (1H, m, H-11), 4.03 (1H, m, H-2), 3.99 (1H, m, H-25), 3.63 (1H, m, H-5a), 3.56 (1H, m, H-5b), 3.26 (2H, m, H-8a, H-23a), 2.99 (1H, m, H-12a), 2.88 (1H, m, H-12b), 2.83 (1H, m, H-8b), 2.59 (1H, m, H-23b), 2.22 (1H, m, H-3a), 2.10 (1H, m, H-21a), 1.87 (1H, m, H-4a), 1.77 (1H, m, H-4b), 1.68 (1H, m, H-35a), 1.67 (2H, m, H-21b, H-26), 1.58 (1H, m, H-35b), 1.57 (1H, m, H-3b), 1.55 (1H, m, H-36), 1.54 (1H, m, H-22a), 1.53 (1H, m, H-28a), 1.24 (1H, m, H-22b), 1.16 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, H-32), 1.10 (1H, m, H-28b), 0.86 (3H, d, J = 5.8 Hz, H-37), 0.82 (3H, m, H-38), 0.80 (6H, m, H-27, H-29); 13C NMR (175 MHz, DMSO-d6) δC 172.6 (C-1), 172.4 (C-24), 172.1 (C-9), 170.6 (C-19), 170.5 (C-10), 170.3 (C-6), 170.0 (C-33), 169.9 (C-30), 155.9 (C-16), 129.6 (C-14, C-18), 127.8 (C-13), 115.1 (C-15, C-17), 62.5 (C-2), 60.4 (C-20), 57.5 (C-31), 56.9 (C-34), 51.6 (C-7), 49.9 (C-11), 47.4 (C-25), 47.0 (C-5), 45.7 (C-23), 40.4 (C-35), 36.1 (C-8), 35.4 (C-12, C-26), 30.4 (C-3), 29.5 (C-21), 25.1 (C-4), 24.7 (C-36), 24.3 (C-28), 22.9 (C-37), 21.4 (C-38), 20.9 (C-22), 15.1 (C-32), 14.9 (C-29), 10.9 (C-27)。以上数据与文献[10]基本一致,故将化合物2鉴定为hymenamide D。
化合物3:无色无定形粉末,茚三酮显色阴性。HRESIMS给出准分子离子峰:m/z 767.4468 [M+H]+ (calcd 767.4456),确定其分子量为766。结合1H和13C-NMR谱确定其分子式为C39H58N8O8,计算不饱和度为15。1D NMR谱图给出典型的肽类化合物特征信号。其中,1H NMR谱显示有5个低场区的酰胺氨基质子信号(δH 8.80, 8.13, 7.98, 7.95, 7.25),7个α-次甲基质子信号(δH 4.65, 4.28, 4.24, 4.19, 4.14, 3.89, 3.83)。13C NMR谱提示有7个酰胺羰基碳信号(δC 171.4, 171.1, 170.9, 170.3, 170.2, 170.1, 169.6),7个α-次甲基碳信号(δC 62.3, 61.5, 60.2, 57.1, 55.2, 51.0, 49.3)。据此推断该化合物可能为七肽。结合ESI-MS/MS质谱数据确定其氨基酸残基组成为两个脯氨酸残基、一个亮氨酸残基、一个苯丙氨酸残基、一个天冬酰胺残基和两个缬氨酸残基,残基连接顺序为cyclo-(Pro-Asn-Val-Pro-Leu-Val-Phe)。通过高级Marfey法确定所有氨基酸残基均为L构型。将核磁共振数据归属如下:1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δH 8.80 (1H, d, J = 5.4 Hz, 21-NH), 8.13 (1H, d, J = 9.5 Hz, 32-NH), 8.01 (1H, s, 9-NH2), 7.98 (1H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, 11-NH), 7.95 (1H, d, J = 6.1 Hz, 7-NH), 7.28 (1H, m, 9-NH2), 7.25 (3H, m, 27-NH, H-35, H-39), 7.18 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, H-37), 7.14 (2H, d, J = 7.6 Hz, H-36, H-38 ), 4.65 (1H, m, H-7), 4.28 (1H, d, J = 7.7 Hz, H-32), 4.24 (1H, m, H-16), 4.19 (1H, m, H-21), 4.14 (1H, t, J = 8.6 Hz, H-27), 3.89 (1H, t, J = 8.6 Hz, H-2), 3.83 (1H, t, J = 7.9 Hz, H-11), 3.75 (1H, m, H-5a), 3.46 (2H, m, H-5b, H19a), 3.26 (1H, m, H19b), 3.06 (1H, m, H-8a), 2.94 (3H, m, H-8b, H33a, H33b), 2.34 (1H, m, H-17a), 2.19 (2H, m, H-3a, H12), 2.02 (1H, m, H-28), 1.96 (1H, m, H-18a), 1.85 (1H, m, H-4a), 1.71 (2H, m, H-18b, H-23), 1.61 (1H, m, H-22a), 1.46 (1H, m, H-4b), 1.23 (1H, m, H-17b), 1.19 (1H, m, H-22b), 0.99 (1H, m, H-3b), 0.92 (3H, d, J = 6.7 Hz, H-13), 0.89 (3H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-14), 0.86 (6H, d, J = 6.7 Hz, H-29, H-30), 0.84 (3H, d, J = 6.7 Hz, H-25), 0.79 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz, H-24); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δC 172.5 (C-9), 171.4 (C-26), 171.1 (C-20), 170.9 (C-31), 170.3 (C-1), 170.2 (C-15), 170.1 (C-10), 169.6 (C-6), 138.4 (C-34), 128.9 (C-35, C-39), 128.1 (C-36, C-38), 126.2 (C-37), 62.3 (C-2), 61.5 (C-11), 60.2 (C-16), 57.1 (C-27), 55.2 (C-32), 51.0 (C-21), 49.3 (C-7), 47.6 (C-5), 45.8 (C-19), 37.9 (C-22), 37.0 (C-33), 35.5 (C-8), 30.5 (C-17), 30.1 (C-28), 29.5 (C-12), 29.2 (C-3), 25.1 (C-4), 24.2 (C-23), 23.3 (C-24), 21.3 (C-18), 20.6 (C-25), 19.7 (C-13), 18.7 (C-14, C-29), 18.3 (C-30)。以上数据与文献[11]基本一致,故将化合物3鉴定为axinastatin 2。
-
采用CCK-8法初步评估化合物对6种人肿瘤细胞株(A2780、HCT-8、HepG2、NCI-H460、SW480、PC-9)的体外细胞毒活性。主要步骤为:取对数生长期的细胞制成细胞悬液,约4×103个细胞/孔接种至96孔板内,每组设3个复孔。过夜培养后,各株细胞分别加入20 μmol/L化合物,并设对照组(顺铂)和空白组(DMSO),继续孵育48 h。随后,避光情况下每孔加入10 µl CCK-8溶液。孵育0.5 ~ 2 h后,450 nm处测其吸光度,每株细胞测3次以上,并计算其细胞活力(%)。对于肿瘤细胞生长抑制率大于50%的化合物,进一步测试其活性剂量依赖关系。结果显示,化合物1对NCI-H460、HepG2、PC-9、HCT-8、A2780和SW480均具细胞毒性,IC50值分别为6.09、9.31、13.24、14.31、14.38和17.26 μmol/L。
-
环肽具有许多独特的生化和治疗特性,目前已有抗生素类达托霉素、止痛剂齐考诺肽、抗肿瘤药帕瑞肽等环肽类药物获批用于临床[12]。海绵是环肽类化合物的重要多产来源,然而,其体内环肽因含量低微、紫外吸收不佳、核磁灵敏度差等,特异识别和定向获取极富挑战。将质谱高灵敏度、高准确度和高选择性的技术优势与环肽独特的质谱碎裂模式有机结合,有助于提高环肽发现的通量和选择性。
本研究以质谱为导向,追踪分离肾指海绵中的潜在新颖活性环肽,分离鉴定出3个环七肽,它们均为首次从该属海绵分离获得。此外,本研究还发现化合物1对多种人肿瘤细胞株具有中等抑制活性。而有趣的是,早期由George R. Pettit课题组分离获得的源于Stylotella属和Phakellia属海绵的同一化合物1,其抑制P388小鼠白血病细胞生长的能力却相差十倍以上[9, 13]。这可能与天然来源环肽能与某些仅生物方法才能检测到的微量强活性抗肿瘤物结合[9, 13],或不同溶剂环境致使环肽分子构象发生改变有关[14]。化合物2先后发现于Hymeniacidon属[10]和Stylissa属[15-16]海绵,对多种肿瘤细胞株开展的活性试验显示其无明显细胞毒性。化合物3此前发现于Axinella属海绵,其对小鼠P388细胞和一系列人肿瘤细胞具有较强的体外细胞毒性[11]。
不同种属的海绵能够产生相同类型的环肽分子,同一类型的环肽分子表现出不同的细胞毒活性,可能和与海绵共生互作的微生物相关。本研究进一步丰富了肾指海绵中环肽类化合物的多样性,也为研究特征结构类型的海洋天然产物提供了新思路、新方法。
Mass spectrometry-guided study on cyclic peptides from sponge Reniochalina sp.
-
摘要:
目的 以质谱为导向对肾指海绵Reniochalina sp.中的环肽类成分进行研究。 方法 采用质谱引导的程序性分离手段定向追踪并分离纯化海绵中的环肽类成分;通过理化常数测定、波谱数据比对确定化合物结构;利用CCK-8法对化合物进行初步细胞毒活性评价。 结果 从肾指海绵Reniochalina sp.中分离获得3个环肽类化合物,分别鉴定为stylopeptide 1 ( 1 )、hymenamide D ( 2 )、axinastatin 2 ( 3 )。化合物 1 对6种人肿瘤细胞株具有细胞毒性,IC50值范围为6.09 ~ 17.26 μmol/L。 结论 化合物 1 ~ 3 首次分离自Reniochalina属海绵,化合物 1 是细胞毒性环七肽。 Abstract:Objective To study the cyclic peptides from sponge Reniochalina sp. under the guidance of mass spectrometry. Methods Mass spectrometry-guided procedural separation methods were used to track and isolate the cyclic peptides from the sponge genus Reniochalina. The structures of compounds were elucidated by the determination of physicochemical parameters and comparison of spectroscopic data. The preliminary cytotoxic activity of compounds was assessed by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) method. Results Three cyclic peptides were isolated from the sponge Reniochalina sp. and identified as stylopeptide 1 ( 1 ), hymenamide D ( 2 ) and axinastatin 2 ( 3 ). Compound 1 exhibited cytotoxicity against six human cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 6.09 to 17.26 μmol/L. Conclusion Compound 1 - 3 were isolated from Reniochalina sp. for the first time, and compound 1 was a cytotoxic cyclic heptapeptide. -
Key words:
- Reniochalina sp. /
- chemical constituent /
- cyclic peptide /
- structure identification
-
[1] 薛松. 海绵活性天然产物分离及结构确定[D]. 大连: 中国科学院研究生院(大连化学物理研究所), 2003. [2] 闫小燕, 靳艳, 虞星炬, 等. 气相色谱-质谱分析新种海绵Reniochalina sp. 中的低极性组分[J]. 色谱, 2004, 22(6):652-654. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2004.06.021 [3] LEE H S, LEE J H, WON H, et al. Identification of novel acetylenic alcohols and a new dihydrothiopyranone from the tropical sponge Reniochalina sp.[J]. Lipids,2009,44(1):71-75. doi: 10.1007/s11745-008-3249-3 [4] ZHAN K X, JIAO W H, YANG F, et al. Reniochalistatins A-E, cyclic peptides from the marine sponge Reniochalina stalagmitis[J]. J Nat Prod,2014,77(12):2678-2684. doi: 10.1021/np5006778 [5] ATINO A, BACA G, WEERAMANGE C, et al. Total synthesis of reniochalistatin E[J]. J Nat Prod,2017,80(12):3234-3240. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00656 [6] ZHOU R, SUN Y G, LI H B, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of reniochalistatins A-E and a reniochalistatin E analogue[J]. ChemMedChem,2018,13(20):2202-2207. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800529 [7] FUJII K, IKAI Y, MAYUMI T, et al. A nonempirical method using LC/MS for determination of the absolute configuration of constituent amino acids in a peptide: elucidation of limitations of marfey’s method and of its separation mechanism[J]. Anal Chem,1997,69(16):3346-3352. doi: 10.1021/ac9701795 [8] FUJII K, IKAI Y, OKA H, et al. A nonempirical method using LC/MS for determination of the absolute configuration of constituent amino acids in a peptide: combination of marfey’s method with mass spectrometry and its practical application[J]. Anal Chem,1997,69(24):5146-5151. doi: 10.1021/ac970289b [9] PETTIT G R, SRIRANGAM J K, HERALD D L, et al. Isolation and crystal structure of stylopeptide 1, A new marine Porifera cycloheptapeptide[J]. J Org Chem,1995,60(25):8257-8261. doi: 10.1021/jo00130a027 [10] TSUDA M, SHIGEMORI H, MIKAMI Y, et al. Hymenamides C~E, new cyclic heptapeptides with two proline residues from the Okinawan marine sponge hymeniacidon sp.[J]. Tetrahedron,1993,49(31):6785-6796. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)80422-1 [11] PETTIT G R, GAO F, CERNY R L, et al. Antineoplastic agents. 278. Isolation and structure of axinastatins 2 and 3 from a western Caroline Island marine sponge[J]. J Med Chem,1994,37(8):1165-1168. doi: 10.1021/jm00034a014 [12] ZHANG H Y, CHEN S Y. Cyclic peptide drugs approved in the last two decades (2001-2021)[J]. RSC Chem Biol,2022,3(1):18-31. doi: 10.1039/D1CB00154J [13] PETTIT G R, TAYLOR S R. Synthesis of the marine sponge cycloheptapeptide stylopeptide 1[J]. J Org Chem,1996,61(7):2322-2325. doi: 10.1021/jo951986b [14] 刘晓庆. 生物大分子序列、结构及活性的计算模拟[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2009. [15] AFIFI A H, EI-DESOKY A H, KATO H, et al. Carteritins A and B, cyclic heptapeptides from the marine sponge Stylissa carteri[J]. Tetrahedron Lett,2016,57(11):1285-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.02.031 [16] SUN J Y, CHENG W, DE VOOGD N J, et al. Stylissatins B-D, cycloheptapeptides from the marine sponge Stylissa massa[J]. Tetrahedron Lett,2016,57(38):4288-4292. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.08.024 -




 下载:
下载: