-
药物不良反应已成为一个公共卫生问题,其中约30%为药物相互作用(drug-drug interactions,DDIs)所导致[1]。DDI指的是2种以上的药物同时或先后使用时,其中一种药物受到另一种药物的影响而发生理化性质、药动学和药效学明显改变。有文献报道,药动学相互作用发生率最高,约占DDIs的40%[2]。已有研究表明,环孢素A(cyclosporineA,CsA)和伏立康唑(voriconazole,VRZ)之间存在着一定的DDI。VRZ体内呈非线性药动学,主要通过肝脏CYP2C19代谢,其次通过CYP2C9和CYP3A4代谢,CYP2C19呈现基因多态性,个体间的药物代谢和相互作用存在很大差异[3]。同时,CYP3A4是CsA的主要代谢酶,而VRZ对CYP3A4代谢酶具有抑制作用。因此,当CsA和VRZ两药联用时,CsA的代谢会受到抑制,血药浓度升高、体内药物蓄积,导致肝肾毒性等不良反应事件的发生。对于临床医生,如何充分认识和管理好DDI具有较大的挑战性。本研究将在Allo-HSCT患者中,通过自身前后对照研究,探讨VRZ血药浓度与CsA血药浓度的升高幅度是否有相关性,CsA与VRZ相互作用是否存在个体性差异,以指导临床对CsA和VRZ的合理使用。本研究已通过联勤保障部队第九四〇医院伦理委员会审批(2019KYLL039),并签署患者知情同意书。
-
患者来源:收集2019年1月—12月在某院造血干细胞移植中心进行Allo-HSCT的患者15例(男性9例,女性6例),平均年龄25.4岁,体重(54.6±12.49)kg,其中再生障碍性贫血8例,急性髓系白血病3例,急性淋巴细胞白血病4例。
纳入标准:Allo-HSCT的患者,在术前已接受了CsA,初始剂量为2.5 mg/(kg·d),分2次,静脉滴注预防移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)。术后第2 天开始静脉滴注VRZ(200 mg,每日2次)预防侵袭性曲霉菌感染(IA)。
排除标准:①肾功能或肝功能不正常;②正在使用其他药物与CsA或VRZ发生中度至重度DDI。
给药方案:CsA(批号:H20150095,250 mg,诺华制药)初始剂量为2.5 mg/(kg·d),分2次,静脉滴注,待患者消化道耐受后,将静脉用药改为口服。VRZ(批号:H20181102,0.2 g,美国辉瑞)预防给药剂量为200 mg,每日2次,静脉滴注。本研究中CsA和VRZ均为静脉滴注,且在研究期间CsA给药剂量未做调整。
血样采集和监测次数:于次日早晨空腹采静脉血2.0~3.0 ml,置抗凝管(EATA)中,摇匀、送检。采用HPLC-MS/MS方法监测谷浓度[4]。测定CsA给药后3~5 d(即给VRZ前1~3 d,CsA达稳态血药浓度)的血药浓度2次,术后测定VRZ 用药5~7 d时(VRZ达稳态血药浓度),CsA和VRZ同一时间的血药浓度2次。
CsA标准化血药浓度[(dose adjusted blood concentration,C/D)(ng/ml)/(mg/kg)]作为反映药物剂量和浓度的参数。为了方便研究CsA血药浓度的变化,计算CsA的C/D比值。
-
数据应用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计分析,不服从正态分布的计量数据以中位数(四分位间距),即M(Q25,Q75)表示,计数及等级资料以构成比(%)表示。采用Wilcoxon符号秩和检验,比较使用VRZ前后CsA的C/D比值的差异。计算VRZ血药浓度和CsA的C/D值之间的Spearman秩相关系数,评估CsA的C/D比值升高与VRZ血药浓度的相关性,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异。
-
本研究在2019年1月—12月期间共收集15例患者,CsA测定为60例/次,VRZ测定为30例/次。
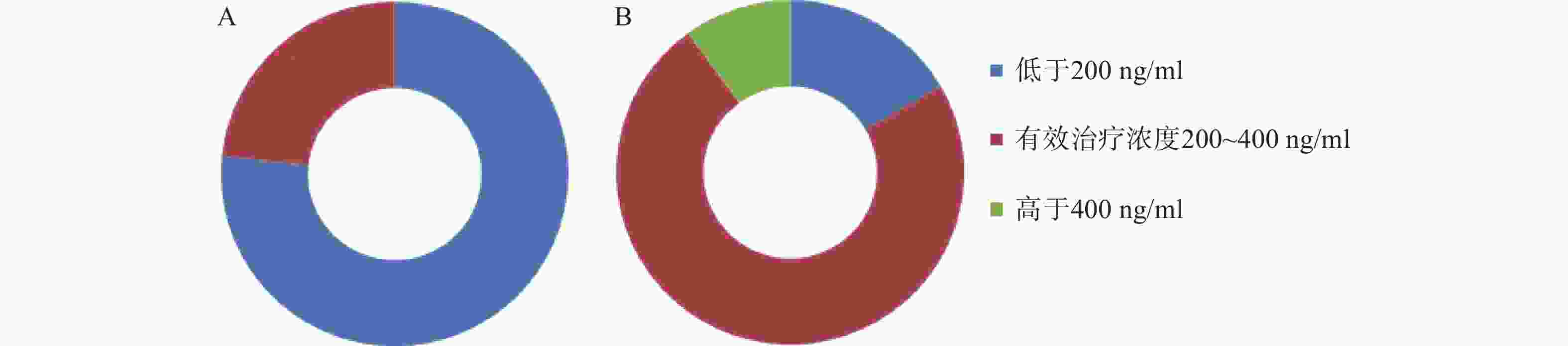
移植前,CsA测定30例/次,血药浓度中位数160.35(106.65,196.85)ng/ml,23例/次测定结果低于200 ng/ml,7例/次测定结果在200~400 ng/ml的范围内;移植后,加用VRZ后,测定30例/次,血药浓度中位数为308.75(212.80,360.37)ng/ml,22例/次测定结果在200~400 ng/ml,5例/次未达到200 ng/ml,3例/次超过400 ng/ml。两药联用后,CsA稳态血药浓度升高了92.54%。合用VRZ后,CsA测定结果在有效治疗范围内的例/次达73.30%(22/30),仅有26.67% (8/30) 例/次的测定结果不在有效治疗范围。而合用前仅有23.30% (7/30) 例/次的测定结果在有效治疗范围内。结果见图1。
VRZ的测定结果:移植后测定30例/次,血药浓度中位数1.74(0.48,3.70) μg/ml,1例/次测定结果低于0.5 μg/ml,占3.33%,6例/次测定结果在0.5~0.1 μg/ml,占20.00%,14例/次测定结果在1.0~2.0 μg/ml,占46.67%,9例/次测定结果在2.0~5.0 μg/ml,占30.00%。15例患者VRZ平均血药浓度变异系数(CV)为52.60%。
-
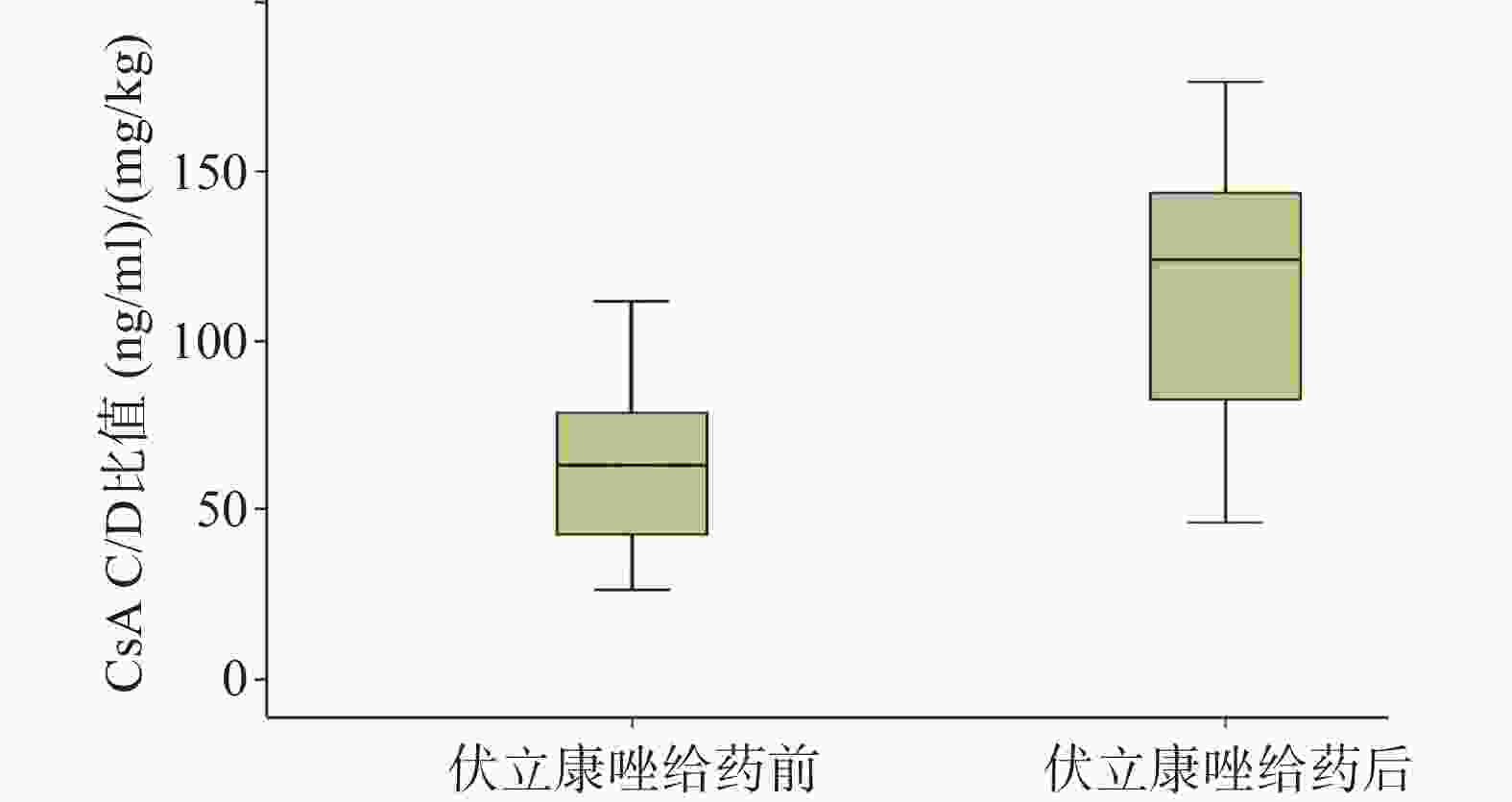
15例患者在开始使用VRZ后CsA血药浓度均升高。使用VRZ前,CsA的C/D比值中位数为64.14(25.35,112.36)(ng·/ml)/(mg/kg),使用VRZ后,中位数为123.5(45.88,178.24)(ng/ml)/(mg/kg),进行配对设计非参数检验(Wilcoxon符号秩和检验),两者之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),可用箱型图表示,见图2。
-
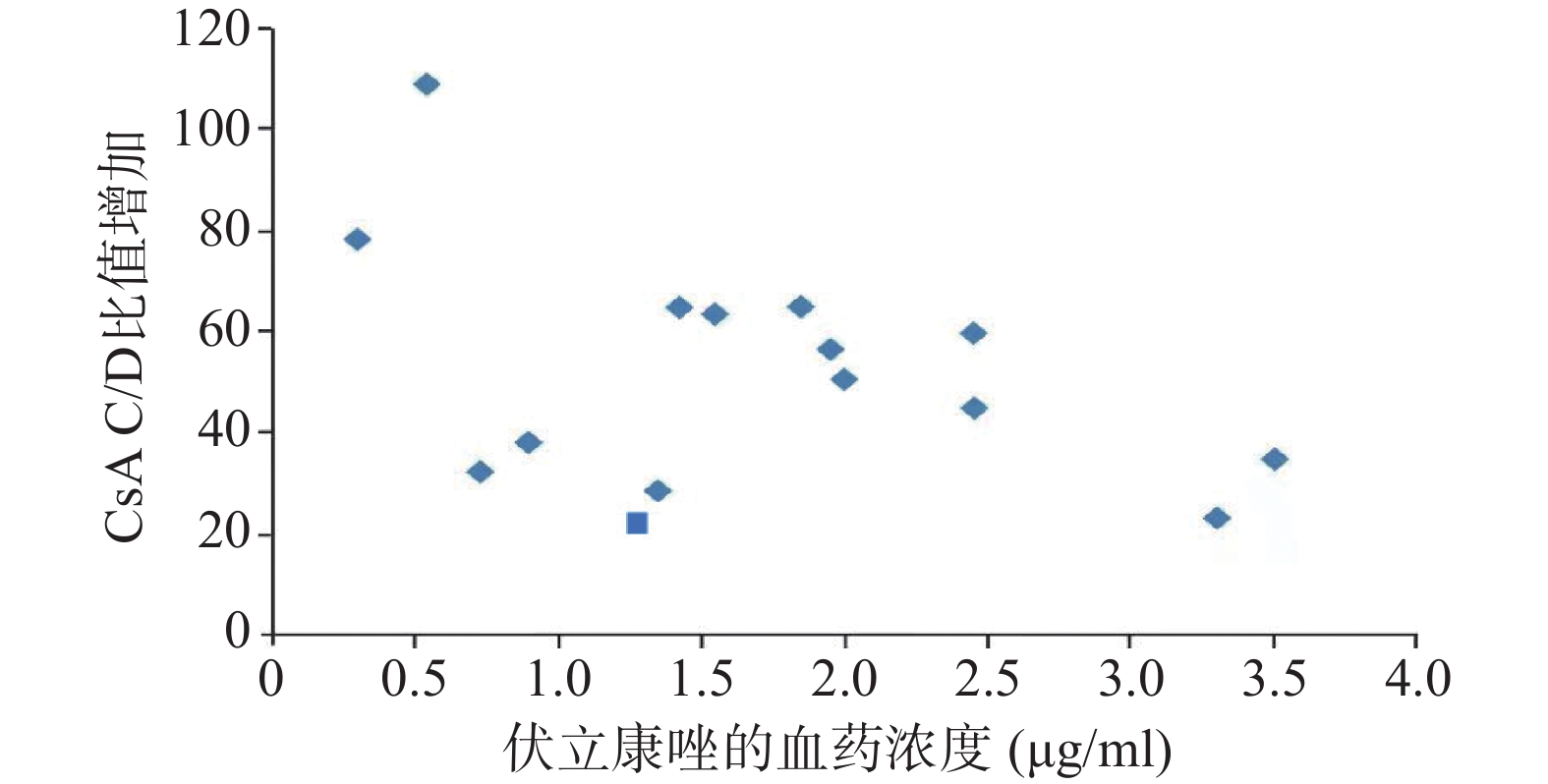
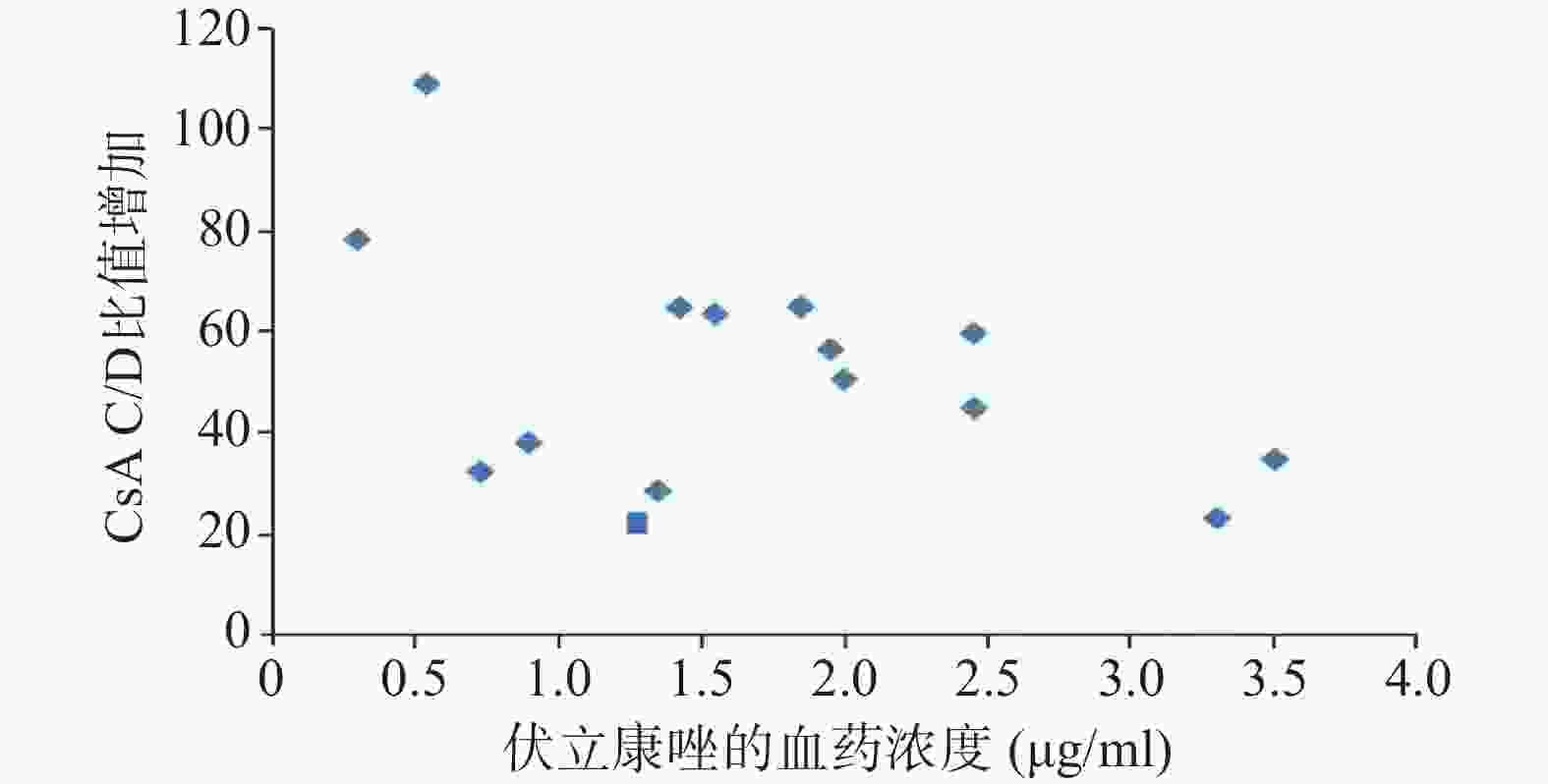
15例患者测定结果显示,VRZ血药浓度的中位数为1.74(0.48,3.70)μg/ml,CsA的C/D比值增幅中位数为82.61%(8.00%,190.00%),进行Spearman相关性分析得ρ=−0.273,P=0.32,即VRZ血药浓度与CsA的C/D比值升高无显著相关,见图3。
-
本研究结果表明,在Allo-HSCT患者中,CsA和VRZ两药联用后,CsA稳态血药浓度升高了92.54%,测定结果在有效治疗范围内达73.30%,比合用前的23.30%提高了214.59%。但是10.00%的测定结果超出治疗范围,容易发生肝肾毒性。
EBMT-ELN工作组的标准化实践建议中[5],预防GVHD 的CsA静脉给药剂量为3 mg/(kg·d),分2次给药。在我们的移植中心,CsA给药剂量为2.5 mg/(kg·d),分2次给药,合用VRZ后,充分利用了DDI,使得大部分CsA血药浓度达到治疗范围。这样降低了过高浓度造成肝肾毒性发生的几率,体现了临床医生用药的合理性。
VRZ的测定结果中,VRZ血药浓度个体变异系数CV为52.60%,充分说明伏立康唑的个体化差异大。VRZ个体化用药:中国药理学学会治疗性药物监测学部实践指南治疗剂量血药浓度要求为0.5~5.0 μg/ml[6],欧美指南和一些研究大多推荐1.0~5.5μg/ml[7]。关于预防用药的血药浓度范围国内没有明确的指南和共识。德国血液肿瘤学会感染性疾病工作组在《预防血液系统恶性肿瘤患者侵袭性真菌感染的推荐意见》中推荐VRZ用于预防真菌感染时浓度范围为1~2 μg/ml[8]。在本研究中,给予预防剂量VRZ,有46.76%的测定结果在1~2 μg/ml内,23.30%的测定结果<1 μg/ml,30.00%的测定结果>2 μg/ml,这表明德国血液肿瘤学会提出的预防剂量的血药浓度,有可能也适用于中国人群。
-
细胞色素P450酶(CYP450)是微粒体混合功能氧化酶系中最重要的氧化酶,在体内几乎90%的药物由CYP450代谢。CYP450酶诱导和抑制所致的代谢性DDI能显著改变联用药物的药动学、药效学及毒副作用[9]。VRZ是一种广谱的三唑类抗真菌药物,用于预防和治疗器官移植患者中曲霉菌感染,它主要是通过肝脏CYP2C19、CYP2C9和CYP3A4进行代谢,有高度可变的药动学,影响治疗效果和安全性。在体内,VRZ也是代谢酶CYP3A4的强抑制剂。CsA经CYP3A4介导的生物转化而消除,两者联用会引起CsA的清除率明显下降,半衰期明显延长,最终导致CsA血药浓度上升[10]。
在之前的几项研究中,VRZ对CsA血药浓度的影响已进行了评估。在一项随机、双盲、安慰剂对照的交叉研究中,Romero等[11]对14例同时接受口服VRZ肾移植术后患者进行了研究,CsA合用VRZ后未调整CsA剂量时,CsA药时曲线下面积(AUC)是合用前的1.7倍;CsA血药峰浓度(cmax)是合用前的1.13倍。他们建议在开始VRZ治疗时,所有患者CsA的剂量减少50%,但是此研究未评估患者个体间差异。
本研究结果证实静脉滴注VRZ与CsA合用后,两者血药浓度之间存在相互影响;VRZ与CsA之间的DDI程度大小存在很大的差异[C/D比值增幅中位数82.61(8.00%,190.00%)]。
Dresser等 [12]对伊朗Allo-HSCT患者研究表明:CsA的C/D比值增幅与VRZ血药浓度呈显著相关性(ρ=0.482,P=0.046),但是亚组分析中口服VRZ(ρ=0.165,P=0.059),静脉(ρ=0.482,P=0.058),没有显著性差异。Kikuchi等[11]研究表明,口服CsA的C/D比值增幅与口服VRZ血药浓度不呈显著相关性。本研究同样表明静脉滴注CsA的C/D比值增幅与静脉滴注VRZ血药浓度不呈显著相关性(ρ=-0.273,P=0.32)。
综上所述,在Allo-HSCT中,移植患者用药复杂,CsA与VRZ之间存在DDI,VRZ使CsA血药浓度显著升高,但VRZ血药浓度与CsA血药浓度升高幅度无显著相关,表明VRZ与CsA之间的DDI程度大小存在个体差异。同时,VRZ本身在体内代谢、清除受CYP2C19基因多态性、药物相互作用等因素影响,呈非线性药动学特点,个体间差异大,导致通过剂量估计给药后的血药浓度不准确。这就体现了监测CsA与VRZ两者血药浓度并做精细化药物剂量调整尤为重要。
Interaction between cyclosporine A and voriconazole in patients with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202111056
- Received Date: 2021-11-12
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-03-16
- Available Online: 2023-11-06
- Publish Date: 2022-05-25
-
Key words:
- CsA /
- VRZ /
- blood concentration /
- therapeutic drug monitoring /
- drug interaction
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Yani, WU Di, RAO Zhi, LI Maoxing, XI Rui, REN Jun. Interaction between cyclosporine A and voriconazole in patients with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2022, 40(3): 277-280. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202111056 |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: